Physiology of the Heart Flashcards
Used to describe a collection of mechanisms that influence the active and changing circulation of blood circulation of different volumes of blood per minute at different times is essential for survival
hemodynamics
the circulation control mechanisms must accomplish 2 function:
- maintain circulation (keep blood flowing) - Vary volume and distribution of the blood circulated
A complete heartbeat, or pumping cycle, consisting of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of both atria and both ventricles
the cardiac cycle
contraction of both ventricles of the heart, forcing blood out of these chambers. The atria are in a relaxed state
systole
The top number of BP, which is also the higher of the 2 numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (contracts)
systolic
The bottom number, which is also the lower of the 2 numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats (when heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood)
diastolic
ventricular muscles relax, allowing for blood to fill these chambers. At the end, the atria start contracting to fill the ventricles
diastole
an electrical fluctuation that travels along the surface of a cell’s membrane mediated by the flow of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane; occurs in nerves and muscles.
action potential
- repeatedly generate action potentials that trigger contraction and continue to stimulate heart even after it has been removed from the body
autorhythmic cardiac muscle fibers
_____, _____, and _____ can alter heartbeat strength and heart rate, but do not change the coordinated contractions of the heart
hormones, chemicals, and nerve impulses
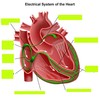
Conduction system of the heart has 4 structures:
- sinoatrial (SA) node - Atrioventricular (AV) node - AV bundle (bundle of His) - subendocardial branches (purkinjie fibers)
- The natural or inherent “pacemaker” of the heart - Initiates each heartbeat and and sets it pace - located high in r atrial wall
sinoatrial node
impulses spread from the ______ to the muscle fibers of both atria causing atrial contraction
SA node
The _____ fires between 60-100 BPM
SA node
- Located at the base of the right atrium - electrically, it acts as the only gateway for electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles
Atrioventricular node (AV)
electrical activity travels very slowly through the _______. The delay allows for contraction of the atria to proceed contraction of the ventricles.
AV node
AV node stimulation sends impulses to the ________.
atrioventricular bundle of His
carries electrical impulses (action potentials) into the ventricles. Impulses travel through the right and left bundle branches to the Purkinjie fibers.
bundle of His
fibers that further spread electrical activity to all parts of the ventricles so that there is a coordinated contraction of each ventricle.
subendocardial branched AKA Purkinjie fibers
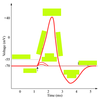
a graphic record of the heart’s electrical activity, specifically the conduction of impulses. It is not a record of the heart’s contractions, but of the electrical events/current that precede them a composite record of action potentials produced by the heart muscle fibers during each heartbeat.
electrocardiogram (ECG)
In an ECG, changes in voltage are seen as _______ of a line drawn on a paper or traced on a video monitor.
deflections
The _______ is composed of deflection waves called the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
normal ECG
A _______ obtains 12 electrical tracings of the heart from different angles or orientations. Patterns of abnormalities can indicate areas of abnormal conduction.
12-lead ECG
represents depolarization of the atria. Deflection related to passage of an electrical impulse from the SA node through the muscle of both atria.
The P wave
larger _______ indicate enlargement of an atria.
P waves
represents depolarization of the ventricles and repolarization of the atria
the QRS complex
represents ventricular repolarization. It is flatter than normal when the heart is not getting enough oxygen.
the T wave
the length of time for atrial depolarization and conduction from the SA node to the AV node. (Beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex)
P-R interval
The time period from the end of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization. Clinically, unhealthy myocardium can affect the height of this interval (either upward or downward)
ST interval/segment
The ________ begins at the end of the S wave and ends at the beginning of the T wave.
ST interval/segment
- a complete heartbeat consisting of systole and diastole of both atria and ventricles - the 2 atria contract simultaneously filling the ventricles more efficiently - as the atria relax, the two ventricles contract, instead of the entire heart contracting as one unit. Allow for pumping of the heart
the cardiac cycle
the 5 important events of the cardiac cycle:
- atrial systole - isovolumetric ventricular contraction - ejection - isovolumetric ventricular relaxation - passive ventricular filling
- begins with the P wave of the ECG - atria contract simultaneously completing emptying blood out of the atria into the ventricles - AV valves are open; SL valves are closed - Ventricles are relaxed and filling with blood
atrial systole
- onset of ventricular systole coincides with right wave and appearance of the first heart sound (S1), as the AV valves close - between the start of ventricular systole and the opening of the SL valves - volume in the ventricles remains constant as the pressure increases rapidly
isovolumetric ventricular contraction
pressure increases enough to open the aortic and pulmonary SL valves and blood is ejected from the heart. - blood enters the systemic and pulmonary circulations via the aorta and pulmonary artery - this period coincides with the ST interval
ejection
the blood that remains in the ventricles at the end of the ejection period (roughly half)
residual volume
in heart failure the residual volume remaining in the ventricles may greatly exceed that ejected during systole.
ejection fraction
beings with an isovolumetric period - occurs between closure of the SL valves and opening of the AV valves - closure of the SL valves produce the second heart sound (S2) - corresponds to the T wave and continues until the next P wave
isovolumetric ventricular relaxation there is a dramatic fall in intraventricular pressure
- returning venous blood increases intraatrial pressure until the AV valves are forced open and blood rushes into the relaxing ventricles - results in a dramatic increase in ventricular volume before the atria conract - lasts about 0.1 sec
passive ventricular filling
the amount of blood that flows out of a ventricle of the heart per unit of time
cardiac output
is measured by the ml of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one stroke (beat)
stroke volume
cardiac output (ml/minute) = ______ (ml/beat) x heart rate (beats/minute) = ml/minute
stroke volume
CO = SV x ___
HR
____ are created by blood turbulence and vibration as valves close
heart sounds
the act of listening to sounds within the body
auscultation
using the bell of a stethoscope is most useful for _____ and may work best with pediatric patients
low sounds
using the diaphragm is most useful for ______.
higher pitch sounds
degree of stretch on the heart prior to contraction
preload
forcefulness on contraction of individual ventricular muscle fibers
contractility
pressure that must be exceeded before the ejection of blood from the ventricles can occur
afterload
pathophysiology: - reduction of blood flow to the myocardium - leading cause of death for men and women - atherosclerosis/arteriosclerosis
CAD
pathophysiology: - physiological: hypertrophy related to fitness training - pathological: related to heart disease
cardiomegaly
pathophysiology: - loss of pumping efficiency by the heart - caused by CAD, congenital defects, long term high BP, valve disorders
CHF
heart rate higher than the normal SA node range of 60-100
tachycardia
a resting heart rate under 50 BPM
bradycardia