Special Senses Flashcards
Sensory Receptors
- peripheral (distal) endings of sensory neurons
- specific for certain types of stimuli (ex: photoreceptors for light)
- depolarize neurons to produce action potential
Modality-based Receptor Classification
- Chemo-
- Thermo-
- Mechano-
- Photo-
- Noci-
- Baroreceptors
Stimulus Origin-based Receptor Classification
- interoreceptors - detect internal stimuli
- proprioceptors - body position/movement
- exteroceptors - detect external stimuli
Distribution-based Receptor Classification
General Senses - widely distributed
Special Senses - limited to head
General Senses
- temperature
- pain
- touch pressure
- vibration
- proprioception
Special Senses
- smell
- taste
- vision
- equilibrium
- hearing
What makes a sense “special”?
- localized (confined to head)
- special receptor cells
- housed in complex sensory organs or epithelial structures
- cranial nerves carry special sensory info to brain
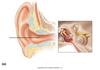
Chemical Senses
- Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals binding to them
- Taste - gustation
- Smell - olfaction

Taste Bud
- 50-100 epithelial cells in a bundle containing long microvilli that receive chemicals from food that create flavors
surface elevations of tongue

Tongue Papillae
- contain taste buds
light blue lateral cells

supporting cell of taste bud
central purple cells

gustatory cell
- taste receptor cells
- have long microvilli known as gustatory hairs that extend through taste pores
Gustatory Pathway
- taste info travels primarily via Facial (VII) and Glossopharyngeal (IX) nerves (some via Vagus (X))
- primary sensory neurons synapse in solitary nucleus of medulla
- secondary neurons synapse in thalamus
- tertiary neurons synapse in gustatory cortex of cerebrum
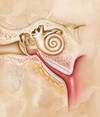
olfactory epithelium

- specialized nasal cavity epithelium containing olfactory receptor cells
purple structure

olfactory neuron
- specialized chemoreceptive cell in olfactory epithelium
- bipolar, basal side has axon, apical side has cilia
- axons gather into bundles that make up olfactory nerve, pass through ethmoid (olfactory foramina of cribriform plate), attach to olfactory bulbs of forebrain
pink structure
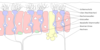
supporting cells
- columnar cells that support olfactory neurons
small green inferior structure
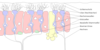
Basal Cell
- form new olfactory neurons
orange structure towards bottom

basal cell
- replace gustatory cells
large yellow structure

olfactory bulb
- structure on inferor side of frontal lobes that sits above cribriform plate of ethmoid bone and connects with olfactory nerve filaments
Olfaction Pathway
- Olfactory Bulb
- Olfactory Tract
- then to 3 areas of brain:
- Limbic Region (associate smell w/ emotion)
- Piriform Lobe of Cortex (conscious perception)
- Thalamus and Orbitofrontal Cortex (analysis and comparison of smell)
olfactory tract
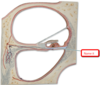
not the muscle, but the structure it moves

Palpebrae
- AKA eyelids
- one upper, one lower per eye

Medial and Lateral Canthi (singular: canthus)
- AKA medial/lateral angles

levator palpebrae superioris
- muscle that opens eyelid
thin layer on anterior whites of eyes and inside eyelids

conjunctiva
- straitified squamous epithelium that produces lubricating mucus
- in eyelids, called Palpebral conjunctiva
number 1

Lacrimal gland
- produces tears
- contains lysozyme, a bactericidal enzyme

lacrimal puncta
- tiny openings for lacrimal fluid to drain into
number 5

lacrimal caruncle
- small, pink, globular nodule at the inner corner of eye
- contains sebaceous and sudoriferous glands
- source of “eye boogers”
6

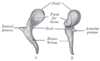
superior oblique muscle
- depresses eye, turns it laterally
8

inferior oblique muscles
- elevates eye, turns it laterally
2
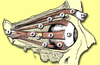
superior rectus muscle
- elevates eye, turns it medially
3

inferior rectus muscle
- depresses eye, turns it medially
4
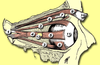
medial rectus muscle
- moves eye medially
5

lateral rectus muscle
- moves eye laterally
Lacrimal Apparatus
system for keeping eye’s surface moist
- three parts:
- lacrimal gland
- lacrimal sac
- lacrimal fluid

lacrimal sac
area just medial to eye where lacrimal fluid gathers and empties into nasal cavity
lacrimal fluid
- made up of mucus, antibodies and lysozyme
7

Trochlea
- point where superior oblique muscle is anchored above eye
Three Tunics of the Eye
Fibrous - sclera and cornea
Vascular - choroid, ciliary body, iris
Sensory - retina
Fibrous Tunic
- most external layer
- two regions:
- Sclera
- Cornea
Vascular Tunic
3 parts:
- Choroid
- Ciliary Body
- Iris
Sensory Tunic
- AKA Retina
two layers:
- pigmented layer
- neural layer
1

Sclera
- poster 5/6s of fibrous tunic
- white, opaque
- gives eye shape, anchors eye muscles