Review of the upper limb Flashcards
Where does the axillary artery run between? [2]
lateral border 1st rib to inferior border of teres major

What are the spinal cords routes of the brachial plexus? [1]
C5-T1
Brachial plexus
What are the anterior cord nerves [3]
What are the posterior cord nerves [2]
Anterior cord (lateral to medial)
* Musculocutaneous
* Median
* Ulnar
Posterior cord
* Axillary
* Radial

brachial plexus qs
How do you differentiate between fractured clavicle or dislocated shoulder?
Look for rounded profile of the shoulder:
Shoulder dislocation:
* Shoulder squared off – can see acromioclavicular joint
Clavicular fracture:
* Rounded profile of shoulder - SCM pulls medium section upwards. Tenting of the joint
Clavicle on left; shoulder dislocation on right

Explain when and why a clavicle fracture is an emergency [2]
If nerve tinglings and loss of sensation. Can cause damage to:
- Subclavian artery underneath damage
- Brachial plexus: sandwiched between clavicle and first rib
Which muscle is causing this fractured clavicle to shorten the width of the shoulder? [1]
Pectoralis major (major adductor – brings arm closer) have lifted the shoulder up and shorten the width

Which nerve is at risk from shoulder dislocation
- Musculocutaneous
- Median
- Ulnar
- Axillary
- Radial
Which nerve is at risk from shoulder dislocation
Axillary
Which structure in the shoulder is at risk of damage from shoulder dislocation that increases liklihood of refracture [1]
Glenoid labrum
Paralysis of the deltoid muscle restricts which type of movement? [1]
Abduction
Where does lymph from lateral [1] and medial [1] breast drain?
Lateral breast drain to axillary nodes
Medial breast drains to parasternal nodes

Describe scapulo-humeral rhythm [2]
Scapula and humerus move in a 1:2 ratio.
When the arm is abducted 180 degrees, 60 degrees occurs by roation of the scapula and 120 degrees by rotation of the humerus at the shoulder joint
During total 180 degrees of abduction, [] degress is from glenohumeral joint and [] degrees from scapulothoracic joint
120: glenohumeral joint
80: scapulothoracic joint
Metastatic breast cancer surgery frequently involves clearance of which lymph node? [1]
axillary lymph node clearance
Which nerves [2] and muscles [2] are at risk of from axillary lymph node clearance? [2]
Injury to thoracodorsal nerve; Latissimus dorsi
Injury to long thoracic nerve; serratus anterior - causes winging scapula

Label 1-5

- Pec major
- Pec minor
- Axillary vein
- Thoracodorsal
- Long thoracic
Label B & C

B = thoracodorsal
C = long thoracic
Label A-C

A: Pec major
B: serratus anterior
C: long thoracic nerve
peripheral odeam?A
Name 4 occassions that long thoracic nerve is at risk [4]
Stab wound
Thoracic surgery
Chest tube insertion
Crushed between clavicle and 1st rib

Which nerve supplies the trapezius? [1]
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)

How does spinal accessory nerve damage present? [4]
- Weak shoulder abduction not as prominent winging of scapula
- Loss of adduction - DOUBLE CHECK
- Atrophy of trapezius
- Shoulder falls
Name a mechanism by which spinal accessory nerve can be damaged? [1]
Which muscles does the spinal accessory nerve innervate? [2]
Tumour around jugular foramen [1]
Innervates trapezius and the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Causes winging of the scapula that is much less pronounced compared to S

What are the two types of joint in the elbow? [2]
A hinge joint: hand to the body
A pivot joint: turns hand over (pronation / supination)
What muscle groups are found in the anterior forearm? [2]
Which arteries are found within the anterior forearm [2]
Which nerves are found within the anterior forearm [2]
Muscle groups:
* Flexors
* Pronators
Arteries;
* Radial artery
* Ulnar artery
Nerves:
* Median nerve
* Ulnar nerve
Which arteries supply posterior forearm? [2]
Ulnar and radial arteries
double chekc !!
State how ulna and radial articulate with the hand
Ulna does not articulate with carpals
Radius articulates with scaphoid and lunate
which of the following is the only articulation between upper limb and axial skeleton?
- sternoclavicular joint
- acromiclavicular joint
- glenohumeral joint
- scapulothrocic joint
ssternoclavicular joint

Sternoclavicular joint:
What is the type of joint? [1]
Which structure is present for shock absorption? [1]
Which type of movement does the joint permit? [1] ?
joint type: synovial, saddle joint
shock absoption: articular disc
movements: around 60 degrees when elevate scapula

