Plasma Proteins and Immunoglobulins ppt Flashcards
Equation that illustrates of hydrostatic and oncotic forces in the movement of fluid across capillary membranes.
Starling Equation
T/F: There is a net outward force in the arteriolar end
True
Note: Blood pressure in the arterioles is higher than the oncotic pressure, hence, the movement of fluid from outward of the arteriolar lumen.

T/F: Gamma-globulins are synthesized in the liver
False
Most plasma proteins are synthesized in the liver except:
gamma-globulins (aka immunoglobulins) = lymphocytes
von Willebrand factor = vascular endothelium
Which characteristic/s of plasma proteins is/are FALSE?
- Mostly synthesized in the liver
- Most are lipoproteins
- Many exhibit polymorphism.
- Each plasma protein has a characteristic halflife
in the circulation.
- Many act as acute phase proteins
- Produced by cytosolic ribosomes
2 and 6 are False.
- Most Plasma proteins are GLYCOPROTEINS except albumin.
- Plasma proteins are synthesized in RER
Albumin has the ff properties, EXCEPT?
A. Major protein of human plasma (60% of plasma proteins)
B. 60% of albumin in plasma and 40% in interstitial space
C. Low molecular weight and high concentration
D. Account for ~75-80% of OSMOTIC pressure
E. Binds various ligands (eg. FFA, calcium, some steroid hormones, bilirubin); transport copper and various drugs
B is False.
60% of albumin occurs in the extracellular space while 40% is in plasma
Matching Type:
- Transports iron around the body
- Binds extracorpuscular Hb
- Stores iron
- Transfers ferrous iron from lumen to enterocyte
- Binds transferrin to cells for endocytosis
- Transfers iron across the enterocyte basolateral membrane
a. Ferritin
b. Transferrin
c. DMT1
d. Transferrin Receptor 1 (TfR1)
e. Ferroportin
f. Haptoglobin
- Transports iron around the body- transferrin
- Binds extracorpuscular Hb - haptoglobin
- Stores iron - ferritin
- Transfers ferrous iron from lumen to enterocyte - DMT1
- Binds transferrin to cells for endocytosis- TfR1
- Transfers iron across the enterocyte basolateral membrane - ferroportin
Downregulates intestinal iron absorption by inhibiting ferroportin via internalization and degradation
Hepcidin
Ferrous iron in the enterocytes is turned to ferric iron to allow for transferrin transport. This conversion is mediated by a ferroxidase called?
Hephaestin, a copper-containing ferroxidase (enterocytes). In macrophage, the ferroxidase is ceruloplasmin
How do high levels of iron alter ferritin and TfR synthesis? (enumerate pathway)
- High levels of iron
- Iron binds to IRE-BP (iron response element-binding protein) aka Iron Regulatory Protein (IRP)
- IRE fails to bind to mRNA
- Ferritin synthesis increases while TfR decreases
- Iron is stored in ferritin
- Normal iron levels
Feedback mechanism of low iron levels (enumerate pathway)
- low iron
- no iron will bind to IRE-BP
- IRE is free to bind to mRNA
- Ferritin is inactivated while TfR synthesis is increased
TfR1 and TfR2 are iron receptors that mediate iron endocytosis for incresed absorption
- Iron level normalizes
Carries up to 90% of copper in the plasma with each protein carrying 6 copper atoms
Ceruloplasmin
Note: “cerulean” means sky. Ceruloplasmin is blue in color due to high copper content
Copper is a cofactor to many enzymes. Match the enzyme to their function:
- Cytochrome c oxidase
- Ceruloplasmin
- Tyrosinase
- Lysyl oxidase
- Superoxidase dismutase
a. protect against oxidants
b. connective tissue synthesis
c. cellular respiration
d. iron hemostasis
e. melanin formation
Cytochrome c oxidase – cellular respiration
Ceruloplasmin – iron hemostasis
Tyrosinase – melanin formation
Lysyl oxidase – connective tissue synthesis
Superoxidase dismutase – protect against oxidants
Kinky or Steely hair disease due to a defect in copper efflux from cells.
Menke’s Disease
Notes: X-linked, only males are affected; mutation in ATP7A gene for copper-binding P-type ATPase.

