(P4) Cardiac: Tuberculous pericarditis Flashcards
Identify slide

Tuberculous pericarditis

Identify slide
The clinical presentation may be?

• Tuberculous pericarditis
it represents a secondary localization with a primary infection in a different organ (most commonly, pleural‐pulmonary infection)
The clinical presentation may be fibrinous pericarditis

Identify slide:
Macro:

Tuberculous pericarditis

– Thickeningandscarringofthepericardiumwithlossof elasticity
– Organisation of the exudate may lead to the fibrosis , and the surfaces of both pericardial layers adhere to each other.
Identify slide
Micro:

Tuberculous pericarditis
• Typical granuloma consists of:
- necrotic center (caseation)
- zone of epitheloid cells (modified histiocytes)
- Langhans’ giant cells
- outer margin of lyphocytes.

Identify:


Identify:

Tuberculous Pericarditis

What causes
Tuberculosis Pericarditis ?
mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Tuberculosis Pericarditis
Direct spread from?

direct spread from tuberculosis foci within tracheobronchial nodes
granulomas in pericardium:
- epithelioid cells
- caseous necrosis
- langhan cells
- lymphocytes

- Tuberculous pericarditis*
- causes what type of inflammation*
- and*
thickening of what tissue?

- fibrinous superficial inflammation
- thickening & scarring of pericardium w/loss of elasticity

Tuberculous pericarditis
Micro:
consists of ?

consists of:
- necrotic center (caseous necrosis)
- zone of epithelioid cells (modified histocytes)
- langhans giant cells
- granulation tissue
- outer margin of lymphocytes
- surface of epicardium is covered by fibrinous exudate* and *inflammatory infiltrate

Pericarditis
define:
infectious: viral, pyogenic bacteria, tuberculosis
immunologically mediated: RF, SLE, scleroderma, Dressler syndrome
miscellaneous: myocardial infarction, uremia, neoplasia, trauma, radiation, surgery
Chronic pericarditis
fibrous (not fibrinous)
adhesive: minor fibrous adhesions in pericardial sac
constrictive: dense fibrous response that compresses the heart and restricts inflow
- previous radiation therapy, cardiac surgery, tuberculosis
- the pericardial space is obliterated by rigid mass of fibrous tissue with deposits of calcium focally
- small heart w/restriction of venous flow into the heart with abnormal contraction
Identify:


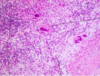
Identify:
Tuberculous Pericarditis

Pericardial tumors

• Primary (rare):
- Mesothelioma
- Sarcoma (lipoma, fibroma, angioma, rhabdomyoma)
Secondary (metastases):
- Lung cancer
- Breast cancer
- Lymphoma/ leukemia
- melanoma


