Anatomy Respiratory System Flashcards
5 respiratory functions:
- warms, filters, and humidifies air - influences speech, homeostasis of body pH, and olfaction - air distribution - gas exchange - alveoli serve as gas exchangers; all other parts of the respiratory system serve as air distributors
the respiratory system is divided into 2 structural divisions:
- upper respiratory tract - lower respiratory tract
the upper respiratory tract consists of (5):
- nose - nasopharynx - oropharynx - laryngopharynx - larynx
the lower respiratory tract consists of (3)
- trachea - bronchial tree - lungs
accessory structures of the respiratory system (4)
- oral cavity - ribcage - diaphragm - muscles
pharynx has 3 divisions:
- nasopharynx - oropharynx - laryngopharynx
____ nose consists of a bony and cartilaginous frame covered by skin
external nose
formed inferiorly by the paired palatine bones and superiorly by the ethmoid bone
internal nose: nasal cavity
sometimes the palatine bones fail to unite completely and produce a condition known as:
cleft palate
plate that separates the roof of the nose from the cranial cavity is a portion of the ethmoid bone perforations allow branches of the olfactory nerve to enter the cranial cavity
cribriform plate
the olfactory receptors cells, supporting cells, and basal cells lie in the respiratory region near the superior nasal conchae and adjacent septum. It contains cilia, but no goblet cells (does not secrete mucus)
olfactory epithelium
_____ divides the nasal cavity into right and left halves.
nasal septum
nasal septum consists of 4 main structures:
- perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone - vomer bone - septal nasal and vomeronasal cartilages
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells that secrete mucus. Has a rich blood supply
nasal/respiratory mucosa
When air enters the nostrils, it passes first through the ___(#1)____, which is lined by skin containing coarse hairs that filter out large dust particles. 3 shelves formed by projections of the Superior, Middle and inferior __(#2)____ (internal nares) extend out of each lateral wall of the nasal cavity. The conchae subdivide each side of the nasal cavity into a series of groove-like air passageways, the superior, middle and inferior __(#3)__. Mucus membranes line the nasal cavity and its shelves.
- vestibule 2. nasal conchae 3. nasal meatuses
- external nose merges with the nasal cavities and posteriorly communicates with pharynx through the internal nares - 4 pairs of air-containing spaces that open, or drain, into the nasal cavity - each is lined with respiratory mucosa
paranasal sinuses
_______ also act as resonating chambers for sound as we speak or sing
paranasal sinuses
functions of the nose (3)
- air that enters through the nasal cavities is filtered of impurities, warmed, moistened, and chemically examined - serves as a passageway for air going to and from the lungs - mucous secretions provide a “trap” for particulate matter removed from air before it travels further into the respiratory tract
- the throat - a tube-like structure that extends from the base of the skull to the esophogus - lies just posterior to the nasal and oral cavities, superior to the larynx, and anterior to the cervical vertebrae - made of muscle and lined with mucous membranes
pharynx
The _____ functions as a passageway for air and food, provides a resonating chamber for speech sounds, and houses the tonsils
pharynx
- lies behind the nose and extends to the soft palate - contains phayngeal tonsils (called adnoids when they are enlarged) - Has 4 openings: R and L eustachian tubes, 2 internal/posterior nares
nasopharynx
- lies from the soft palate to the level of the hyoid bone - contains palatine and lingual tonsils - has 1 opening: fauces
oropharynx
- begins at the level of the hyoid bone - inferior end opens to the esophagus posteriorly and larynx anteriorly - contains NO tonsils - has 2 openings: esophagus and larynx
laryngopharynx
3 functions of the pharynx:
- common pathway for both respiratory and digestive tracts - traps foreign particles from going further into the respiratory tract - effects phonation
- commonly called the voice box - lies between the root of the tongue and the upper end of the trachea - triangle shaped and made up of muscles and cartilage
larynx
the ____ lies in the mid-line of the neck anterior to the esophagus and C3-C6
larynx
larynx consists of:
- vestibule - vestibular folds - glottis (includes the vocal folds and rima glottidis)
laryns is composed of 9 cartilages:
- thyroid - epiglottis - cricoid (following 3 occur in pairs) - arytenoid - cuneiform - corniculate
2 fused plates of hyaline cartilage that form the anterior wall of the larynx and give it the triangular shape
thyroid cartilage
a large leaf-shaped piece of elastic cartilage that is covered with epithelium. it tapers and connects to the anterior rim of the thyroid cartilage
epiglottis cartilage
a ring of hyaline cartilage that forms the inferior wall of the larynx. it is attached to the first ring of cartilage of the trachea
cricoid cartilage
influence changes in position and tension of the vocal cords
arytenoid cartilage
4 functions of the muscles of the larynx:
- control vocal cord length - regulate the shape of the larynx - aid in respiration by abducting the vocal folds - during swallowing the laryngeal muscles prevent food from entering into the trachea
3 overall functions of the larynx:
- mucous membrane helps in the removal of dust particles and in warming and humidification of inspired air - integral in voice production - prevents food from entering respiratory tract
the windpipe - lies from the larynx to te primary bronchi - about 11 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter - contains smooth muscle with cartilage rings
trachea
3 functions of the trachea:
- open passageway for air to reach the lungs - aid in trapping foreign particles from entering the lung - obstruction of this airway for even a few minutes causes death from asphyxiation
the lower end of the trachea divides into 2 primary _____, right and left. The division occurs at the superior border of the 5th thoracic vertebra
bronchi
Right ____ is larger and more vertical than the left
bronchus
bronchi and bronchioles are also lined with _______________.
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
the respiratory bronchioles eventually divide into _______
alveolar ducts
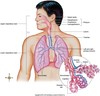
_____ are primary gas exchange structures
alveoli
__#___ alveoli are estimated to be present in the lungs
300 million
each ____ has thin walls allowing for easy exchange of gases to nearby capillaries
alveolus
the inside of the respiratory membrane of each alveolus has a slick surfactant that:
- reduces surface tension (force of attraction between water molecules) - helps prevent each alveolus from collapsing and sticking shut
alveoli function:
gas exchange between air and blood
bronchi functions (5):
- similar to trachea - conduct air - moisten and humidify air - aid in trapping foreign particles - cilia responsible for moving to mucus upward towards the pharynx
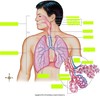
paired, cone-shaped structures - located from just above clavicles to T10 - has a hilium - has inferior aspect (base) and superior aspect (apex)
lungs
- slit in medial surface of each lung - root of the lung enters through this
hilium
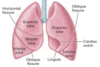
the lungs are divided into lobes by _____.
fissures
The left lung is divided into 2 lobes:
- superior - inferior
The right lung is divided into 3 lobes:
- superior - middle - inferior
Due to space that is occupied by the heart, the left lung is about _#%_ smaller than the right lung
10%
Secondary bronchi are also called ______ because the branch into lobes are named according to the lobe they enter
lobar bronchi
lungs have 2 functions:
- air distribution - gas exchange
lines the thoracic wall and visceral organs
pleura
lines entire thoracic cavity
parietal pleura
lines the lungs
visceral pleura
space filled with fluid that allows for smooth respiration
intrapleural space




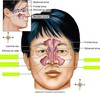
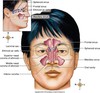









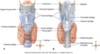









Bronchus/Trachea

Secondary/Lobar Bronchi

Tertiarr/Segmental Bronchi