Formative Quiz Review 1 Flashcards
(99 cards)
A 4-year-old child is referred to you with the diagnosis of leukocyte adhesion defect. She has a history of recurrent bacterial infections, including pneumonias and skin abscesses. Radiography demonstrates granuloma-like lesions in her lungs and liver. However, the data in Table 1 suggests this condition has not been properly diagnosed. Which one of the following elements of these data is INCONSISTENT with a diagnosis of LAD?
CD2 values
CD19 values
CD18 values
CD4 values
CD3 values

CD 18 values - C. Correct. Leukocyte adhesion defect is an absence of LFA-1, CR3 and CR4. CD11a is a component of one of these receptors (LFA-1) and its expression is altered in these patients. CD11a pairs with CD18 to form the LFA-1 receptor. Because the actual defect in LAD is the absence of CD18, any receptor that uses CD18 would be absent from LAD cells. In this patient, the normal numbers of CD18-positive cells also indicate that she has been misdiagnosed.
A patient arrives at a clinic with a number of boils on his back, and a sample of pus from one of the lesions was sent to the laboratory for culture. The microbiology laboratory cultures heavy growth of Staphylococcus aureus, a gram-positive bacterium. Which of the following innate immune components is probably NOT involved in the protective response to this pathogen?
C5a
C3b
Superoxide
Lysozyme
TLR4
TLR 4 - LPS is not present in gram-positive bacteria.
The cartoon of the portly mouse below depicts the vascular and lymphatic systems, showing a T cell that will travel through both duct systems. Which of the following best represents the path taken by a naïve T cell?
Aorta, Heart, Lung, Lymphatic vessel, Gut, Lymph node, Aorta
Aorta, Spleen, Heart, Aorta, Lymph node, Lymphatic vessel, Heart, Lung, Aorta
The T cell is most likely to remain in the blood stream only, as there is no antigenic challenge.
Aorta, spleen OR lymph node; the T cell will remain at one of these secondary lymphoid structures until it encounters antigen.
Aorta, Spleen, Heart, Aorta, Lymph node, Lymphatic vessel, Heart, Lung, Aorta - T cells travel through the blood stream to gain access to the secondary lymphoid structures, where they reside and ‘travel’ for a short time in search of antigen. If they do not encounter antigen (Question 4) within the lymphoid structure they exit via the draining veins (spleen) or efferent lymphatic ducts (lymph nodes), recirculate by making their way back to the heart where they begin their journey once again.
The neutrophils (N) in the accompanying photomicrograph are attracted to their extravascular location primarily by which one of the following factors?

C3a
C5a
C5b
Collagen
Fibrin
Neutrophil chemotactic factor
C5a - Neutrophils follow a gradient formed by complement factor C5a to the site of injury. Other factors may also be involved, including certain bacterial peptides, but C5a is the most widely known and understood
TAP is a component of which MHC pathway?
MHC class I pathway
Polymorphisms in HLA-A are most likely to influence the affinity of the interaction between which of the following pairs:
HLA-A and anchor residues
HLA and ß2m
HLA-A and CD8
HLA-A and chaperones
HLA and TAP
HLA-A and anchor residues - polymorphisms in HLA influence the ability of HLA to bind peptides and the TCR. The amino acids of the peptides that associate with HLA are called anchor residues.
You are characterizing the macrophage response to the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruoginosa. Knowing that this gram-negative bacterium has a potent endotoxin, you decide to determine if IL-1 transcription is activated by the pathogen through a Toll-like receptor. Which of the following signaling intermediates is involved in this pathway?
IκB
NFAT
NOD
PLCγ
Stat-1
IkB
Which one of the following is a “pattern recognition receptor” of the innate immune system that can distinguish host and microbial structures?
- Fc receptor
- Complement receptor 3 (CR3)
- Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)
- α-defensin
- BCR
Toll-like receptor 9 - Correct. Toll-like receptors are good examples of receptors capable of recognizing molecular patterns on microbes and distinguishing them form host structures.
Which one of the following processes contributes most to the increase in affinity of an antibody response over time (affinity maturation), especially following multiple immunizations?