Genetic disease wherein copper cannot be excreted from the bile and so accumulates in the liver, brain, kidney and RBC.
Wilson’s Disease

Note: Due to mutation in the gene for a copper-binding P-type ATPase (ATP7B)
Increase in level of copper in liver cells inhibit coupling to apoceruloplasmin which leads low ceruloplasmin in plasma
Copper toxicosis
A clinical finding in Px with Wilson’s Disease wherein there is a green or gold pigment around the cornea due to deposition of copper in the Descemet’s membrane
Kayser-Fleischer ring
Extra: si Georgina Wilson kay Gold ang mata

Treatment of Wilson’s disease is a diet low in copper and administration f a copper-chelating agent called
Penicillamine
The principal serpin (SERine Protease INhibitor) in human plasma which inhibits trypsin, elastase, and other serine proteases.
alpha1-antiproteinase (formerly alpha1-antitrypsin).
Note: They are synthesized by hepatocytes and macrophage
Deficiency in a1-antiproteinase has been linked witha. lung condition called:
Emphysema
Note: Without a1-antiproteinase, elastase will not be inhibited. Elastase degrades lung alveoli leading to emphysema.
Smoking oxidizes what amino acid residue of the protease-bindong site of a1-antiproteinase?
Methionine (specifically Met358)
Pathway: Smoking oxidizes methionine rendering the a1-antiproteinase unable to neutralize serine proteases that destroy alveoli.
A large plasma glycoprotein synthesized by monocytes, hepatocytes, and astrocytes that acts as a panproteinase inhibitor
alpha2-macroglobulin
Note: Comprises 8-10% of total plasma protein
The ff are function of a2-macroglobulin, EXCEPT:
A. Transport of 10% of zinc in plasma
B. Major member of plasma proteins that include complement proteins C3 and C4
C. Binds many cytokines (PDGF, TGF b, etc) and targets them toward particular tissues
D. Inhibits specific proteases
D is FALSE. As a panptoteinase, a2-macroglobulin acts as a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor
An impairment of tissue function that leads to the accumulation of various insoluble fibrillar proteins in the interstitial spaces between cells of tissues.
Amyloidosis
Note: the term is a misnomer because it was origially thought that starch-like fibrils accumulate in interstitial spaces. Later, it was found out that it was the accumulation of plasma proteins in beta-pleated sheet conformation

MATCH the Amyloidosis Classification to the protein that is implicated:
- Primary amyloidosis
- Secondary amyloidosis
- Familial amyloidosis
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Dialysis-related amyloidosis
- Primary amyloidosis - light chains of Immunoglobulins
- Secondary amyloidosis - Serum amyloid A (SAA)
- Familial amyloidosis - various, i.e., transthyretin
- Alzheimer’s Disease - Amyloid beta peptide
- Dialysis-related amyloidosis- Beta2-microglobulin
Mnemonics(?): Primary = 1 = 1mmunoglobulin
Secondary = SAA
Family = iba-iba
Alzheimer’s= Amyloid beta (A=A)
B lymphocytes are derived from ____ while T lymphocytes develop in ___
B- bone marrow
T- thymus
Describe a typical plasma immunoglobulin (IgG)
- has 2 light chains and 2 heavy chains linked by disulfide bonds forming a Y-shaped molecule
- both chains have a Variable region (at amino end) and a Constant region (at Carboxyl end)
- Variable regions of both light and heavy chains form the antigen-binding sites (Fab)
- The rest make up the constant region (Fc)
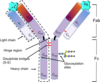
The site on an antigen where an antibody binds
Epitope or antigenic determinants
The hinge region of an immunoglobulin confers flexibility to Fab region. This region is easily cleaved by?
Pepsin or Papain

