neck/suboccipital LOs Flashcards
1
Q
deep cervical fascia
A
- investing fascia
- surrounding sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
- encircles neck
- pretracheal fascia
- around thyroid cartilage, trachea, esophagus
- prevertebral fascia
- encircles deep muscle and vertebra
- carotid sheath
- around internal jugular vein, common carotid artery, vagus nerve (CN X)
- medial to SCM m.

2
Q
investing fascia
A
- like deep fascia of extremities
- surrounding SCM and trapezius mm.
- encircles neck
3
Q
pretracheal fascia
A
- around thyroid cartilage, trachea, esophagus
4
Q
prevertebral fascia
A
- encirocles deep muscle and vertebra
5
Q
carotid sheath
A
- medial to SCM m.
- around internal jugular vein, common carotid artery, vagus nerve (CN X)
- posterior to ansa cervicalis
6
Q
triangles of neck
A
- anterior
- submental
- submandibular
- muscular
- carotid
- posterior
- supraclavicular
- occipital

7
Q
submental triangle
A
- superior to hyoid bone, anterior to anterior belly of digastric muscle, inferior to mandible

8
Q
submandibular triangle
A
- posterior to anterior digastric, superior to posterior digastric, inferior to mandible

9
Q
muscular triangle
A
- inferior to hyoid bone, anterior to superior omohyoid, superior to sternocleidomastoid muscle

10
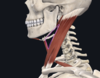
Q
carotid triangle
A
- inferior to posterior digastric, posterior to superior omohyoid, superior to SCM
- contains common carotid artery
11
Q
supraclavicular triangle
A
- anterior to inferior omohyoid, posteroinferior to SCM, superior to clavicle
- contains subclavian artery (with thyrocervical trunk: transverse cervical, suprascapular, ascending cervical, inferior thyroid)

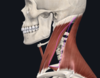
12
Q
occipital triangle
A
- posteroinferior to SCM, superior to inferior omohyoid, anterior to anterior border of trapezius m.
- contains accessory nerve (CN XI), trunks of brachial plexus
13
Q
cervical plexus
A
- C1: ventral ramus of C1 (to geniohyoid). superior root of ansa cervicalis (to superior omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid, inferior omohyoid)
- suboccipital (dorsal ramus)
- C2: inferior root of ansa cervicalis
- greater occipital (S)
- lesser occipital (S)
- greater auricular (S)
- C3: inferior root of ansa cervicalis, phrenic nerve (1)
- greater auricular (S)
- supraclavicular (S)
- C4: phrenic nerve (2)
- supraclavicular (S)
- C5: phrenic nerve (3)

14
Q
branchial/pharyngeal arches
A
- 1: mandibular
- 2: hyoid
- 3: third
- 4: fourth
- 6: sixth

15
Q
first branchial arch
A
- mandibular
- mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric
16
Q
second branchial arch
A
- hyoid
- facial expression, posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid
17
Q
third branchial arch
A
- third
- stylopharngeus
18
Q
fourth branchial arch
A
- fourth
- cricothyroid, inferior pharyngeal constrictor
19
Q
sixth brnachial arch
A
- sixth
- intrinsic laryngeal
20
Q
branchial motor axon function related to function of cranial nerves
A
- BMAs from pharyngeal arches innervated by corresponding CNs
- BMAs are special sets of axons from embryologic pharyngeal arches, homologous to somites in skeletal muscle
- branchial axons innervate muscles from pharyngeal arches
- CNs are “called” to sites of each arch (like dermatomes and myotomes)
21
Q
unique features of cervical vertebrae
A
- C1 is atlas
- no spinous processes
- C2 is axis
- has dens
- C7 is vertebral prominens
- all except C7 have bifid spinous processes
- vertebral artery travels through transverse formaina of cervical vertebrae


