Lab #4: animal tissues Flashcards
the four categories of tissues are…
Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous
(Epithelium) 3 main functions are:
Protection, secretion, absorption
(Epithelium) Location:
covers and lines organs (epidermis; respiratory, digestive and urinary tracts)
(Epithelium) Lacks ___? (receives nutrients from underlying connective tissue)
blood supply
(Epithelium) “___” with tightly packed cells Named by:
sheet-like Number of layers of cells Simple (1 layer), Stratified (>1 layer) Cell Shape
(Epithelium) Cell shape Types:
Squamous, Cuboidal, and Columnar
(Squamous Epithelium) Cells very ___, much ___ than they are thick (like a fried egg)
thin wider
(Squamous Epithelium) Simple Squamous Epithelium examples:
- Air sacs of respiratory system - Lining of blood vessels, heart and lymphatic tubes
(Squamous Epithelium) Stratified Squamous Epithelium examples:
Skin Vagina Esophagus Mouth

simple squamous epithelium

Stratified Squamous Epithelium
(Cuboidal Epithelium)
Cells cube shaped- ___ and absorption
examples
secretion
- Kidney tubules
- Duct and small glands
- Surface of ovary

Cuboidal Epithelium
(Columnar Epithelium)
___cells, much longer than they are wide
Elongated
(Columnar Epithelium)
Simple Columnar Epithelium
A single layer of cells that function in ___ and secretion
Found in the ___ and ___ tract
May be ciliated or nonciliated
Cilia move mucus, debris and foreign up away from lungs up toward throat
absorption
digestive
respiratory

simple columnar epithelium

Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
(Connective Tissue)
Tissue ___ and ___
protects
supports
(Connective Tissue)
Contains specialized cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM)
ECM composed of two regions
Ground Substance
- Liquid, Gel-like, solid
Fibers
- Collagen (strongest fiber)
- Elastic (stretchy fiber)
- Reticular (form a network)
(Connective Tissue)
cells that make the fibers are called ___
Fibroblasts
Types of Connective Tissue are?
- Loose (Areolar) Connective Tissue
- Dense Connective Tissue
- Adipose
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Blood
Loose Connective Tissue (Areolar)
- Lots of ___ between cells and fibers
- ___ and protects organs
- Collagen and elastic fibers run in many directions
space
Cushions

Loose Connective Tissue (Areolar)
(Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue)
___ closely packed together
Dense regular connective tissue – fibers run in___
examples : ___ and ligaments
Fibers mostly ___ (appear white)
Fibers
one direction
Tendons
collagen

Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue
Adipose
Stores ___
___ = fat cells
Closely packed cells
Cell nuclei are ___
Stores ___ , supports and protects organs, insulates
fat (lipids)
Adipocytes
pushed out to edge of cell
energy

Adipose
(Cartilage)
Contains ___ -like matrix
Cartilage cells = ___
Enclosed within a space called a ___ within the matrix
Avascular
gel
chondrocytes
lacuna
(Cartilage)
Hyaline Cartilage (most common type)
- Costal cartilage (___)
- Articular cartilage (___)
- Fetal skeleton
joins ribs to sternum
end of bones in a joint

Hyaline cartilage
(Bone)
Matrix is ___ (from deposits of calcium and phosphate salts)
Has ___ supply and ___ (cartilage doesn’t)
Bone cells = ___ (small black cells)
Lucunae are connected by channels called canaliculi (fine dark lines)
Solid
blood, nerves
osteocytes

Bone
Blood
Liquid matrix =___
plasma
___ = (Red blood cells)
Erythrocytes
___ = (white blood cells)
Leukocytes
___ - blood clotting
Thrombocytes (platelets)
(Blood)
blood performs what two functions?
Transports:
- Oxygen and nutrients to tissues
- Carbon dioxide away from tissues
- Hormones
Fights disease
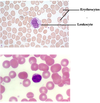
Blood
(Muscle Tissue)
Cells have fibers specialized for___
contraction
(Muscle Tissue)
Skeletal Muscle (Striated, voluntary)
- Parallel elongated cells (fibers)
- multinucleated and each cell is the length of the muscle.
(Muscle Tissue)
Smooth Muscle (Not striated, involuntary)
- Cells are spindle-shaped with a central nuclei
- Organized into sheets of muscle
- Found in walls of hollow organs
(Muscle Tissue)
Cardiac Muscle (Striated, Involuntary)
- In walls of heart
- Intercalated discs join cardiac muscle cells
- branched

Skeletal Muscle

Smooth Muscle

Cardiac Muscle
(Nervous Tissue)
Conducts___
impulses
(Nervous Tissue)
Functions in ___
- Sensory input, motor output
communication
(Nervous Tissue)
2 types of cells ___ and ___
Neurons
Neuroglia
(Nervous Tissue)
Neuron structure:___, ___, ___, and ___
body, nucleus, axon, dendrites

Nervous Tissue


