CNS Brain Flashcards
layer of the meninges made of strong, white, fibrous tissue. Connected to periosteum of cranium
dura mater
certain areas of the ____ ____ engage predominantly in one particular function
cerebral cortex
inferior elevations of tectum. Part of the auditory pathway, relaying impulses from the receptors for hearing in the inner ear to the brain. Also reflex centers for the startle reflex
inferior colliculi
In the _____ lipid-soluble substances, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, alcohol, and most anesthetic agent, are able to access brain tissue freely.
blood brain barrier


region of the hypothalamus that contains dorsomedial nucleus, ventromedial nucleus, and arcuate nucleus
tuberal region
when the _____ ____ is electrically stimulated, no movement occurs; however, the symptoms of Parkinson’s indicate the ____ ____’s influences movement
substantia nigra
space located immediately outside the dura mater, but inside the bony coverings. Contains a supporting cushion of fat and other connective tissues
epidural space
oval projection appearing one on each side of the ventral surface lateral to the pyramids
olive
the surface of the cerebral cortex is irregular - each ridge is called a _____.
gyrus
primary auditory area in the cerebral cortex
transverse gyrus




- associated with emotions, survival instincts, and memory
- plays a significant role in fear response
- prolonged stress seems to cause hypersensitivity which increases anxiety and reaction to fear
- prolonged stress results in enlargement
amygdala
limbic system structures:
- cingulate gyrus
- hippocampus
- and primary connections with thalamus, amygdala, and more
lies superior to the medulla and inferior to the midbrain. Latin for bridge. Fibers run transversely across the ___ into the cerebellum
pons


sensory, primary visual area of the cerebral cortex
occipital lobe
localization of function varies from person to person, and even at different times in an individual’s life when the brain has sustained damage
cerebral plasticity
4 main integrative functions of the cerebral cortex
- consciousness
- language
- emotions
- memory
superior elevations of the tectum. Serve as reflex centers for certain visual activities; also serve as reflexes that govern movements of the head, eyes, and trunk in response to stimuli
superior colliculi
- primary role in converting short-term to long-term memory
- regulates activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) by shutting down the stress response when it is no longer needed
- prolonged stress interferes with memory, spatial navigation, and the ability to regulate the HPA axis
- Prolonged stress can cause atrophy
hippocampus
layer of the meninges that is a delicate, cobweb-like layer that lies between the dura mater and the pia mater
arachnoid mater
thin ventricle, vertical pocket of fluid below and medial to lat ventricles.
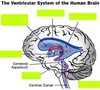
third ventricle
lobe that processes hearing
temporal lobe
- translated means “little brain”. - Located inferior to the posterior portion of the cerebrum. - second largest part of the brain, but contains more neurons than all other parts of the nervous system combined
cerebellum
____ centers are located in the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
speech
extensions of ascending, or sensory, spinothalamic tracts and descending, or motor, corticospinal tracts
projection tracts
lesions in the speech centers give rise to language defects (2):
aphasia, dysphasia
____ is composed of white matter and reticular formation. Contains centers for reflexes mediated by cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII. Contains the pneumotaxic centers that help regulate respiration
pons
2 bulges of white matter on the ventral surface of medulla oblongata
pyramids
lies beneath the thalamus and forms the floor of the 3rd ventricle. It is a major regulator of the ANS
Hypothalamus
functions of _____:
- arousal or alerting system
- crucial for maintaining consciousness
- alertness and attentiveness
reticular activating system
region of the hypothalamus that contains medial and lateral ____ nuclei and regualtes certain autonomic activities
preoptic region
targeted injection to anesthetized a region of the spine. Nerve roots around this region will be anesthetized as well.
epidural injections
space located between dura mater and arachnoid mater. Contains a small amount of lubricating serous fluid
subdural space


Because it is continuous with the periosteum on the interior surface of the cranial bones, no _____ ____ is normally present in the brain.
epidural space


ascending and descending tracts, white matter and gray matter
reticular formation
most numerous cerebral tracts:
extend from one convolution to another in the same hemisphere
association tracts
_____ space shares space with the ventricles… usually arterial bleeds and fast.
subarachnoid space
_____ ____ lie under the cerebral cortex and are made up of white matter
cerebral tracts
- a dumbell-shaped mass of gray matter made up of many nuclei. - Each lateral mass forms one lateral wall of the 3rd ventricle. - major center for relaying sensory input to cerebral cortex from the spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, basal nuclei, and various parts of the cerebrum
thalamus
primary functions of ____: - impulses from receptors produce conscious recognition of crude (non critical) sensations of pain, temperature, and touch - cell bodies in nucleus of the thalamus relay various sensory impulses (except possibly olfactory) to the cerebrum - associates sensory impulses with feelings of pleasantness and unpleasantness - relays info from cerebellum and basal nuclei to motor area of cerebral cortex - plays a part in arousal or alerting mechanism - plays a part in production of complex reflex movements
thalamus
layer of the meninges that adheres to the outer surface of the brain and spinal cord
pia mater
_____ bleed is usually venous. This is clinically relevant in terms of “slow bleed”. If a person falls and doesn’t notice changes for 24-48 hrs it can be because venous blood is not under pressure like arterial and bleeds slower.
subdural
islands of gray matter that lie deep in white matter in each hemisphere
basal nuclei
_______ nucleus serves as the body’s internal clock in the hypothalamus.
suprachiasmatic

