Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction (Test 3) Flashcards
___ is the transmission of traits from one generation to the next
•Heredity
•Variation is demonstrated by ___ that offspring show from parents and siblings
the differences in appearance
•Genetics is ___
the scientific study of heredity and variation
- In a literal sense, children do not inherit particular physical traits from their parents
- It is ___ that are actually inherited
genes
•Genes are the ___, and are made up of ___. Genes are packaged on chromosomes.
units of heredity
segments of DNA
•The ___ is the entire set of genetic instructions within an organism.
genome
•Each gene has a specific location called a ___ on a certain chromosome
locus
•Genes are passed to the next generation through reproductive cells called ___ (sperm and eggs)
gametes
•After FERTILIZATION - fusion of a sperm cell and ovum (egg), genes from both parents are present in the nucleus of the fertilized egg, or ___.
ZYGOTE
•Every living species has a characteristic number of chromosomes. Humans have ___ in their somatic cells.
23 pairs (or 46) chromosomes
•In asexual reproduction, one parent produces genetically identical offspring by___
mitosis
•In ___, two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents
sexual reproduction
•A ___ is the generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
life cycle
•A life cycle starts at ___ and continues until the organism ___.
conception of an organism
produces its own offspring
•Human ___ cells (any cell other than a gamete) have 23 pairs of chromosomes
somatic
•A ___ is an ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
karyotype
•___, are pairs of chromosomes that are the same length and carry genes controlling the same inherited characters
Homologous chromosomes

- Each human somatic cell has ___ of sex chromosomes.
- Human females have a ___
- Human males have ___
ONE pair
homologous pair of X chromosomes (XX)
one X and one Y chromosome (XY)
•The other 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes that do not determine sex are called ___
autosomes
- Each pair of homologous chromosomes includes one chromosome from each parent
- The 46 chromosomes in a human somatic cell are two sets of 23: one set from the mother and one set from the father
just review
- A ___ (2n) has two sets of chromosomes. Somatic cells are DIPLOID.
- For humans, the diploid number is 46 (2n = 46)
diploid cell
- In a cell in which DNA synthesis has occurred, each chromosome is ___
- Each replicated chromosome consists of two ___
replicated
identical sister chromatids

•Sperm cells or ova (gametes) contains a single set of chromosomes, and is ___(n)
haploid
- Each set of 23 consists of ___
- An unfertilized ovum contains ___
- A sperm cell contains ___
22 autosomes and a single sex chromosome
22 autosomes and an X
22 autosomes and an X or Y

•Fertilization is ___ (the sperm and egg).Each gamete is haploid (n)
the union of gametes
•The fertilized egg is called a ___ and has one set of chromosomes from each parent. The zygote is ___(2n)
zygote
diploid
•At sexual maturity, the ovaries and testes produce ___
haploid (n) gametes
- Gametes are the only types of human cells produced by ___, rather than mitosis
- Meiosis results in ___ in each gamete (gametes are haploid)
meiosis
one set of chromosomes
•Gametes fuse to form a ___ that divides by mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism
diploid zygote
•Like mitosis, meiosis is preceded by ___
the replication of chromosomes
- Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called ___
- The two cell divisions result in ___, rather than the two daughter cells in mitosis
meiosis I and meiosis II
four daughter cells
The Stages of Meiosis I
- In the first cell division (meiosis I), ___ separate
- This results in 2 haploid cells (each daughter cell only has one set of replicated chromosomes)
homologous chromosomes
Animal cell division 1 of 2

Animal cell division 2 of 2

The stages of Meiosis II
- In the second cell division (meiosis II), ___ separate
- The two cell divisions result in ___,
- Each daughter cell has ___ as the parent cell
sister chromatids
four daughter cells
only half as many chromosomes

A comparion of Mitosis and Meiosis
- Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes sets from two (diploid) to one (haploid), producing cells that differ genetically from each other and from the parent cell
- Mitosis conserves the number of chromosome sets, producing cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell
you remember?
Three events are unique to meiosis I and these events result in VARIATION amongst gametes
– Synapsis and crossing (prophase I): Homologous chromosomes physically connect and exchange genetic information
– Alignment of homologous chromosomes (homologs) on the metaphase plate instead of individual replicated chromosomes as in mitosis
– Separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase I instead of sister chromatids as in mitosis
remember?
Genetic variation produced in sexual life cycles contributes to evolution
- Mutations (changes in an organism’s DNA) are the original source of genetic diversity
- Mutations create different versions of genes called ___
- Reshuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction produces genetic variation
alleles
Origins of Genetic Variation Among Offspring
- The behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization is responsible for most of the variation that arises in each generation
- Three mechanisms contribute to genetic variation:
–Independent assortment of chromosomes (metaphase I/anaphase I of meiosis)
–Crossing over (prophase I of meiosis)
–Random fertilization
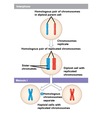
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
- Homologous pairs of chromosomes orient randomly at metaphase I of meiosis
- In independent assortment, each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologues into daughter cells independently of the other pairs
remember?
- The number of combinations possible when chromosomes assort independently into gametes is 2n, where n is the ___
- For humans (n = ___), there are more than 8 million (223) possible combinations of chromosomes
haploid number
23
Crossing Over (Prophase I)
- Crossing over produces ___, which combine genes inherited from each parent
- In crossing over, homologous portions of two nonsister chromatids trade places at___
- A “hybrid” chromosome is produced by combining two non-identical chromatids into a single chromosome (contains shuffled genetic info from maternal and paternal chromosomes)
recombinant chromosomes
synapsis
Random Fertilization
- Random fertilization adds to genetic variation because any sperm can fuse with any ovum (unfertilized egg)
- The fusion of two gametes (each with 8 million possible chromosome combinations from independent assortment alone) produces a zygote with any of about 70 trillion diploid combinations!!!!!
remember?

hopefully this makes sense to you lol