Which nerve is at risk here? [1]

median
Which nerve is damaged if atrophy of thenar group occurs? [1]
median
If you break your clavicle, which structures act and cause different movements of the clavicle? [3]
What do u need to help bring bones back together to heal? [1]
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle: pulls medial aspect of clavicle up
- Pectoralis major muscle pulls arm and clavicle medially
- Gravity will pull down
- need an internal fixation

Acromioclavicular joint?
Which joint is present? [1]
What type of movement does this allow? [1]
which bones does this joint connection? [2]
what type of joint is the acromioclavicular joint? [2]
- synovial [1]; plane joint [1]
- gliding movement [1]
what is a connection between? [1]
- acromonion of scapula
- clavicle
label these xox
which of these labels are joining points for muscles? [3]

which of these labels are joining points for muscles? [3]
- coracoid process
- supraspinous fossa
- infraspinous fossa

glenohumeral joint:
What is the type of joint? [2}
Which movements does this joint permit? [5]
Joint:
- synovial [1]; ball & socket [1]
Movements:
- flexion-extension
- abduction
- adduction
- rotation
- circumduction

what are two prominent structures / features of the the glenohumeral joint? [2]
Why is this clinically significant [1]
what are two prominent features of the glenohumeral joint?
glenoid cavity accomodates approx/ 1/3 of the humeral head: means that should can have wider range of movement
inferior joint capusule is lax. allows elevate above head. but means is much weaker than superior portion

what is most common type of dislocation of the glenohumeral joint? [1]
What type of movements cause ^ [3}
what is most common type of dislocation of the glenohumeral joint? [1]
- anterior dislocation
what type of movements cause ^ [3}
- abduction
- external rotation
- external extension
which nerve can be effected glenohumeral dislocation? [1]
which muscle does this nerve particularly effect if damaged? [1]
axillary nerve
deltoid muscle
Which structures deepen the shallow glenoid fossa? [2]
what is the shallow glenoid fossa deepened by? [2]
- glenoid labrum (fibrocart. ring that surrounds articular surface). helps deepen the socket and support the joint
- long head of the biceps - attaches to superior aspect of labrum
Scapulotharacic joint
What is the type of joint [1]?
Which movements does this joint allow? [3]
not a true joint articulation between scapula and thoracic wall
movements:
- elevation & depression
- protraction & retraction
- rotation - important in abduction

what is the scapula-humeral rthym?
First 30 degrees of shoulder elevation involves a “setting phase”:
- the movement is largely glenohumeral.
- scapulothoracic movement is small and inconsistent.
And after the first 30 degrees of shoulder elevation:
- The glenohumeral and scapulothoracic joints move simultaneously.
- Overall 2:1 ratio of glenohumeral to scapulothoracic movement.
(e.g. when the arm is abducted 180 degrees, 60 degrees by rotation of the scapula & 120 degrees occurs by rotation of the humerus at the glenohumeral joint)
which part of the humerus is most likely to break? [1]
surgical head !
label A-E

A: acromioclavicular joint
B: corocoid process
C: clavicle
D: acromion
E: glenoid fossa

which nerve is the trapezuius innervated by? [1]
why is this special?
accessry nerve (CNXI) special bc all other muscles are innervated from brachial plexus
latissimus dorsi
Movements of the latissimus dorsi? [3]
runs from lower thoracic vertebra onto the lumbar vertebra & iliac crest. runs from iliac crest to anterior aspect of the humerus
movements:
- extend, adduct and medially rotate the shoulder
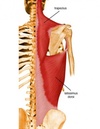
teres major
Movements of the teres major? [3]
runs from:
- inferior angle of scapula to anterior aspect of humerus
movements:
- extend, adduct and medially rotate the shoulder
deltoid muscle
What are the three heads of the deltoid muscle? [3]
What movements do each head permit? [3]
Which nerve innervates the deltoid muscle? [1]
Heads:
* anterior : flexion of arm
* posterior: extension of arm
* middle abduction of arm: major one
Innervation
* axillary nerve

Rotator cuff musles
What are names of the different rotator cuff muscles [4]
What rotator cuff muscles are located posterioly? [3]
Which rotator cuff is found anteriorly? [1]
- surround the glenohumeral joint and stabilise the joint
- deep !
Posterior:
* supraspinatus muscle: superior to scapula spine
* infraspinatus muscle: inferior to scapula spine
* teres minor: inferior to infraspinatus
Anterior:
subscapualris muscle

