Lecture Two Flashcards
(19 cards)
What are the two main structures that comprise the external nose?
Refers to the external nose being comprised of the nasal cavity and the external sinuses
What type of tissue is the external nose composed of?
highly cornified stratified squamous epithelium
What species has hair around its nose?
horse
How is the nose made moist in pigs/cows and in dogs?
Pig/cow- moistened by serous glands Dog- overflow of nasal secretions
What is a nasal vestibule?
funnel shaped entrance to the sinus (the bit that you can get your finger into)
What is particularly special about a horses nostrils?
they are highly distensible making it possible for them to increase air intake
What is an obvious visible feature in a horses nostril near the musculocutanous junction?
nasolacrimal duct
What is the filtrum?
vertical indentation that is often observed within the upper lip of animals
What is the ala?
simply refers to the wings that are in the nose
What is the nasal diverticulum?
refers to a false nostril and is often seen within horses. Pouch like and very highly distensible
What are the nasal cartilages?
Refers to the cartilage that makes up the nose and can be separated in dorsal and ventral alar cartilages
What are the nasal conchae and what is there function?
- Main function of these is to purify air, cleanse air and to generate turbulence to spin the toxic material to be outside of the sinuses. - There are three main one’s being dorsal, ventral and ethmoidal
What are the three main meatuses and where do they lead ?
• Ventral and common meatus = main airway (nasogastric tubing) • Middle meatus = to paranasal sinuses • Dorsal meatus = to ethmoidal sinuses
Where are the lateral nasal glands located and what is the primary function of them?
• Very well developed in most species especially the dog • In maxillary recess/sinus • Duct discharges behind the alar fold • Secretions will often increase on a hot day
Describe the location and the function of the nasal cavities:
• Vestibule to choana • Left and right cavities are completely separated by nasal septum. Rostral 2/3rd cartilage and then caudal 1/3rd is bone • Continuous with cartilages • Potential space is filled with nasal conchae and paranasal sinuses, the mucosa is thickened by the vascular plexuses • The space between the conchae and septum = nasal meatuses
Name the structures shown below:

- ala
- philtrum
- nasal vestibule
Name the structure that is shown below:

Nasolacrimal duct
Name the structures that are shown below:

- dorsal concha
- ventral concha
- ethomoidal concha
Name the following features:
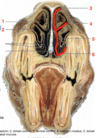
- Dorsal Concha
- Ventral concha
- Dorsal meatus
- Middle meatus
- Common meatus
- Ventral meatus