In an immunoglobulin, the ____ confers binding specificity while the ____ determines class-specific effector function
Variable region - specificity via combinatorial diversity
Constant region- effector
Rank immunoglobulins according to serum concentration
Ig GAMDE (according to Harper’s 31st ed)
Ig for hypersensetivity via mast cells and basophil secretion. Anti-helminthic
IgE
Secretory Ig; prevents attachment of microbes to mucosa
IgA
the Lectin pathway makes use of a lectin called ____ to bind to glycoproteins and lipopolysaccharides usually present in gram-positive abcteria, some viruses and several fungi
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or mannan-binding protein (MBP)
Found in B cell surface as antigen receptor
IgD
Ig for primary response and does not cross placenta
IgM
Ig for secondary response; opsonization; neutralize bacterial toxins and viruses; crosses placenta
IgG
Which immunoglobulins fix complement
IgG and IgM
An enzyme that enhances antibody diversity by converting cytidine to uracil, hence increasing the mutation of immunoglobulin Variable genes
Activation Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID).
Note: Since AID causes random mutation, it may also induce autoimmunity
The process where there is a transition of synthesis from one type of Ig to another, usually involving the same antigen-specific light chain such as what happens in the transition from IgM to IgG.
Class or Isotype Switching
Immunoglobulins of different class but have the same hypervariable and variable regions, and antigen specificity share a common ____
Idiotype
Draw diagram for Classical, Lectin, Alternative Complement Pathways
Diagram

The failure of the immune system to differentiate between host and foreign antigen can trigger an ____
Autoimmune Response
Which Complement pathway activates by direct chemical hydrolysis of C3 in a process called ticking over
Alternative Pathway
Deficiency in blood clotting cascade resulting in excessive bruising and bleeding
Hemophilia
______ is a condition of protein malnutrition while _____ is a genetic defect where plasma is devoid of albumin
Kwashiorkor- protein malnutrtion
Analbuminemia- no albumin in blood
A plasma protein that stimulates the complement pathway and may increase 100-fold during chronic inflammation, and is hence used as biomarker for tissue injury, infection, and inflammation.
C-reactive protein (CRP) named so because it reacts to the C polysaccharide of pneumococci
A cytokine released by phagocytes that stimulate hepatocytes to synthesize acute phase reactants i.e., CRP, a1-antiproteinase, haptoglobin, a1-acid glycoprotein, and fibrinogen
Interleukin-1 (IL-1). IL-6 may also participate
Iron from dead/senescent RBCs is recycled by macrophage through the ff steps (enumerate):
- Heme oxygenase turns heme to biliverdin, CO2, and iron
- Iron released from macrophage by Ferroportin to blood
- Ceruloplasmin, a copper-containing plasma enzyme, oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+
- Ferric iron taken up by transferrin in blood to be transported to other tissues

Hypochromic, microcytic RBCs are usually found in PBS of Px with which anemia?
Iron-deficiency anemia
Protein concentration in human plasma is ____
resulting in an oncotic pressure of ____
7-7.5 g/dL;
25 mmHg
Arteriolar hydrostatic pressure is ____ while hydrostatic pressure in venules is ____
37 mmHg;
17 mmHg
Accumulation of fluid in extravascular compartment
Edema
Plasma proteins that exhibit polymorphism, except?
a. alpha1-antitrypsin
b. haptoglobin
c. transferrin
d. ferritin
e. ceruloplasmin
f. immunoglobulin
D is not in the book
Half-life of:
A. albumin
b. haptoglobin
a. 20 days
b. 5 days
Example of protein-losing gastroenteropathy where half-life of protein is altered or is lost into bowel through inflamed mucosa
Crohn’s disease (regional ilietis)
____ g of albumin is synthesized per day.
____ g/dL of albumin is found in plasma which is 3/5 of the total plasma protein weight
Albumin accounts for ___ of the plasma oncotic pressure
12 grams
3.4-4.7 g/dL
75-80%
Describe albumin structure
- 3 functional domains
- ellipsoidal conformation