Which muscle initates the first 10 degrees of abduction? [1]
supraspinatus



Why is the long thoracic nerve easy to damage? [1]
Runs anterior to the muscle [1]


Which of the following is the glenoid labrum?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the glenoid labrum?
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the acromion?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the acromion?
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the scapula?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the scapula?
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the supraspinatus muscle?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the supraspinatus muscle?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the glenoid labrum
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the glenoid labrum
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the glenoid cavity
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the glenoid cavity
A
B
C
D
E
What is muscle D? [1]
What is bone E? [1]

D: supraspinatus
E: Acromion
Which of the following is the articular capsule
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the articular capsule
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the articular capsule
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the articular capsule
A
B
C
D
E
which arteries, found in the hand, do the ulnar [1] & radius [1] arteries supply?
radial artery gives rise to deep palmar arch
ulnar artery gives rise to superficial palmar arch


3 main superficial veins of upper arm? [3]





what are the 5 branches of brachial plexus?
- Muscularcutaneous
- axillary
- median
- radial
- ulnar nerve
most alcoholics must really urinate !
where do each of the following arrive from?
- Muscularcutaneous
- axillary
- median
- radial
- ulnar nerve
where do each of the following arrive from?
- Muscularcutaneous: C5-C7
- axillary: C5-C6
- median: C5-T1
- radial: C5-T1
- ulnar nerve; C8-T1


What is the best way to id the different nerves of the brachial plexus?
Musculocutaneous, median & ulnar are anterior to axillary artery & form M shape
Behind axillary artery: **
superior - axillary, inferior - radial**


median nerve
Musculocutaneous nerve
Which group of muscles does the musculocutaneous nerve supply? [1]
Name the muscles [3]
Where is the sensory area that the musculocutaneous arm supplies? [1]
musculocutanous supplies the flexor compartment motor supply:
- bicep brachialis
- brachialis
- corachbrachialis
musculocutanous supplies the flexor compartment sensory supply:
- skin of lateral forarm

which of the nerves from brachial plexus, if damaged, would result in a loss of shoulder abduction beyond 15 degrees?
- Muscularcutaneous
- axillary
- median
- radial
- ulnar nerve
which of the nerves from brachial plexus, if damaged, would result in a loss of shoulder abduction beyond 15 degrees?
axillary
Median nerve
Describe the path of the median nerve to the hand [3]
Which muscles does median nerve supply motor innervation to? [2]
Which area of skin does median nerve provide sensory innervation for? [1]
Path:
* medial to biceps brachii with the brachial artery
* then runs anteriorly at the cubital fossa to enter the forearm.
* It then passes through the carpal tunnel to reach the hand
Motor:
- supplies the majority of the flexor compartment - wrist flexion
- thumb
Sensory:
-Sensory fibres innervate the skin over lateral palm, digits 1-3.

Radial nerve
Describe the path of the radial nerve [1]
Which muscles does the radial nerve supply motor innervation to [2]
which skin does it provide sensory innervation for? [3]
Path:
- runs posteriorly all down arm
Motor innervation:
* tricep brachii
- all muscles on posterior aspect of arm and forearm -
Movement:
- extension of the wrist
Sensory innervation:
* posterior arm to wrist
- dorsal hand
- base of digits 1-3 and thumb

Ulnar nerve
Describe the path of the ulnar nerve [1]
Which muscles does the ulnar nerve provide motor innervation to? [2]
Where does ulnar nerve provide sensory innervation to [3]
Path:
- runs medially in the arm and passes posterior the medial epidcondlye
Motor innervation:
* flexor carpi ulnaris
* ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus in forearm
Sensory innervation:
- medial dorsal and plantar hand, digits 3.5-5





What is Erb’s palsy caused by damage to? [1]
which nerves? [3]
what does it result in? [3]
Erbs palsy:
- Damage to the superior trunk of the brachial plexus.
- This happens quite commonly in difficult birth (pulling the head away from the upper limb) results in nerve palsy.
- Damaging C5 and C6 mainly affects musculocutaneous, axillary and medial nerve. It results in:
- Adducted shoulder
- Medially rotated arm
- Extended elbow

Name 3 important nerves from brachial plexus that do not do not enter the upper limb? [3]
State which muscles do they provide motor innervation for?
Long Thoracic: C5, C6, C7. This innervates the serratus anterior muscle, which is important in keeping your scapula attached to your thoracic cage. C5,6,7, wings to heaven (damage to this causes winged scapula)
Thoracodorsal: C6, C7, C8. This supplies the Latissimus dorsi.
Suprascapular: C5, C6 This innervates the _Supraspinatus, infraspinatu_s (other rotator cuff innervated by axillary nerve)

radial nerve
Label A-D

A: Latissimus dorsi muscle forming the posterior axillary fold
B: Subscapularis muscle
C:Deltoid
D: External abdominal oblique muscle
Label A-D

