20. Vascular Histology Flashcards
whats the commonality btn As & Vs when it comes to histo
both have tunics
(3 layers)
what are the 3 tunics
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
what layers are found w/i the tunica intima & what are their fxns
- endothelium: 1 layer of squamous epithelial cells - reduce friction
- basal lamina: endothelial cells- thin layer w/collagen, proteoglycan, glycoproteins
- subendotheial layer (loose CT) - contain internal elastic mem =fenestrated elastic material w/i As & arterioles (allow recoil)

what are the characterisitcs of tunica media & what are the fxns of each
-circumferential Sm. M (allow continous pumping of blood)
-external elastic mem- extends from internal elastic mem & is a layer of elastin that seperates tunica media from adventitia
-varying amount of elastic, reticular fibers & proteoglycans
*A’s have thicker tunica media

what are the characteristics of tunica adventitia
-longitudinally arranged collagenous tissue w/ few elastic fibers - prevent overexpansion
As- thin & Vs thick
merge with loose CT of neighboring vasculature
contain vaso vasorum & nervi vasorum

what is represented in the solid circles? & what is its fxn

vasa vasorum
-in tunica adventitia- supply blood to vascular tunics themselves
found in large As & esp large Vs (bc carrying deoxy blood)
what is represented w/i the dashed circle & what is its fxn

nervi vasorum
ANS input that control contraction of vascular Sm. M
what is this and what are its components

Large As (elastic)
- majority = tunica media
- elastin makes concentric layers btn Ms cells (stretch/recoil)
NO FIBROBLAST
Sm M makes collagen, elastin, ground substance of ECM
what is this & what are its components

Medium As (muscular)
more Sm M, less elastin
Sm M in spiral - produce ECM components
thick tunica adventitia & media
internal elastic mem & external elastic mem present

large As (elastic)
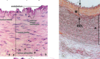
medium As (muscular)
what are the differences btn small arterioles & arterioles
small arterioles - up to 8 layers of sm. m in tunica media w/ internal elastic mem present
arterioles - 1-2 layers of sm. M - internal elastic mem may/may not be present - contain sym/parasym innervation for flow regulation for cap beds

arterioles

small arterioles
what is this & what are its components

capillaries (=caps)
metabolic exchange & diameter same size or smaller than RBC
single endothelial cell layer
contain pericytes: perivascular contractile cells w/ branching cytoplasmic processes - controlled by NO - & provide stability of capillaries and postcap venules
when are pericytes enclosed by basal lamina
when basal lamina is continous with that of the endothelium
what is the fxn of the single layer of endothelial cells in capillaries
form inner tunica intima
connected via cell-cell jxn (# of jxns alter permeability)
support basal mem & collagen
metabolically involved in blood coagulation & thrombosis, local vasodilation/constriction
(highlights = weibal palate bodies & arrow = storage granulaes)

what are the ways capillaries can be organized?
how do these differ in fxn
- continous cap - most common - very selective about what can go in/out
- fenestrated cap- porous - allow large items to go in/out - make filtrate in urine production
- discontinous (sinusoidal) cap- leaky, not selective - found in spleen, liver, bone marrow
explain the relationship of :
metarterioles,
thoroughfare channels,
precap sphincters,
true caps
& postcap venules
metarterioles - first branch of arteriole supplying tissue –> distal end forms the thoroughfare channel –> entry towards cap beds –> precap sphincters regulate the flow thru true cap –> true cap has no sm. m, contain pericytes and allow gas exchange –> out thru thoroughfare channels into postcap venules
what happens if the precap sphincter is closed
prevent gas exchange (dont let blood into true caps)
-shunt blood to venous return
what is the difference btn postcap venules, muscular venules & small Vs
postcap venules: drain caps, no true tunica media
muscular venules: 1-2 layer sm. m in tunica media w/ thin tunica adventitia
small Vs: all 3 layers present, tunica media = 2-3 layers & tunica adventitia = thick
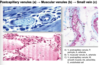
what is this & what are its components

medium Vs
travel w/ muscular Ss
tunica media & adventitia thicker than small Vs
contain valves
what is this & what are its components

Large Vs
thickest wall = tunica adventitia (contain longitudinal Sm M cells, collagen, elastic fibers & fibroblasts)
tunica media - thin circumferential Sm M, collagen fibers and some fibroblasts
tunica intima - thin & blends w/ media

Medium Vs





