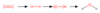CH 4 Flashcards
(77 cards)
A type of process where bacteria and archaea increase in size and multiply in an exponential form.

Binary Fusion
The average time between two consecutive generations in the lineages of a population.
Generation Time
A group of microorganisms that attach to surfaces and live in polymer-incased communities.

Biofilms
A type of formation when planktonic (free-floating) cells move to a surface and adhere, multiplying, releasing polysaccharides, DNA and other hydrophilic polymers.

Biofilm Formation
This substance gives the appearance and characteristics of slime and is composed of accumulation of polymers.

EPS (Extracellular Polymeric substances)
In Biofilm Formation, this phase is where the bacteria move to the surface and adhere.

Phase 1

In Biofilm Formation, this phase is where the bacteria multiply and produce EPS (extracellular polymeric substances.

Phase 2

In Biofilm Formation, this phase is where other bacteria may attach to the EPA and grow.

Phase 3

In Biofilm Formation, this phase is where the cells communicate and create channels in the EPA that allow nutrients and waste products to pass.

Phase 4

In Biofilm Formation, this phase is where some cells detach and then move to other surfaces to create additional biofilms.

Phase 5

A method in the laboratory where bacteria and archaea are isolated and grown.

Pure Culture
A technique used for pure cultures where a set of procedures minimizes the chances of other organisms being accidentally introduced.

Aseptic Technique
This requirement is for obtaining a pure culture, consisting of a medium, container and methods of separation of individual microbial cells.

Basic
A distinct mass of cells from a single microbial cell.

Colony
A growth medium that is a polysaccharide extracted from marine algae to solidify culture media.

Agar
A two-part covered container made of glass or plastic for cultures.

Petri Dish
The simple term referred to a petri dish with a growth medium.

Agar Plate
A culture technique used for isolating microorganisms with a sterile inoculating loop dipped into a sample then lightly drawn several times across the face of an agar plate.

Streak-Plate Method
A cultures grown in the laboratory using closed systems where nutrients or waste are untouched.

Batch Cultures
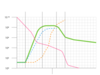
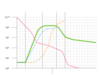
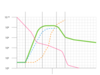
A type of pattern where grown batch cultures the populations increase in distinct patterns of stages and decline, it contains 5 distinct stages.
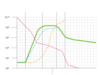
Growth Curve

A type of pattern phase where a culture is transferred into a different medium and no increase of cell number occur.

Lag phase

A type of pattern phase where cell divide at a constant rate, medically important due to sensitivity of antimicrobial meds.

Log Phase

A type of valuable molecule produced by microbial growth in the log phase of cell culture.

Primary Metabolites

A type of waste compounds not required for growth that result of accumulation, causing cells to shift into hibernation.

Secondary Metabolites