Review of lower limb Flashcards
Shenton’s line is between which two areas of the hip joint? [2]
Superior pubic ramus - inferomedial border of the neck offemur
L has neck of femur fracture: shenton line not normal

The hip joint’s stability is increased by which three ligaments [3]
Which is the strongest? [1] - Why is this clinically significant? [1]
Pubo-femoral ligament
Ilio-femoral ligament- strongest & found on anterior aspect of the joint - so anterior more strong than posterior
Ischio-femoral ligament
Together - they push the head of the femur into the hip

Which is the ligament found within the hip joint that strengthens the joint? [1]
Ligamentum teres

Describe the blood supply to the head and neck of femur [
Profunda femoris: give off medial and lateral circumflex arteries
- from these two arteries get Retinacular arteries- majority of blood to head and neck
Obturator artery: Artery to the head of the femur

The obturator artery is important for which patient population & why? [2]
Paedatric population: important for ossification for head of femur
line things
Which qudrant do you used for IM injection?
A
B
C
D

Which qudrant do you used for IM injection?
A - avoid sciatic nerve
B
C
D
nerve supply in the pelvis
Gluteus maximis inserts onto which structure? [1]
Which nerve supplies gluteus maximus? [1]
Inserts onto iliotibial band
Supplied by inferior gluteal nerve
Which nerve supplies gluteus medius and minimus? [1]
What movement do they cause? [1]
Superior gluteal nerve
Hip abduct and internally rotate the thigh
Tensor fascia lata
Lateral rotators
How do gluteus minimus and medius work to provide hip stablity? [1]
How does gluteus minimus and medius damage present? [1]
Opposite side contract when you walk to stop hip dropping,
Damage to them causes contralateral hip drop / Positive Trendelenburg test

thigh compartments
Sciatic nerve
What are the borders of the femoral triangle? [3]

Superior border: inguinal ligament
Lateral border – medial border of the sartorius muscle.
Medial border medial border of the adductor longus muscle. The rest of this muscle forms part of the floor of the triangle.
Order of neurovascular in femoral triangle? [4]
NAVL:
Nerve
Artery
Vein
Lymphatics

What are the borders of the popliteal fossa? [3]
Medial superior: semimembranosus and semitendinosus
Medial inferior: Gastrocnemius
Medial lateral: bicep femoris
Medial inferior: Gastrocnemius

After leading the popliteal artery
- what is the anteiror segment?
- what is the lateral sgement?
- what is the posterior segment?
Anterior
* anterior tibial: dorsalis pedis
Lateral
* perforating branches of deep penoneal (fibular)
Posterior
* posterior tibial: medial and lateral plantar
Neck of femur fractures (typically with significant displacement) will classically present with a [] and [] rotated limb.
Neck of femur fractures (typically with significant displacement) will classically present with a shortened and externally rotated limb.

NICE recommends offering total hip replacement over hemiarthroplasty in patients whom are [3]
- Able to walk independently outdoors with no more that one stick
- Not cognitively impaired
- Medically fit for the operation
Which muscle is responsible for shortening of the limb and external rotation following a NoF fracture? [1]
Iliopsoas
Common complication of posterior hip dislocation? [1]
Sciatic nerve involvement
Presentation of patellar dislocation? [1]
Knee held in flexion
How to reduce a patellar dislocation? [1]
Push patella medially whilst extending knee
Structures at risk in an anterior dislocation of the tibiofemoral joint? [3]
Popliteal artery
Tibial nerve
Common peroneal nerve
In which direction is the patella usually dislocated? [1]
Laterally due to pull of quadriceps
What is a bimalleolar fracture (Pott’s fracture)? [1]
fracture involving the lateral and medial ankle

Explain which malleolar fracture is more common [2]
Lateral malleolar:
lateral malleolar fractures as they result from forced inversion, which is easier as the lateral ankle ligaments are weaker
Lateral malleolar ligaments? [3]
Anterior talofibular
Posterior talofibular
Calcaneofibular
Which three muscles of the thigh form pes anserinus?
Obturator internus, gracilis and sartorius
Sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus medialis
Sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus
Biceps brachii, brachialis, triceps brachii
Gracilis, pectineus, adductor magnus
Which three muscles of the thigh form pes anserinus?
Obsartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus

State the role of sartorius in moving hip and knee joints [2]
Sartorius can flex the hip AND flex the knee joint.