A: Brachialis
B: Long head of biceps brachii muscle
C: Deltoid muscle (insertion on humerus)
D: Short head of biceps brachii muscle
Label A-E

A: bicep brachii
B: triceps brachii
C: brachioradialis
D: subscapularis
E: Axillary artery
Label A

Brachioradialis muscle
Label A-C

A: Coracobrachialis muscle
B: Teres major
C: Medial head of triceps brachii muscle
Label 1-5

1: bicep brachii
2: brachialis
3: Pronator teres muscle
4: Brachioradialis muscle
5: Pronator quadratus muscle
Which of the following is the median nerve
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the median nerve
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the radial nerve
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the radial nerve
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the brachial artery
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the brachial artery
A
B
C
D
E
Label E [1]

Pronator teres
Label E [1]

Pronator teres
Label A [1]
supinator muscle
Label A [1]

supinator muscle
Which of the following is the radial nerve
1
2
3
4

Which of the following is the radial nerve
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is the median nerve
1
2
3
4

Which of the following is the median nerve
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is the ulnar artery and nerve
1
2
3
4

Which of the following is the ulnar artery and nerve
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is the carpal tunnel
1
2
3
4

Which of the following is the carpal tunnel
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is the carpal tunnel
1
2
3
4

Which of the following is the carpal tunnel
1
2
3
4
Label A-D

A: radial artery
B: ulnar artery
C: Anterior interosseous
arteries
D: ulnar artery

A - musculocutaneous nerve
B - median nerve
C - axillary nerve
D - ulnar nerve

what is 1 & 2?

2 coracobrachialis
1. brachialis

which is this muscle?

bicep brachii
what muscle is this

brachialis
Bicep brachii
Where do the 2 heads of the bicep brachii attach? [2]
The two heads join together and attach onto which bone? [1]
Describe the movements of the bicep brachii muscle [2]
Location of 2 heads:
- short head - found medially. attaches to **corocoid process **
- long head - found laterally (L4L) attaches to supraglenoid tubercle
Join together to form one muscle, together inserts onto radius at the radial tuborisity
movements:
- powerful supinator
- flexor and shoulder and elbow
which muscles are used to flex your forarm when:
a) pronated
b) supinated
pronated forearm - brachialis used to flex elbow joint
supinated forarm - brachiali and bicep brachii flex elbow joints


ruptured one of bicep brachii tendons -> causes muscles to bunch and shoot down arm
Tricep brachii
What are the three heads of the tricep brachii? [3]
Where does the tricep brachii insert inferiorly [1]
Which movements does tricep brachii permit? [2]
Which nerve is the tricep brachii innervated by? [1]
Heads:
* long head - passes over shoulder joint
* lateral head
* medial head
Insertion:
* Join together to form one common muscle: tendon inserts on olecranon process of elbow (pointy bit)
Movements:
- extend elbow
- weak shoulder extensor
Innervation:
* radial nerve

Describe path of the median nerve [2]
- Rruns in anterior compartment of upper arm
- Crosses over the anterior aspect of the elbow to enter anterior compartment of the forearm


A: short head of bicep brachii
B: radial nerve
C: brachial artery
D: tricep (long head)
E: musculocutaneous nerve


capitulum articulates with which bone? [1]
trochlea articualtes with which bone? [1]
capitulum articulates with which bone? [1]
- radius
trochlea articualtes with which bone? [1]
- ulnar
which is the stablilisng bone of the forearm? [1]
which is the moblile bone of the forearm?[1]
which is the stablilisng bone of the forearm? [1]
- ulnar
which is the moblile bone of the forearm?[1]
- radius


State which ligaments are found around the elbow joint [2]
Which movements do they help cause movement of? [1]
Ligaments:
- annular ligament
- radial collateral ligament
- ulnar collateral ligaments
together reinforce hinge movement

which ligament is commonly torn in young girls?
Ulnohumeral joint
Radio humeral joint
Proximal radioulnar joint
why?
which ligament is commonly torn in young girls?
Ulnohumeral joint
Radio humeral joint
Proximal radioulnar joint
bc annular ligament if loosely attached to the ulnar in infants
What are the 3 joints of the elbow?
Ulnohumeral joint is where movement between the ulna and humerus occurs.
Radio humeral joint is where movement between the radius and humerus occurs.
Proximal radioulnar joint is where movement between the radius and ulna occurs
what are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
Boundaries of the cubital fossa:
- superior border: line from the lateral to the medial epicondyle
- flexor muscles of the forearm and the bracioradialias acting as borders also.






median nerve !

