8.1s PRINCIPLES OF CONSTRUCTION Flashcards
S1 - 2 TYPES OF LOADS
Ching 2.08
STATIC & DYNAMIC
S2 - 2 TYPES OF STATIC LOADS
Ching 2.08
DEAD & LIVE
S3 - 4 TYPES OF LIVE LOADS
Ching 2.08
1 - OCCUPANT & MOVEABLE FURN/EQUIPMENT
2 - SNOW
3 - RAIN
4 - IMPACT (KINETIC LOADS OF SHORT DURATION - CONSIDERED STATIC BY CODE - AMPLIFY LOAD TO COMPENSATE FOR DYNAMIC NATURE)
S4 - 2 COMMON TYPES OF DYNAMIC LOADS
Ching 2.09
WIND & SEISMIC
S5 - NEWTON’S 3RD LAW
Ching 2.12
For every force acting on a body (building) there is an equal force of opposite magnitude.
S6 - LIST & DEFINE THE 3 TYPES OF FORCES WHICH MAY IMPACT A STRUCTURAL BODY.
Ching 2.11
1 - COLLINEAR = along the same line of action *sum of vectors = magnitude along same line of action
2 - CONCURRENT = vectors that intersect at one point *sum of vectors with parallelogram polygon method
3 - NON-CONCURRENT = moment or rotation forces *sum of vectors = moment arm = F X d
S7 - SHEAR & MOMENT FORCES ARE BEST RESISTED WITH WHICH CONSTRUCTION TYPES.
- RIGID CONNECTIONS (Least efficient, only good for small buildings)
- SHEAR PLANES
- BRACING
S8 - 3 TYPES OF STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS & MATERIALS TYPICALLY USED FOR EACH
1 - LINEAR - columns & beams (steel/timber/concrete beams)
2 - PLANAR - walls & slabs (light wood/steel framing/masonry/concrete walls & slabs)
3 - COMPOSITE - columns/walls & beams/slabs
S9 - 3 MAIN TYPES OF SHEAR STRENGTH IN HIGH RISE CONSTRUCTION
1 - CONVENTIONAL - shear walls/bracing &or rigid frames
2 - CORE - vertical circulation key to lateral strength
3 - TUBE - lateral bracing along perimeter
S10 - BEST CONSTRUCTION TYPE FOR TALL BUILDINGS IN SEISMIC ZONES
STEEL = DUCTILE & LIGHT
NOT CONCRETE FOR EXAMPLE = HEAVY & BRITTLE
S11 - 2 TYPES OF DAMPENING
1 - TUNED MASS DAMPER - heavy mass on rollers towards the top of a tall building
2 - BASE ISOLATION - isolate the base from the ground so building can ‘float’ - prevents resonance
S12 - Define underpinning.
rebuilding / strengthening foundation of existing buillding
S13 - Describe 5 main types of excavation support systems
1 - SHEET PILING steel (corrugated), timber or precast planks driven vertically into ground
2 - SOLDIER PILES steel h-sections driven down vertically to support horizontal lagging
2 - TIE BACKS used if rakers would interfere with const. steel cables anchored into predrilled soil or rock
3 - CROSS BRACING sheet piling and soldier beams are supported by horizontal steel cross bracing or by steel rakers bearing on heal blocks
4 - SLURRY WALL poured into a trench and often becomes permanent wall
Describe the dimensions shown below:

width of foundation wall = W
projection = 1/2 W
height of footing = W
width of footing = 2 W

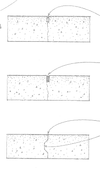
Describe the cone of bearing, how in impacts footing spacing, and what angle is shaped by rock and soil/sand respectively.
- Cone of bearing is the compacted soil below the footing
- each footing must be separated by the width of two footings @ min.
- rock results in an angle of 60deg
- soil and sand results in an angle of 30deg
(see below)