chapter 16: DNA test 5 Flashcards
(31 cards)
In 1953, ___ and ___ introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick
DNA is unique in its ability to ___. (and cells can repair their DNA)
When is DNA copied?
The resemblance of offspring to parents depends upon ___ and its transmission from one generation to the next
direct its own replication
information encoded in DNA
When T. H. Morgan’s group showed that genes are located ___, the two components of chromosome ___ became candidates for the genetic material
The role of DNA in heredity was first discovered
by studying microorganisms such as ___
on chromosomes
DNA and protein
bacteria and the viruses that infect them
The discovery of the genetic role of DNA began with research by ___ in 1928
Griffith worked with two strains of a bacterium (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
one strain: harmless
one strain: pathogenic (disease causing)
Frederick Griffith
(Frederick Griffith 1928 research: two strains of bacterium)
When he mixed heat-killed remains of the pathogenic strain with living cells of the harmless strain, some living cells became ___
He called this phenomenon ___, now defined as a change in ___ due to uptake of foreign DNA
genotype: genetic makeup
phenotype: physical observable characteristics (traits)
pathogenic
transformation
genotype and phenotype
(Evidence That Viral DNA Can Program Cells)
A virus is ___ (sometimes RNA) enclosed by a protective coat, often simply protein
To replicate, a virus infects a ___ and takes over the machinery.
Viruses that specifically attack bacteria are called ___ (or phages).
DNA
cell
bacteriophages
In 1952, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase showed that DNA is the genetic material of a phage known as ___
They designed an experiment showing that only one of the two components of T2 (___) enters an E. coli (bacteria) cell during infection
They concluded that the injected DNA of the phage provides the genetic information (___)
T2
DNA or protein
transfection
(1952, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase showed that DNA is the genetic material of a phage)
They concluded that the ___ of the phage provided the genetic information that made the infected cells produce new ___
injected DNA
viral DNA and proteins to assemble into new viruses.
(Additional Evidence That DNA Is the Genetic Material)
It was known that DNA is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting of a ___, a ___, and a ___
Nitrogenous Bases: ___
nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
In 1950, Erwin Chargaff reported that DNA composition ___ from one species to the next
This evidence of diversity made DNA a more credible candidate for the genetic material
varies
Two findings became known as Chargaff’s rules
- The base composition of DNA ___
- In any species the number of A and T bases are ___ and the number of G and C bases are ___
The basis for these rules was not understood until the discovery of the double helix
varies between species
equal, equal

After DNA was accepted as the genetic material, the challenge was to determine how its three dimensional structure accounts for its role in heredity
Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin were using a technique called ___ to study molecular structure
Franklin produced a picture of the DNA molecule using this technique
X-ray crystallography
Franklin’s X-ray crystallographic images of DNA enabled Watson to deduce that DNA was ___
The X-ray images also enabled Watson to deduce the width of the helix and the spacing of the nitrogenous bases
The pattern in the photo suggested that the DNA molecule was made up of two strands, forming a ___
helical
double helix
Franklin had concluded that there were two outer ___ backbones, with the ___ paired in the molecule’s interior
Watson built a model in which the backbones were parallel however their subunits run in opposite directions or are ___.
sugar-phosphate
nitrogenous bases
antiparallel

Watson and Crick reasoned that the pairing was more specific, dictated by the base structures
They determined that adenine (A) paired only with ___, and guanine (G) paired only with ___
The Watson-Crick model explains Chargaff’s rules: in any organism the amount of A = T, and the amount of G = C
Each gene has a unique sequence of nucleotides
thymine (T)
cytosine (C)
Since the two strands of DNA are complementary, each strand acts as a template for building a new strand in replication
In DNA replication, the parent molecule ___, and two new daughter strands are ___ based on base-pairing rules
unwinds
built

Watson and Crick’s ___ model of replication predicts that when a double helix replicates, each daughter molecule will have ___ and ___
semiconservative
one old strand (derived or “conserved” from the parent molecule) and one newly made strand

The copying of DNA is remarkable in its ___ and ___
More than a dozen enzymes and other proteins participate in DNA replication
speed and accuracy
Replication begins at particular sites called ___, where the two DNA strands are separated, opening up a replication “bubble”
A eukaryotic chromosome may have hundreds or even thousands of origins of replication
Replication proceeds in both directions from each origin, until the entire molecule is copied
origins of replication
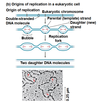
At the end of each replication bubble is a ___, a Y-shaped region where
new DNA strands are elongating
___ are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks
___ corrects “overwinding” ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
___ bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
replication fork
Helicases
Topoisomerase
Single-strand binding proteins

___ cannot initiate ___; they can only add nucleotides to an existing 3′ end
The initial nucleotide strand is a short RNA ___
An enzyme called ___ can start an RNA chain from scratch and adds RNA nucleotides one at a time using the parental DNA as a template
The primer is short (5–10 nucleotides long), and the 3′ end serves as the starting point for the new DNA strand
DNA polymerases
synthesis of a polynucleotide
primer
primase
Enzymes called ___ catalyze the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork
Most DNA polymerases require a ___ and a ___ strand
The rate of elongation is about 500 nucleotides per second in bacteria and 50 per second in human cells
DNA polymerases
primer
DNA template
Each nucleotide that is added to a growing DNA strand is a ___ (dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP)
As each monomer of nucleoside triphosphate joins the DNA strand, it loses two phosphate groups as a molecule of pyrophosphate
The ___ of the pyrophosphate to two inorganic phosphates drives the ___ of the nucleotide to the new strand
nucleoside triphosphate
exergonic hydrolysis
addition/polymerization







