CH 3 Flashcards
(180 cards)
Discovered two forms of bacteria under a microscope by staining, the frame positive and gram negative.

Hans Gram
This study has revealed the cells of the domains bacteria, archaea and prokaryotic. The chemicals that interfere with prokaryotic cells are used to selectively distort bacteria without hurting humans.

Microscopy
This type of microscope uses visible lights and a series of lenses to magnify objects. Simple. Up to 1,000x. Used routinely in laboratories to absolve cell size, shape, and motility.
Light Microscope

A type of microscope that can view up to 100,000x power. Find details of cell structure.

Electron Microscope

This type of microscope produces images of individual atoms on a surface.

Atomic Force Microscope

A technique of microscopy that involves light passing through a specimen and then through a series of magnifying lenses.

Light Microscopy

A type of microscope that illuminates the field of view and generates a bright background.

Bright-Field Microscope
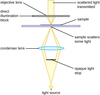
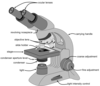
The modern microscope uses multiple magnifying lenses.

Compound Microscope

Lenses that allow selection of different magnification.

Objective Lens

Also known as eyepiece is a lens close to the eye.

Ocular lens

A lens that focuses light on a specimen.

Condenser Lens
A unit of measurement of ability to see two objects very close and sets the minimum distance. This unit is in the result of quality, type of lens, the wavelength of light, magnification and how specimens are prepared.

Resolving Power
The maximum resolving power of the best light microscopes that are able to see morphology of prokaryotic cells but not viruses is µm?

0.2 µ

A type of technique that affects resolution and achieving the max/min?
Typically by using immersion oil to displace air between lens and specimen.

Maximum Resolution
A type of light bending that result of some light rays missing relative small openings of higher-power objective lenses causes fuzzy image.

Refraction

A type of lighting that results in color intensity between object and background helps with colorless origins is s instead of killing them with a stain.

Contrast

A type of light microscope that increases the contrast between microbes and surroundings.

High Contrast light Microscopes
A technique used in microscopy that results in a dark background image, helps organisms stand out.

Dark-Field Microscope
A type of microscope that reflects light slightly different, resulting in cells and dense materials appearing darker.

Phase-Contrast Microscope
A technique/microscope in microscopic resulting in a 3D looking image by using differences in refractive index.

Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)

A type of microscope used to observe cells or materials that are stained UV dye or fluorescent t.

Fluorescence Microscope

A type of microscope that uses fluorescent molecules to create HD or 3D images.

Scanning Laser Microscope (SLM)

A type of microscopy that focuses laser beams to a point on one plane of a specimen. Like a mini cat scan that kills cells.

Confocal Microscopy

A type of microscopy with lower energy that focuses a laser beam on a point on one plane of a specimen. Improved. Live cells can be obtained. A safe mini cat scan.

Multi-photon Microscopy