Describe the role of the:
annular ligament [1]
Which joint does it help to create? [1]
Which movements does this joint allow? [2]
Annular ligament: encircles the head of the radius and keeps in the radial notch of the ulnar: creates proximal radioulnar joint
Permits:pronation and supination of the formarm
Label 20-22 & A-C

20 Site of humero-ulnar joint
21 Site of humeroradial joint
22 Site of proximal radio-ulnar
A = humerus
B = radius
C = ulna
Label 1-3

1: ulnar collateral ligament
2: olecranon
3: radius
Which of the following is the median nerve
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the median nerve
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the radial artery
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the radial artery
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the ulnar nerve
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the ulnar nerve
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following is the ulnar artery
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following is the ulnar artery
A
B
C
D
E
Which bones does the radiocarpal joint connect? [3]
What type of joint is it? [1]
scaphoid & lunate to radius not the ulna
condyloid joint extension and flexion and ulnar and radial devaitation (side to side)

what is 1-5?

1 = flexion
2 = extension
3 = adbuction
4 = adduction
5 = oppostion

muscles of the superficial layer of forearm:
names? [4]
where do they run from / to?
muscles of the superficial layer of forearm:
- Pronator teres (pronates the arm)
- Flexor carpi radialis (flexes the wrist)
- Palmaris longus (small muscle)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris (flexes the wrist)
(Pass Fail Pass Fail)
muscles of the superficial layer do not extend into the digits so they act to
- **flex the wrist
- pronate the arm**

which muscle is this?

palamaris longus
which superficial forearm muscle is this?

palmaris longus
Which is the muscle of intermediate layer of forearm?
Where does it run to from the medial epidcondyle?
What movements does it cause? [3]
which is the muscle of intermediate layer of forearm?
* flexor digitorum superficialis
where does it run to from the medial epidcondyle?
* middle phalanx
Movements:
- flexes the wrist
- flexes the MCP
- flexes the PIP

What are deep layer muscles of the forarm? [3] where run to ? what movements?
flexor digitorum profundus:
- makes way to fingers and distal phalanx !
- causes flexion of the wrist, MCP, PIP and DIP joints
flexor pollicis longus
- forearm to distal phalanx of thumb
- thumb flexion
pronator quadratus
- between ulnar and radius
- initiates pronation of the forearm

what are ganglion cysts?
- synovial sheath is filled with fluid - get accumulation of fluid = lump

Pronation of the forearm is undertaken by pronator quadratus (deep layer) and pronator teres muscle (superficial layer).
which of these is the main muscle involved in pronation and which assists pronation?
pronator quadratus (deep layer): main
pronator teres muscle (superficial layer): assists
what is the carpal tunnel?
what is the layer at the top called?
which nerve runs through?
- At the base of the palm of the hand, there is a groove/tunnel through which 9 flexor tendons pass.
- Across the top is the flexor retinaculum (thickening of the deep fascia)
- median nerve runs through the carpal tunnel

what is carpal tunnel syndrome caused by?
what does it present as? a) short term? b) long term?
compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (oedema, reptitive strain)
presents as:
i) short term: numbness of tingling of first 3.5 digits
ii) long term muscle wasting away

which tendons are from muscles A & B?
which joints of the fingers are these muscles acting on?

A= **flexor digitorum profundus:** all the way to distal phalanx. **PIP &** **DIP flex** B = **flexor digitorum superficialis:** middle phalanx. **PIP flex**

name the muscles of the posterior compartent that run laterally and what movements they permit

Brachioradialis: humurus –> radius: only flexes the elbow (as doesnt cross wrist)
extensor carpi radialis longus: extend and adbuct the wrist
extensor carpi radialis brevis: extend and adbuct the wrist

what do these tendons from these muscles cause movement of? [3]

what do these tendons from these muscles cause movement of the thumb !!
abductor pollicis longus: abducts thumb
extensor pollicis longus & brevis: extend thumb

What are the borders of the anatomical snuffbox? [3]
abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis


lumbricals: flex MCP
dorsal interrossei: abduct fingers (DAB)
palmar interrossei adduct the fingers (PAD)

fyi





