infratemporal fossa LOs Flashcards
1
Q
boundaries of infratemporal fossa
A
- laterally: ramus of mandible
- medially: lateral pterygoid plate
- anteriorly: posterior maxilla
- posteriorly: styloid and mastoid processes (of temporal bone)
- superiorly: greater wing of sphenoid bone
- inferiorly: mandibular attachment of medial pterygoid (medial surface of angle of mandible)
2
Q
infratemporal fossa arterial supply
A

3
Q
pterygoid plexus in spread of infection to cranial cavity
A
- facial veins (like superior labial vein) drain to the pterygoid plexus that has connections all over brain
- to cavernous sinus through emissaries
4
Q
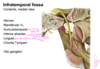
nerves found in infratemporal fossa
A
- mandubular V3
- auriculotemporal
- inferior alveolar
- lingual
- chorda tympani
5
Q
components of TMJ
A
- articular tubercle: temporal bone, limits anterior translation of mandiblular head
- articular disk: synovial fibrocartilage, across joint
- mandibular fossa: of temporal bone
- head of mandible: into articular tubercle

6
Q
ligaments of TMJ
A
- joint capsule
- lateral ligament
- from zygomatic process of temporal bone to neck of mandible
- supports joint capsule in maintaining articulation, helps to limit depression and retraction
- stylomandibular ligament
- from styloid process to angle of mandible
- taut during moderate opening
- sphenomandibular ligament
- from spine of sphenoid to lingua
- check ligament to prevent excessive depression

7
Q
innervation of TMJ
A
- branches of V3: auriculotemporal, deep temporal, massateric

8
Q
muscle for elevation/closing TMJ
A
- masseter
- temporalis
- medial pterygoid
9
Q
muscle for depression/opening TMJ
A
- lateral pterygoid
- suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles
- mainly gravity assisted: muscles are relaxed
10
Q
muscles for protrusion of TMJ
A
- lateral pterygoid
- medial pterygiood
- masseter
11
Q
muscles for retrusion of TMJ
A
- temporalis
- masseter
- masseter can do both protrusion and retrusion due to superior and deep heads
12
Q
muscles for lateral movement of TMJ
A
- same side medial and lateral pterygoids and masseter
- opposite side temporalis