The unhappy triad is made from which 3 ligaments? [3]
Medial collateral ligament, lateral meniscus and anterior cruciate ligament

Which of the following muscles is the strongest flexor of the hip joint?
Sartorious
Iliopsoas
External oblique
Rectus femoris
Which of the following muscles is the strongest flexor of the hip joint?
Sartorious
Iliopsoas
External oblique
Rectus femoris
What is the insertion of the gluteus minimus muscle?
Femoral neck
Lesser trochanter
Femoral head
Greater trochanter
What is the insertion of the gluteus minimus muscle?
Femoral neck
Lesser trochanter
Femoral head
Greater trochanter
What nerve supplies the anterior compartment of the lower leg?
Superficial fibular nerve
Deep fibular nerve
Posterior tibial nerve
Femoral nerve
What nerve supplies the anterior compartment of the lower leg?
Superficial fibular nerve
Deep fibular nerve
Posterior tibial nerve
Femoral nerve
Apart from the anterior cruciate ligament, which other structure prevents overextension of the knee joint?
Meniscus
Posterior cruciate ligament
Arcuate popliteal ligament
Medial collateral ligament
Apart from the anterior cruciate ligament, which other structure prevents overextension of the knee joint?
Meniscus
Posterior cruciate ligament
Arcuate popliteal ligament
Medial collateral ligament

Which statement about the posterior cruciate ligament is true?
It prevents overextension of the knee joint
It restricts internal and external rotation of the extended knee
It prevents anterior rolling and displacement of the femoral condyle
It prevents posterior rolling and displacement of the femoral condyle
It is a shock absorber
It prevents anterior rolling and displacement of the femoral condyle
Which of the following nerves is involved in tarsal tunnel syndrome?
Deep peroneal nerve
Femoral nerve
Tibial nerve
Common peroneal nerve
Superficial peroneal nerve
Which of the following nerves is involved in tarsal tunnel syndrome?
Deep peroneal nerve
Femoral nerve
Tibial nerve
Common peroneal nerve
Superficial peroneal nerve
Contents of the tarsal tunnel? [5]
TARSAL TUNNEL
The tarsal tunnel is described as a region posterior to the medial malleolus and is bounded by the flexor retinaculum, turning it into a ‘tunnel’ through which important structures run. It is a useful landmark as it is where a clinician palpates the posterior tibial pulse and is the site of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Contents of the tarsal tunnel:
Tendon of tibialis posterior
Tendon of flexor digitorum longus
Posterior tibial artery (and venae comitantes)
Tibial nerve
Flexor hallucis longus
“Tom Dick And Very Nervous Harry” is a useful way to remember it!

“The hamstrings are made up of the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and the ______________ muscles.”
Vastus intermedius
Biceps brachii
Rectus femoris
Psoas major
Biceps femoris
“The hamstrings are made up of the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and the ______________ muscles.”
Vastus intermedius
Biceps brachii
Rectus femoris
Psoas major
Biceps femoris

Which of the following muscles inserts onto the most superior aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur?
Obturator externus
Gluteus medius
Piriformis
Gluteus minimus
Obturator internus

Which of the following muscles inserts onto the most superior aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur?
Obturator externus
Gluteus medius
Piriformis
Gluteus minimus
Obturator internus
What is the medial border of the femoral triangle?
Medial border of adductor magnus
Medial border of adductor longus
Lateral border of adductor magnus
Lateral border of adductor longus
Medial border of sartorius
What is the medial border of the femoral triangle?
Medial border of adductor magnus
Medial border of adductor longus
Lateral border of adductor magnus
Lateral border of adductor longus
Medial border of sartorius
Which of the following is not a recognised region of an adult long bone?
Endophysis
Epiphysis
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Synostosis
Which of the following is not a recognised region of an adult long bone?
Endophysis
Epiphysis
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Synostosis

Which of the following collection of bones constitute the ankle joint?
Tibia fibula
Tibia, fibula, and talus
Tibia and talus only
Tibia, fibula, talus and calcaneus
Which of the following collection of bones constitute the ankle joint?
Tibia fibula
Tibia, fibula, and talus
Tibia and talus only
Tibia, fibula, talus and calcaneus
Which muscles comprise the deep posterior compartment of the leg?
Tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, and plantaris
Flexor hallucis brevis, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, and popliteus
Gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris
Tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, and popliteus
Which muscles comprise the deep posterior compartment of the leg?
Tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, and plantaris
Flexor hallucis brevis, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, and popliteus
Gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris
Tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, and popliteus

The femoral artery is palpable at the mid-inguinal point, which is halfway between which two structures?
Pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine
Pubic symphysis and anterior inferior iliac spine
Pubic tubercle and lesser trochanter of the femur
Pubic tubercle and anterior superior iliac spine
Pubic tubercle and anterior inferior iliac spine
The femoral artery is palpable at the mid-inguinal point, which is halfway between which two structures?
Pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine
Pubic symphysis and anterior inferior iliac spine
Pubic tubercle and lesser trochanter of the femur
Pubic tubercle and anterior superior iliac spine
Pubic tubercle and anterior inferior iliac spine
What type of hip dislocation would occur because of a car accident like this? [1]
How would a patient present prior to treatment?

