SM_85b: Neurological Disease in Women Flashcards
Migraine is more common in ____
Migraine is more common in women
_____ migraine is migraines that regularly occurs 2 days before to 3 days after menstrual period but can occur at other times
Menstrual-related migraine is migraines that regularly occurs 2 days before to 3 days after menstrual period but can occur at other times
____ migraine is migraine that only occurs 2 days before to 3 days after menstrual period
Pure menstrual migraine is migraine that only occurs 2 days before to 3 days after menstrual period
Rapid withdrawal of ____ is responsible for hormone fluctuations in migraine
Rapid withdrawal of estrogen is responsible for hormone fluctuations in migraine

Migraine frequency ____ in pregnancy and menopause
Migraine frequency decreases in pregnancy and menopause

Describe treatment for hormone-sensitive migraine
Treatment for hormone-sensitive migraine
- Abortive therapy: NSAIDs, triptans
- Perimenstrual NSAIDs
- Prophylactic therapy: B-blocker, calcium channel blocker, topiramate, tricyclics
____ and ____ may greatly influence susceptibility to seizures in some
Estrogen and progesterone may greatly influence susceptibility to seizures in some
(incidence same in men and women)
____ is a sex hormone that is excitatory like glutamate
Estrogen is a sex hormone that is excitatory like glutamate

____ is a sex hormone that is inhibitory like GABA
Progesterone is a sex hormone that is inhibitory like GABA

Progresterone modulates _____ which upregulates GABA
Progresterone modulates allopregnalone which upregulates GABA (-)

____ upregulates glutamate and downregulates GABA
Estradiol E2 upregulates glutamate and downregulates GABA
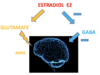
Serum ____ is high and ____ is low in catamenial epilepsy
Serum estrogen is high and progesterone is low in catamenial epilepsy

Describe treatment options for catamenial epilepsy
Treatment options for catamenial epilepsy
- Anti-epileptic medications or surgery
- Pulse doses of anti-epileptics: benzodiazepines, acetazolamide
- Oral progesterone
- Depo-medroxyprogesterone
- GnRH agonists
Multiple sclerosis is more common in ____
Multiple sclerosis is more common in women
In females, TH0 cells become ____ cells which are responsible for ____
In females, TH0 cells become TH1 cells which are responsible for intracellular immunity

Low estrogen favors maturation of TH0 cells into ____ cells which are responsible for ____
Low estrogen favors maturation of TH0 cells into TH1 cells which are responsible for intracellular immunity

Pregnancy estriol or high estrogen favor maturation of TH0 cells into ____ cells which are responsible for ____ and ____
Pregnancy estriol or high estrogen favor maturation of TH0 cells into TH1 cells which are responsible for extracellular immunity and immune tolerance

Major cogenital malformations occur early in the ____ and can result from ____
Major cogenital malformations occur early in the 1st trimester and can result from AEDs

____ is the AED with greatest risk of fetal malformations
Valproic acid is the AED with greatest risk of fetal malformations
AED levels and seizure control are affected by ____, ____, and ____
AED levels and seizure control are affected by increased fluid volume, increased urine output, and changes in drug metabolism
Most women demonstrate a ____ in lamotrigine clearance during pregnancy
Most women demonstrate a marked increase in lamotrigine clearance during pregnancy

Describe syptomatic management of migraine in pregnancy
Symptomatic anagement of migraine in pregnancy
- 1st line: non-pharmacologic measures, acetaminophen
- 2nd line: NSAIDs (1st and 2nd trimester only), metoclopromide
- 3rd line: sumatriptan

Prophylactic treatment is ____, and ____ and ____ should be avoided
Prophylactic treatment is rarely required / indicated in pregnancy, and valproic acid and topiramate should be avoided

____ for disease modification of MS is acceptable for pregnant women
Glatimer acetate for disease modification of MS is acceptable for pregnant women





