mediastinum LOs Flashcards
1
Q
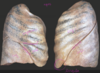
ID external features of the right and left lungs
A
- right
- 3 lobes: superior lobe, middle lobe, inferior lobe
- 2 fissures: oblique fissue (inferior), horizontal fissure (superior and middle)
- left:
- 2 lobes: superior lobe, inferior lobe
- 1 fissure: oblique fissure
- also lingula
2
Q
explain pattern of branching and structural anatomy of bronchial tree
A
- trachea: rings, carina
- carina is internal bifurcation
- bronchi:
- primary (right and left main)
- right primary is larger and more vertical, more likely to take aspirated food particles
- secondary: lobar
- tertiary: segmental
- primary (right and left main)

3
Q
medial surfaces of lungs
A
- right
- superior vena cava, esophagus, azygos vein, heart
- pulmonary artery anterior to primary bronchus
- left
- aortic arch, thoracic aorta, heart, esophagus, lungula
- pulmonary artery superior to primary bronchus

4
Q
pleural coverings of lungs including regions and recesses
A
- parietal pleura
- around wall
- parts: cervical, costal (most extensive), diaphragmatic, mediastinal
- recesses: sites of fluid accumulation
- costomediastinal (costal to mediastinal): anteromedial
- costodiaphragmatic (costal to diaphragmatic): anteroinferior
- visceral pleura
- around organ

5
Q
layers of pericardium superficial to deep
A
- fibrous pericardium
- parietal pericardium
- visceral pericardium/epicardium
- myocardium
- endocardium
- fibrous pericardium + parietal pericardium: bonded together
- parietal pericardium + visceral pericardium: serous pericardium
- visceral pericardium + myocardium + endocardium: heart

6
Q
ID surfaces features of heart
A
- anterior
- right auricle on right atrium
- coronary sulcus between right atrium and right ventricle
- anterior interventricular sulcus between left and right ventricles
- ligamentum arteriosum connection ascending aorta/arch and pulmonary trunk
- right auricle on right atrium
- posterior
- arch, pulmonary arteries
- pulmonary veins on left atrium
- coronary sinus between left atrium and left ventricle

7
Q
internal features of right atrium
A
- interatrial septum: wall between right and left atria
- fossa ovalis: remnant of fetal circulation
- pectinate muscle: rough, anterior wall
- crista terminalis: where pectinate muscle and interatrial septum meet
- valved orifice of inferior vena cava
- valved orifice of coronary sinus (drains heart surface)
- right atrioventricular orifice with AV valve

8
Q
internal features of right ventricle
A
- conus arteriousus
- supraventricular crest
- right AV valve (tricuspid)
- chordae tendineae
- papillary muscles: anterior, posterior, septal
- septomarginal trabeculae (near apex, septum to lateral wall)
- trabeculae carneae (rugated)
- interventricular septum (wall between ventricles)
- valve of pulmonary trunk
- pulmonary trunk

9
Q
internal features of left atrium
A
- left superior pulmonary valve
- valve of foramen ovale (like fossa ovalis)
- interatrial septum
- pectinate muscle: anterior, posterior

10
Q
internal features of left ventricle
A
- left atrioventricular valve (mitral)
- chordae tendineae
- papillary muscles
- trabeculae carneae of IV septum

11
Q
arrangement of chordae tendineae and the valves of heart
A
- valves open: blood flowing from high pressure to low pressure (atria to ventricles)
- tendinous cores/valve cusp: loose
- valves closed: preventing backflow of blood from ventricles (ghigh pressure) to atria (low pressure)
- chordae tendineae keep flaps from opening into atria

12
Q
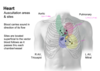
cardiac auscultation sites
A
- sites located superficial to vector blood flows as it passes through each chamber/vessel
- aortic semilunar: right second intercostal space
- pulmonary semilunar: left second intercostal space
- right AV/tricuspid: left fifth intercostal space
- left AV/mitral: medial left fifth intercostal space
13
Q
blood flow through heart, including chambers and valve
A
- SVC/IVC > RA > tricuspid/right AV > RV > pulmonary valve > pulmonary trunk > pulmonary arteries > lung
- pulmonary veins > LA > mitral/left AV > LV > aortic valve >. ascending aorta > aortic arch

14
Q
conduction system of heart
A
- sinoatrial (SA) node: at apex of crista terminalis (RA)
- atrioventricular (AV) node: between RA and RV
- atrioventricular bundle (of His): between right and left AV valve
- left bundle of branche (LV), right bundle of branch (RV)
- moderator band (septomarginal trabeculae): in RV, rapid access for ventricular contraction timing

15
Q
underlying anatomy of (cardiac) referred pain
A
- pain receptors in myocardium have visceral afferent sympathetic axons to cell bodies in DRG
- DRG shared with general somatic axons
- brain interprets pain from skin (left pectoral, shoulder, medial UE)

16
Q
remnants of fetal circulation
A
- ductus arteriosus (ligamentum arteriosum): pulmonary trunk to arch of aorta
- foramen ovale (fossa ovalis): right to left atrium
- lungs aren’t functional, pulmonary circulation bypassed