What type of hip dislocation has occured? [1]
In which leg? [1]
Describe how you can tell [1]

Right posterior hip dislocation:
Right limb adducted, flexed, internally rotated, and shortened.
What type of hip dislocation has occured? [1]
In which leg? [1]
Describe how you can tell [1]

anterior dislocation
hip and leg in extension, abduction, and external rotation
Describe the presentation of this patient after the crash [3]

Posterior dislocation:
limb adducted, flexed, internally rotated, and shortened.
How would the effected limb present in this injury? 3]

anterior dislocation
hip and leg in extension, abduction, and external rotation
where does the aorta bifuricate into common iliac artery? [1]
L4
Which leg compartments and nerves are responsible for toe:
Flexion [2]
Extension [2]
Flexion: posterior compartment; tibial nerve
Extension: anterior compartment & deep peroneal nerve
which three arteries branch off the internal iliac artery? [3]
which out of ^^ are medial compartment of thigh?
which out of ^^ are posterior compartment of thigh?
from which artery does the superior gluteal artery arise from? [1]
internal iliac artery –> superior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> inferior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> obturator artery
superior & inferior gluteal: posterior region
obturator: medial region
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
piriformis !
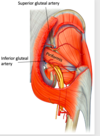
at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
after going through the adductor hiatus


arcuate artery
lumbosacral plexus:
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3] what are nerve roots?
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3]
femoral nerve: L2, L3, L4
obturator nerve: L2, L3, L4
lateral cut. nerve of thigh: L2 & l3
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [2]
main muscles of anterior [3]
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
anterior
what movement does this cause? [2]
flex hip
extend knee
main muscles for ^?
quadriceps
sartoruis
iliopsoas
obturaror nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [1]
main muscles of this? [1]
- *obturaror** nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
- *medial compartment**
what movement does this cause? [1]
adduction of thigh
main muscles of this? [1]
adductors
lateral cutaenous nerve occurs from which Vert levels? [2]
what is role? [1]
lateral cutaenous nerve occurs from which Vert levels? [2]
L2 & L3
what is role? [1]
sensory innervation to lateral aspect of thigh

which three nerves arise from sacral plexus? [3]
which three nerves arise from sacral plexus? [3]
•Sciatic nerve (Tibial and common peroneal nerves)
•Superior gluteal nerve
•Inferior gluteal nerve
sciatic nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [2]
main muscles of this compartment [3]
sciatic nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
posterior compartment
what movement does this cause? [2]
extend hip
flex knee
main muscles of this compartment [3]
•Semitendinosus
•Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris (long head
what are the 3 muscles compartments of the leg (knee - foot)
what are the muscle movements each compartment do?

posterior dep compartment:
innervation?
movement? [2]
blood supply?
posterior dep compartment:
innervation: tibial nerve
movement: plantar flexion, flexion of digits
blood supply: posterior tibial artery


anterior leg compartment:
innervation?
movement? [2]
blood supply?
anterior leg compartment:
innervation: deep peroneal nerve
movement: dorsiflexion, extension of digits
blood supply: anterior tibial artery
lateral leg compartment:
innervation?
movement?
blood supply?
lateral leg compartment:
innervation: superficial peroneal nerve
movement: eversion
blood supply: fibular artery
which nerves provide sensory innervation to the image? [2]


damage to sciatic nerve is characterised by? [3]
oFoot drop
oWasting of hamstrings, calf muscles and dorsiflexors
oLoss of Achilles reflex
a postive trendelenburg test is likely to occur from damage to which nerve?
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
femoral nerve
common peroneal nerve
superficial peroneal nerve
a postive trendelenburg test is likely to occur from damage to which nerve?
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
femoral nerve
common peroneal nerve
superficial peroneal nerve

Describe the role of the the acetabulur labrum [1]
Acetabulur labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ring that helps with suction of the femur into the acetabulum. Doesn’t really add to the surface area, 10%, but acts with the synovial fluid to suction the head of the femur into the acetabulum


