LEC65: Our Ears Flashcards
(68 cards)
greek, latin, olde english, pinna for ear?
greek: oto (otic)
latin: auris (auricular)
olde english: eare
pinna: from latin, feather, wing, fin
identify the temporal bone


parts of the temporal bone?
squamosal
zygomatic
mastoid
tympanic

what is within temporal bone?
sensory organs for balance and hearing
what connects to styloid process of temporal bone?
stylyhyoid ligament
stylomandibular ligament
styloglossus m (XII)
stylohyoid m (VII)
stylopharyngeus m (IX)
what is different about a baby’s temporal bone?
no mastoid process - it’s a developmental feature
where does internal acoustic meatus open?
into petrous part of temporal bone
which region of skull is temporal bone in?
middle cranial fossa
what is within the mastoid process here?

mastoid air cells
neumatized bone in the mastoid process
bone lessens with aging there - normal - air circulates. but can have infection spread here.
what provides sensory innervation to inner ear canal? nerve and fiber type
what other nerves do you find in the inner ear canal?
GSA of CN VII, facial n
also see vestibular nerve, cochlear nerve - balance
if facial nerve is knocked out when exits internal acoustic meatus, what is lost?
all function of VII
if VII is knocked out distal to greater petrosal nerve, what remains / is lost?
retain lacrimal gland GVE
lose sublingual/submandibular gland GVE
lose taste to anterior 2/3 tongue SVA
lose facial expression SVE
if VII is knocked out distal to chorda tympani, what is retained/lost?
retain:
lacrimal GVE (greater petrosal n)
sensation of inner ear GSA (n to stapedius)
taste to anterior 2/3 tongue SVA submandibular, sublingual glands’ GVE (chorda tympani)
lose:
facial expression SVE
sensory ganglion of facial n?
geniculate ganglion
where do motor branches of facial n traverse?
across parotid gland
then span out, do mm of facial expression
what are our 6 ears?
external, middle, inner on each side of the head
boundaries of each part of ear?
external: pinna - canal - tympanic membrane
middle: tympanic membrane - oval window
inner: deep w/in crevices of petrous
parts of external ear?
1) auricle aka pinna - what we see on outside
2) external acoustic meatus - external ear canal, leads to tympanic membrane
ID: helix, anti-helix, tragus, concha, pinna


first arch syndrome re: ear? what might result?
poor developed meckel’s cartilage
poorly developed pinna
mandible underdeveloped
functions of external ear?
capture, direct, amplify sound
dissipate heat
communicate / mood signaling
what provides auricular sensation?
V - auriculotemporal branch
VII - posteiror canal wall
IX - medial, inner part of tympanic membrane (via tympanic n)
X - most of ear canal, part of outer surface of tympanic membrane (auricular br)
C2, C3 - greater auricular n
C2 - lesser occipital n
where is sexual stimulation on ear? sexual suppression?

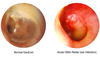
what causes cauliflower ear?
blows, damage that separate cartilage of pinna from surrounding tissue
tissue fills with fluid so difficult for blood or other serous fluid to escape