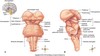
contains: - cerebral peduncles (anterior) - tectum (posterior) - red nucleus - substantia nigra
midbrain
translated means “between brain”. Located between the cerebrum and midbrain. Contains: - thalamus - hypothalamus - pineal gland - optic chiasma
diencephalon
responsible for planning, logic, self-regulation, and higher mental functioning
- stress results in shrinkage and loss of dendrites in this area which results in impaired decision making, self-regulation and higher mental function, and decreases the ability to cognitively adapt
prefrontal cortex
the ______ plays a primary role in converting short-term to long-term memory
hippocampus
- acts with the cerebral cortex to produce skilled movements by coordinating the activities of groups of muscles - helps control posture; operates at a subconscious level to make movements efficient and coordinated - controls skeletal muscles to maintain balance - coordinates incoming sensory information from skeletal muscles
functions of the cerebellum
reddish due to rich blood supply and an iron-containing pigment in their neuronal bodies. Axons from the cerebellum and cerebral cortex form synapses in the ______, which help control muscular movements
red nuclei
functions of _____:
- play role in regulating initiation and termination of movement
- helps regulate muscle tone required for body movement
- control subconcious contraction of skeletal muscles
- help initiate and terminate attention, memory, planning
- help regulate emotional behaviors
basal nuclei




important player in brain function, in particular in eye movement, motor planning, reward-seeking, learning, and addiction.
substantia nigra
located superior to the pons and inferior to the cerebrum. Composed of both white matter and reticular formation
midbrain
fissure with the deepest groove; division of cerebrum into right and left halves (cerebral hemispheres)
longitudinal fissure
pH of the CSF affects pulmonary ventilation and cerebral blood flow, which is important in maintaining homeostatic controls for brain tissue. Also serves as a transport system for polypeptide hormones secreted by hypothalmic neurons
homeostatic function of CSF


consists mainly of tight junctions that seal together the endothelial cells of brain blood capillaries and a thick basement membrane that surrounds the capillaries The processes of many astrocytes press up against the capillaries and secrete chemicals that maintain the permeability characteristics of the tight junctions.
Blood Brain Barrier BBB


Contains the abilities: - logic - math - language - reading - writing - analysis
left hemisphere
the ability to speak and write words. the ability to understand spoken and written words
language
right cerebral hemisphere (3):
- perception of auditory material
- perceiving and visualizing spatial relationships
- creativity
lobe that processes vision
occipital lobe

epidural space
_____ is found within the subarachnoid space, around the brain and spinal cord, and within the cavities and canals of the brain and spinal cord
cerebro spinal fluid CSF
functions of ____: - an important part of the body’s biological clock mechanism - sets/regulates the body’s biological clock - secretes hormones, the most notable is melatonin, a sleep inducer
pineal gland/body
the ____ lies hidden from view, burried in the lateral fissure
contains the abilities: - personality - creativity - intuition - music - art - spatial abilities
right hemisphere
composed of all ascending and descending tracts and located just above the foramen magnum and extends to inferior border of the pons. Also contains pyramids and olive
medulla oblongata
____ bones encase the brain. _____ encase the spinal cord.
cranial, membranes
2 protective coverings of the brain:
- bones - Membranes
deep groove between the temporal lobe and the frontal and parietal lobes
lateral fissure

corpus callosum
space located between arachnoid mater and pia mater. Contains a significant amount of cerebrospinal fluid
subarachnoid space
2 functions of medulla oblongata
contains vital reflex centers: cardiac, vasomotor (vessel muscle), and respiratory centers - contains nonvital reflexes: vomiting, coughing, sneezing, hicupping, and swallowing
medium for minor exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and adjacent nervous tissue
circulation of CSF
Cranial dura mater has 2 layers:
- periosteal layer (outer) - meningeal layer (internal)
hypothalamus is composed of a dozen or so nuclei in these 4 major regions:
- mamillary - tuberal - supraoptic - preoptic
3 types of cerebral tracts:
- projection tracts
- association tracts
- commissural tracts
contains nuclei, some are called control center for cardiac, respiratory, and vasomotor control
reticular formation
groove that separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
parietooccipital fissure
receptive sensory speech area of the cerebral cortex
- can speak but not arrange words in a coherent fashion
wernicke’s area
the 3 functions of CSF:
- mechanical protection: shock absorbing medium 2. homeostatic function 3. circulation
the ____, ____, and ____ lobes are among the areas responsible for short and long term memory
region of hypothalamus that lies most posteriorly. ____ bodies serve as relay stations for reflexes related to sense of smell
mamillary region
cerebrum: _____ divide each hemisphere into lobes
fissures
4 ventricles of the brain:
- lateral ventricles (2, first and second) - third ventricle - fourth ventricle