A: ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine)
B: pubic tubercle
C: PSIS
D: ischial spine
E: ischial tuborisity
F: inferior pubic ramus

* the hip joint is most stable is which position ? *
* the hip joint is most stable is which position ? *
extension !
which is the major extensor muscle of the hip? [1]
which are the major abductor muscles of the hip? [2]
which are the lateral rotators muscles of the hip? [2]
which is the major extensor muscle of the hip? [1]
gluteus maximus
which is the major abductor muscles of the hip? [2]
gluteus medius and minimus
which are the lateral rotators muscles of the hip? [2]
piriformis and lateral rotators

during locomotion, which muscles stabilise the hip? [2]
how? [1]
during locomotion, which muscles stabilise the hip? [2]
gluteus medius and minimus: contract to keep pelvis aligned during locomotion (otherwise, get contralateral (hip drop)

what is iliotibial tract? [1]
what movement does tensor fascia lata cause? [1]
what is iliotibial tract? [1]
long band of fascia that runs down lateral aspect of the knee. its a thickened portion of the fascia lata (fascia that covers the thigh)
what movement does tensor fascia lata cause? [1]
abductor of hip

the lateral rotators of the hip are innervated by which nerve supply? [3]
which is the most important lateral rotator? [1]
the lateral rotators of the hip are innervated by which nerve supply? [3]
L5, S1 & S2
which is the most important lateral rotator? [1]
piriformis (important for neurovasc landmark)


A = gluteus medius B = gluteus maximus C = piriformis D = other lateral rotators

medial compartment of the thigh
- cause what movement on the hip?
- made by which muscles?
- innervated by?
medial compartment of the thigh
- cause what movement on the hip?
- *adduction**
- made by which muscles?
- *adductor longus, brevis and magnus, gracilis, pectineus and obturator externus **
- innervated by?
- *obturator nerve**

posterior compartment of the thigh
- cause what movement on the hip?
- made by which muscles?
- innervated by?
posterior compartment of the thigh
- cause what movement on the hip?
extension
- made by which muscles?
gluteus maximus
hamstrings
- innervated by?
hamstring - sciatic nerve


A: flexor muscle (anterior comparment)
B: abductor
C: adductor
what is blood supply to the head of femur like?
which is main blood supply from?
which is main blood supply from: retinacular artery


A: Rectus femoris muscle
B: Gracilis muscle
C: Adductor magnus
D: femoral artery / vein
which is this muscle?
innervation?
movement [2]

which is this muscle: sartorius
innervation: femoral nerve
movement [2]: flexes hip AND knee
which muscles do you find in the anterior compartment of leg? [3]
sartoruis
iliopsoas
quadriceps
medial compartment of thigh:
- innervated by?
- which muscles (dont worry too much)
- movement?
- generally, where do they attach proximally and distally?
medial compartment of thigh:
- innervated by: obturator nerve
- which muscles (dont worry too much):
i) adductor magnus
ii) adductor longus
iii) adductor brevis
iv) gracilis - movement: adduction of leg
- generally, where do they attach proximally and distally: proximally: pelvis, distally: linea asperea

whats this muscle called?

semitendinosus: really long tendon !!
which is muscle A?

semitendinosus muscle (bc superior portion is almost aporneurotic)
which muscle is A&B?
what are origins of A&B?

Bicep femoris
A - long head - comes from common hamstring - ischial tuboristy
B - short head - comes from posterior aspect of femur, laterally

where do the Biceps femoris, Semimembranosus & Semitendinosus attach ? (medially or laterally)?
Biceps femoris: laterally
Semimembranosus: medially
Semitendinosus: medially

what are the 3 different muscles that insert at the medial aspect of the knee? [3]
which compartment are they all originally from? [3]
what is name for this meetin of three muscles? [3]
- Sartorius - anterior
- Gracilis - medial
- Semitendinosus - posterior
= pes anserinus !!

what is the Q line?
where is at a line between? [2]
what s the angle in men? (compared to vertical) [1]
whats the angle in women? (compared to vertical) [1]
Q line: asis –> centre of patella
what s the angle in men: 14 degress
whats the angle in women: 17 degrees

whats it called when have a small q angle?
whats it called when you have a large q angle?
which condyle does this cause increased presssure on for small q [1] / large q [1]?
whats it called when have a small q angle: genu varum - medial condyle
whats it called when you have a large q angle: genu valgum - lateral condyle

reflex test of patella: tests which nerve? [1] & which spinal segments[1]
reflex test of patella: tests **femoral nerve and spinal segments L2-L4
causes contraction of quads**


