October 27, 2015 - Upper Limb I Flashcards
Scapula
The bone in your shoulder. It has several parts to it.
The acromion process is posterior
Coracoid process is anterior
Glenoid cavity connects to the humerus
Scapular spine is the ridge along the back.

Clavicle
The only bony attachment for the upper limbs. Attached via the acromioclavicular joint to the acromion process of the scapula, and also attached to the sternoclavicular joint on the sternum.

Glenohumeral Joint
Where the humerus and the scapula meet.
The head of the humerus interacts with the glenoid cavity on the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint. There is articular cartilage and synovial fluid inside the joint.
Acromioclavicular Joint
Also known as the AC joint.
Connects the acromion with the clavicle.

Coracoacromial Ligament
Connects the acromion to the coronoid process. Provides an upper slung to prevent the shoulder from moving too far.
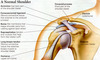
Coracoclavicular Ligament
Connects the coracoid process to the clavicle.

Condyles
Are sites of muscular attachment.
For example, the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
Capitulum (humerus)
The round protuberence on the distal part of the humerus.
It consists of a smooth, rounded eminence which articulates with the cup-shaped depression on the head of the radius.

Trochlea (humerus)
The medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint, which articules with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm.

Interosseous Membrane
The membrane between the radius and ulna (as well as between the tibia and fibula).
This allows movement, but also allows them to stay together.

Scaphoid
Big carpal in the hand that is at the base of the wrist and the thumb.
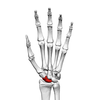
Lunate
A carpal at the base of the wrist furthest from the thumb (near the ulna)
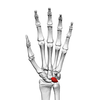
Joints in the Hand
Interphalangeal joints (between phalanges)
Carpometacarpal joint (between metacarpals and carpals)
Intercarpal joint (between carpals)
Radiocarpal joint (between carpals and the radius)
Arterial Circulation
Begins with the subclavian artery, which becomes the axillary artery, which becomes the brachial artery, which then branches into both the radial artery and the ulnar artery.

Blood Supply to Shoulder
The subclavian artery has several branches to feed the shoulder. The transverse cervical artery goes down the side of the scapula. The suprascapular artery goes over the top of the artery. The subscapular artery branches off below the scapula.

Arteries of the Forearm and Hand
The radial artery and the ulnar artery anastimose in the hand.
The radial artery takes a dive under the thumb, while the ulnar artery comes up near the pinky before diving.
Scapulothoracic Joint
An articulation of the scapula with the thorax.

Winged Scapula
Caused by a non-functioning (torn or paralyzed) serratus anterior. When the patient pushes against a wall, the scapula will push out the back.

Rotator Cuff Muscles
Supraspinitus
Infraspinitus
Subscapularis
Terres minor