epidural space
extend from a point in one hemisphere to a point in the other hemisphere (compose the corpus callosum)
commissural tracts
lobe that processes senses other than hearing and vision
parietal lobe
The brainstem consists of (4):
- medulla oblongata (lowest part) - pons (middle part) - midbrain (uppermost part) - the start of 10 sets of cranial nerves


the _____ ___ is the outer rim of the cerebrum composed of gray matter and contains more than one billion neurons
cerebral cortex
The 3 meningeal spaces:
- epidural space - subdural space - subarachnoid space
lobe that controls emotion
frontal lobe
the largest and uppermost division of the brain. Contains bulk of brain’s mass and contains 2 hemispheres: right and left hemispheres
cerebrum
primary motor area of the cerebral cortex
- impulses from neurons in this area descend over motor tracts and stimulate skeletal muscles
precentral gyrus
Name the cerebral lobes

blue: frontal
green: parietal
yellow: occipital
orange: temporal
red: insula
Between adjacent gyri in the cerebral cortex lie either shallow grooves called ____, or deeper grooves called _____.
- sulci 2. fissures
network of capillaries that project from the pia mater into the lateral ventricles and into the third and fourth ventricles
choroid plexuses
centers of the brainstem’s reticular formation that receive impulses from the spinal cord and relay to the thalamus. From the thalamus to all parts of cerebral cortex
- sensory or ascending
reticular activating system


both the subjective experiencing and objective expression of emotions involve the cerebrum’s _________, known as the emotional brain
limbic system
just superior to the junction of the medulla with the spinal cord, 90% of the axons in the left pyramid cross to the right side, and 90% of the axons in the right pyramid cross to the left side. This is called:
decussation of pyramids
the 4 cerebral fissures:
- longitudinal fissure
- central sulcus
- lateral fissure
- parietooccipital fissure

corpus callosum
inflammation of the meninges caused by either a virus or bacterial infection.
Meningitis

reticular activating system
Around S3 the _____ blends with the dura mater to form a fibrous cord that is continuous with the periosteum of the coccyx
filum terminale

white matter connecting nuclei
internal capsule
Research findings indicate that the cerebrum’s _______ plays a key role in memory
limbic system
- a state of awareness of one’s self, one’s environment, and other humans
- very little is known about the neural mechanisms that produce consciousness
- depends on excitation of cortical neurons by impulses conducted by the reticular activating system
consciousness
many cerebral functions have a typical location. This is known as:
cerebral localization
The ______ space holds veins, arteries and penetrating vessels. Concussions and other trauma can result in tearing of these delicate vessels resulting in a subarachnoid hemorrhage
subarachnoid space
located just above the corpora quadrigemina. Named because it looks like a pine nut.
pineal gland/body
the _____ _____ extend through the midbrain and conduct impulses between the midbrain and cerebrum
cerebral peduncles


The 3 layers of the meninges:
- Dura mater (outer) - Arachnoid mater (middle layer) - Pia mater (inner layer)
nerve tissue connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres. Much of the inter-hemispheric communication in the brain is conducted across the ___ ____.
corpus callosum


Blood is filtered by the _____ and CSF is produced. After circulating through the ventricles of the brain, the central canal, and the subarachnoid spaces. It is then absorbed back into the blood.
choroid plexuses
the formation of the CSF occurs mainly by separation of fluid from blood in the ______.
choroid plexuses
The pressure and volume of CSF normally is constant due to:
rates of formation and reabsorbtion are the same
The _____ contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and pituitary gland.
diencephalon
regions of the brain:
- brain stem (medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain) - cerebellum - diencephalon - cerebrum
ventricles, one in each cerebral hemisphere
lateral ventricles
left cerebral hemisphere (3):
- language functions
- analytic and logical thought
- pattern sequencing
In the spinal cord the pia mater forms a slender filament known as the
filum terminale
primary somatosensory area in the cerebral cortex
- receives impulses from receptors activated by heat, cold, and touch stimuli
- cortex contains a somatic sensory map of the body
- AKA sensory homunculus
postcentral gyrus
region of the hypothalamus that contains paraventricular nucleus, supraoptic nucleus, anterior hypothalamis nucleus, and suprachiasmatic nucleus
supraoptic region
expressive motor speech area of the cerebral cortex
- clear thoughts but unable to form words
broca’s area
the hippocampus, amygdala, and limbic system are affected by ______.
prolonged stress
The _____ continue down inside the spinal cavity.
meninges


functions of the _____: - major regulator of ANS (HR, respiration, GI tract, urinary bladder) - major regulator of homestasis; it receives input that is interpreted to correct for changes in osmotic pressure, hormone concentrations, and blood temperature - it affects emotions of aggression, pain, and pleasure - regulation of circadian rhythms and states of consciousness - regulates thirst and hunger responses - controls body temp via vasoconstriction, dilation, and sweating
hypothalamus
A reservoir of circulating fluid that, along with blood, the brain monitors for changes in the internal environment. Provides supportive and protective cushion around and within brain and spinal cord.
cerebro spinal fluid
groove between the frontal and parietal lobes
central sulcus
tiny ventricle, diamond-shape space where cerebellum attaches to the back of the brainstem
fourth ventricle


