spinal cord Flashcards
Functions of the Spinal Cord
- sensory and motor innervation via spinal nerves
- two-way conduction path between body & brain
- center for reflexes
The spinal cord begins at _______ and ends at _______.
(begins at) foramen magnum; (ends at) L1/L2 vertebrae
The spinal cord is superiorly contiguous with _______.
the medulla oblongata of the brainstem
Spinal cord protection
- vertebrae
- meninges
- CSF
The spinal cord passes through the _________ of the vertebrae.
vertebral foramina
of paired spinal nerves
31
Divisions of spinal cord
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar - same as vertebrae
region at end of spinal cord

conus medullaris
- cone-shaped inferior end of spinal cord at L1/L2
root-like area toward bottom of image

cauda equina
- collection of nerve roots at inferior end of vertebral column
starred area

filum terminale
- long extension from pia mater of spinal cord
- CT connecting spinal cord to coccyx for longitudinal support

cervical enlargement (of SC)
- thicker area of SC from which upper limb nerves arise

lumbar enlargement
- thicker area of SC from which lower limb nerves arise
part D

shallow, narrow sulcus on posterior side of spinal cord
part Q

anterior median fissure
- deeper/wider than PM Sulcus
part R

central canal
- filled with CSF and continuous with brain ventricles
part N

anterior (ventral) horns
- contain somatic motor nuclei, providing nerve impulse to skeletal muscle
part J (two of them)

lateral horns
- contain autonomic motor nuclei for smooth/cardiac muscle and gland innervation
part I

posterior horn
- somatic and autonomic sensory nuclei
- closest gray matter to periphery of spinal cord
- contains interneurons
part S

posterior funiculi
- white matter, axon bundles at dorsal side of SC
part O

anterior funiculi
- bundles of myelinated axons (white matter) at ventral side of SC
part G

lateral funiculi
part P

gray commissure
- thin strip of gray matter that surrounds central canal
- unmyelinated axons for communication between two sides of SC
number 5

white commissure
- bundle of myelinated axons that cross the midline of the white matter of the spinal cord

epidural space
- space outside of dura mater of spinal cord
- filled with adipose tissue and blood vessels

dura mater
- outermoust meningeal layer surrounding spinal cord
- unlike cranial dura mater, spinal dura mater has no periosteal layer
part A

arachnoid mater
- similar in structure to arachnoid mater of brain
part F

subarachnoid space
- also similar to S.A. space within skull
part C

pia mater
- thin layer on surface of SC
part 2

dorsal root
- AKA posterior root
- sensory (afferent) axons only
part 1

dorsal root ganglia
- ganglia just lateral to the dorsal roots of spinal nerves
- contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
- good landmark to identify orientation of a diagram of spinal nerves and the direction of nerve impulse travel
part 7
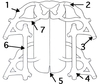
ventral root
- AKA anterior root
- motor axons only, leading to muscles/glands
- axons come from cell bodies in anterior/lateral horns of spinal cord gray matter
reddened area where dorsal and ventral roots come together

spinal nerve
- union of dorsal and ventral roots within the intervertebral foramen
- contain both efferent and afferent nerve fibers
part H

dorsal ramus
AKA posterior ramus
- smaller branch of spinal nerve lateral to its roots and their union within the intervertebral foramen
- innervates muscles and skin of back
part I

ventral ramus
(AKA anterior ramus)
- larger branch of spinal nerve lateral to its roots
- innervate anterior and lateral trunk and limbs
- many anterior rami form nerve plexuses elswhere
part 5

rami communicantes
- additional rami which communicate with autonomic nervous system


