Anatomy nasal cavities Flashcards
why do nasal cartilage require diffusion of nutrients from associated vasculature
they do not have their own vasculature
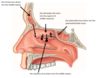
the ethmoid bone is broken down to how many sections
3 sections
- roof
- lateral wall
- septum
where would you find the cristi gali and the cribriform plate on the ethmoid bone
on the roof

the orbital plate
ethmoid air cells
superior concha
middle concha
are all located in which region of the ethmoid bone
the lateral wall of the ethmoid bone

the perpendicular plate and vomer are located where of the ethmoid plate
septum

which of the Le Fort Fractures can disrupt the cribriformform plate
Le Fort II and III

what is the complication of incurring a Le Fort fracture II and III
This increases the danger of infection spreading from the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses into the anterior cranial fossa

why would a septal haematoma cause necrosis of the septal hyaline cartilage
a septal haematoma eliminates the ability of the diffusion of nutrients to the septal hyaline cartilage, along with oxgygenated blood. this slowly causes necrosis of the cartilage
how would you treat a septal haematoma
the septal haematoma would be incised and drained to prevent the avascular necrosis
where would expect to find keratinised stratified squamous epithelium

1
where would you epect to find respiratory epithelium

2
where would you expect to find olfactory mucosa

3
which epithelieum of the nasal cavity would contain goblet cells and cillia

respiratory epithelium
where would you expect to find first order neurones of the olfactory nerve
the receptor cells located in the olfactory mucosa
where would presynaptic neurones of the receptor cells synapse to
to the olfactory bulb, which is a ganglion
which order neurones travel to the temporal lobe
2nd order neurones leave the olfactory bulb as postsynaptic
which division of the trigeminal nerve supplies somatic sensory, anteriosuperiorly in the nasal cavity
the opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1)
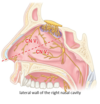
which division of the trigeminal nerve supplies somatic sensory, posterioinferiorly in the nasal cavity
the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)

the nasal region is supplied blood by both internal and external carotid arteries
what are the external arteries that supply to that region
facial artery
maxillary artery

the nasal region is supplied blood by both internal and external carotid arteries
which internal artery supplies to that region
opthalmic artery

The ophthalmic artery supplies the nasal cavity via the
anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries

the maxillary artery branches off to form which arteries to supply the nasal cavity
the sphenopalatine and greater palatine arteries

the facial artery branches off to form which arteries
the lateral nasal branch of facial or septal branch of superior labial artery.

what is kiesselbach’s area
This little area is an anastomosis on the nasal septum
a common site for nosebleeds (epistaxis)