Somatic hypermutation
BCR editing
Ig class switching
Joining of V, D and J segments in memory B cells
Activation of Th1 cells
Somatic hypermutation - Affinity maturation is the process by which an animal’s antibody response over time acquires a higher average affinity. This results from the selective activation of B cells that bear antigen receptors (BCR) with high affinity for the immunizing antigen. Somatic hypermutation occurs during memory B cell development and generates mutated BCR, some with much higher affinities for the antigen.
Recently, a patient was described who had a defect in TLR4-initiated cell signaling. Which of the following groups of microbes would be expected to cause recurrent infections in this patient?
Respiratory viruses
Fungi that cause vaginal yeast infections
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
Insect vector-borne parasites
Gram-negative bacteria - Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a member of receptors that recognize conserved microbial components and initiate innate immune responses. TLR4 is a specific signaling receptor for the lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found on gram-negative bacteria. It is not known to bind to fungal, viral or parasitic ligand.
Which one of the following properties would distinguish (be different between) IgG and IgM antibody molecules?
Their ability to activate complement
Their ability to bind to human mast cell Fc receptors
Their presence of κ light chains
Their ability to cross the placenta
Their ability to precipitate soluble antigens
Only human IgG can cross the placenta; IgM cannot.
Which one of the following properties of the complement system requires the terminal components, including C9?
Chemotaxis
Inflammation
Membrane attack (lysis)
Opsonization
Recognitition of microbes
Membrane attack - lysis
Which one of the following cytotoxic cells is most active against host cells that DO NOT express MHC class I molecules?
Cytotoxic T cells
Natural killer cells
Natural killer T cells
Neutrophil
Macrophage
NK cells bear an inhibitory receptor for MHC class I molecules that keeps the NK cells quiescent in the presence of class I molecules. In cells that lack class I expression (e.g., tumor cells or virus-infected cells), the inhibitory receptor is not engaged allowing the NK cell to become activated.
An immune-deficient patient is diagnosed with a congenital defect in RAG-2 expression. Which
of the following observations would MOST LIKELY be seen in this patient?
Aberrant B cell development in the thymus
A lack of peripheral B cells, T cells, and NK cells
An absence of double positive and single positive thymocytes
Normal peripheral B cell numbers and a lack of CD4+ T cells
Normal peripheral CD4+ T cell numbers and a lack of B cells
An absence of double positive and single positive thymocytes - RAG is required for the rearrangement of genes that encode the BCR and TCR. Cells of the B and T cell lineages dependent on expression of a pre-BCR or pre-TCR would be absent or extremely low. This includes any cell beyond the pre-B stage or the DN stage.
In which of the following infectious diseases is a Th1 pattern of cytokine production the most beneficial?
E. coli urinary tract infections
Tuberculosis
Streptococcal pneumonia
Pseudomonas-associated sepsis
Staphylococcal skin infections
Tuberculosis - Th1 cytokines, such as IFN-g, are important against intracellular bacterial pathogens, such as M. tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis. IFN-g serves to activate infected macrophages for bacteriocydal activity.
Mixed lymphocyte reaction does what?
C. The MLR is used to measure HLA incompatibility between two individuals.
Approximately how many Ig gene segments are required to produce antibodies with 1 billion different specificities?
1 billion
1 million
10
100 million
100
100
VLA-4 binds?
VCAM-1
The image below depicts a portion of the Peyer’s Patches of the small intestine. Match the following functions with the letters that appear in the photomicrograph. Note that for clarity, some duplicate structures are labeled with the same letters. The location of the cells responsible for initial antigen uptake is:
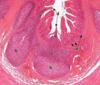
D - villi
ABO blood antigens are:
Carbohydrates
Anaergy is a form of central or peripheral tolerance?
Both Central and Peripheral
What is the role of CR3?
The CR3 receptor binds Ag-Ab-iC3b complexes, and CR3 and CR4 are expressed on neutrophils and monocytes,
The ligand for this cell surface receptor requires TAP for its expression. Which of the following is the cell surface receptor?
CD3
CD8
CD18
CD19
CD154
CD8 - CD8 binds to MHC class I molecules, which require the transporter of antigenic peptides (TAP) for their expression.
Which of the following processes contributes the most to the size of the repertoire of T cell antigen receptors of an individual?
DNA recombination
Large pools of V region genes
Somatic hypermutation
Polymorphism
Active immunization
DNA recombination - Recombination of the V, D, and J regions accounts leads to the production of 10^9 unique B and T cell clones.