what is the role of the cruciate ligaments?
connecting the tibia and the femur to prevent displacement of the tibia relative to the femur
PCL prevents which movement of the tibia on the femur [1]
ACL prevents which movement of the tibia on the femur [1]
which is stronger - ACL or PCL?
PCL prevents posterior movement of the tibia P4P
ACL prevents anterior movement of the tibia - stops hyperextension
PCL is stronger
what is the medial menisci attached to [2] (anteriorly / posteriorly)
what is the lateral menisici attached to? [1]
what is the medial menisci attached to [2]
- *anteriorly:** ACL
- *posteriorly:** tibial collateral ligament
what is the lateral menisici attached to? [1]
- *pcl**
- *NOT ATTACHED TO LATERAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT**
which ligaments make up the unhappy triad? [3]
Tearing of;
- Medial meniscus
- ACL
- Tibial collateral ligament


which ligament structure stabilises the medial side of ankle? [1]
what does ^ attach to? [3]
what movement does it prevent? [1]
which ligament structure stabilises the medial side of ankle? [1]
medial / deltoid ligament
what does ^ attach to? [3]
medial malleoulus of tibia
calcaneus
navicular
what movement does it prevent? [1]
prevents subluxion

which 3 ligaments make the the lateral ligament? [3]
which are they clinically significant? [1]
which 3 ligaments make the the lateral ligament? [3]
anterior talofibular
posterior talofibular
calcaneofibular
which are they clinically significant? [1]
because theyre seperate structures - really likely to tear: lateral collateral ligament tear
dorsiflexion and toe extension:
- innervated by which nerve?
- which muscles? [3]
- which compartment of leg? [1]
eversion:
- innervated by which nerve?
- which muscles? [2]
- which compartment of leg? [1]
dorsiflexion and toe extension:
- innervated by which nerve: deep branch of common peroneal nerve
- which muscles: **tibialis anterior, E. digitorum longus and E. hallicus longus
- anterior compartment**
eversion
- innervated by which nerve: superficial branch of common peroneal
- which muscles: fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
- lateral compartment

plantarflexion:
which muscles do this ? - of superficial plexor and deep muscles
**plantarflexion:
superficial plexors:**
- gastrocnemius
- soleus
- plantaris
- *deep muscles: toe flexion**
- flexor digitorum longus
- flexor hallucis longus
- tibialis posterior - also does foot inversion

what is arrow pointing to?

extensor reticulum


which muscles cause inversion of foot? [2]
which muscles cause eversion of foot? [2]
which muscles cause inversion of foot? [2]
tibialis anterior
tibialis posterior
which muscles cause eversion of foot? [2]
peroneus longus
peroneus brevis

which ligaments of foot get stretched out when foot planted, sot that when you take a step, release energy and help lift off?
a) medial side [1]
b) lateral side [2]
which ligaments of foot get stretched out when foot planted, sot that when you take a step, release energy and help lift off?
a) medial side: spring ligament
b) lateral side: long and short plantar ligaments

explain the arches of the foot? [3]
medial longitudinal arch:
- open footprin side: middle of foot isnt it
- contact with ground: big toe & calcaneous
- resilient due to large no. of bones
lateral longitudinal arch:
- flatter
- less bones
- talus transmits body weight through it - weight not central though - either goes forward or backwards
transverse arch:
not a true arch - maintained by some mscles and ligaments as longuitnial arches
- bony fit is particularly good

where is weight distribution in foot?
found in medial & longitudinal arch - not the transverse arch !!

How do you treat a intertrochantric fracture? [1]
Dynamic hip screw: blate with barrel inserted to outside of femoral shaft. Screw goes through to femoral head gives controlled compression

How do you treat subtroch. hip fracture? [1]
IM nail
How does NOF present? [3]
Short, abducted and externally rotated

Which views are used for NOF fracture x-ray? [2]
AP - otherwise can’t see shentons line & lateral
What does A point to? [1]
What is the innervation? [1]

Tensor fascia lata
Superior gluteal nerve
Which nerves supply sensory to colours shown?


PCL helps to stabilise knne joint particularly in which movement? [1]
What is other role? [1]
Helps stabilise knee especially in flexion
Stops tibia moving backward on femur
Stronger the ACL
Describe the role of ACL [3]
Stabilise knee in extension and prevents hyperextension and excessive internal rotation
Stops tibia moving forward on femur
Label the contents of the popliteal fossa


Compression of the tarsal tunnel can cause impingement to which nerve? [1]

Tibial nerve
Which artery is found within the ligamentum teres? [1]
Foveal artery



