MSK lower limb 2 Flashcards
(53 cards)
What type of joint is the proximal and distil tibiofibular joint
Proximal = Plane
Distil= syndesmososis (fibrous joint)
what inserts into this groove

Tibialis posterior tendon
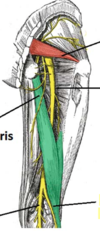
What are the two division of
- the scitatic nerve
- the popliteal artery
- common fibular nerve
sciatic nerve -> tibial & common fibular nerve
Popliteal artery = Anterior tibial & Posterior tibial artery
Common fibular nerve = superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve

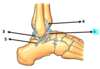
Label the diagram


Label the diagram

what is the motor function of the tibial nerve
The tibial nerve innervates the muscles of the posterior leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles.
including the popliteus of the knee

What is the sensory function of the tibial nerve
Cutaneous branches of the tibial nerve combine with branches from the common fibular nerve to form the sural nerve. This sensory nerve innervates the skin of the posterolateral side of the leg and the lateral side of the foot.
The tibial nerve also supplies all the sole of the foot via three branches:
Medial calcaneal branches: These arise within the tarsal tunnel, and innervate the skin over the heel.
Medial plantar nerve: Innervates the plantar surface of the medial three and a half digits, and the associated sole area.
Lateral plantar nerve: Innervates the plantar surface of the lateral one and a half digits, and the associated sole area.

The muscles listed below are all innervated by the tibial nerve. Which of the following produces flexion of the knee joint?
- gastrocnemius
- tibialis posterior
- soleus
- flexor digitorum longus

Which of these cutaneous nerves does not arise from the tibial nerve?
- Medial plantar
- Lateral plantar
- Medial calcineal
- Saphenous
Saphenous- this is a terminal branch of the femoral nerve
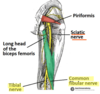
What is the motor and sensory function of the common fibular nerve
Motor: Innervates the short head of the biceps femoris directly. Also supplies (via branches) the muscles in the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg.
Sensory: Innervates the skin of the lateral leg and the dorsum of the foot.

Explain the clinical relevance of damage to the common fibular nerve
common fibular nerve wraps around the neck of the femur and so fractures of the fibular neck can cause nerve palsy
this can result in foot drop- loose the ability to dorsiflex the foot at the ankle
loss of sensation over the dorsum of the foot, and lateral sideof the leg. Innervation is preserved on the medial side of the leg (supplied by the saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral), and the heel and sole (supplied by the tibial nerve, a branch of the sciatic)
What is the route of the common fibular nerve distal to the knee?
- Around the head of fibula
- Around the neck of fibula
- Along the tibial shaft
- None of the above
Around the neck of the fibula
Which fibular nerve supplies the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg
Superficial fibular nerve
What can damage to the superficial fibular nerve result in
Loss of eversion of the foot
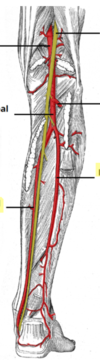
Fill in the diagram of the arterial suooky of the leg
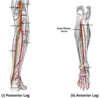
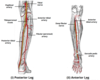
what artery does the posterior tibial and the dorsalis pedis arise from
Posterior tibial= popliteal artery
Dorsalis pedis= Anterior tibial artery
Complete the sentence: The adductor canal ends at the adductor hiatus, a space within the _____________ muscle
Adductor magnus muscle
What nerve supplies the lateral compartment of the leg?
Superficial fibular nerve
Where can damage to the fibular nerve occur & what can it result in
The fibular neck
It can result in footdrop
label: dorsum of foot
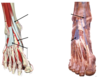

where is the posterior tibial pusle felt
posterior to the medial maleolus

What type of joint is the ankle joint
Mortise joint
Synovial hinge
When is the malleolar grip the strongest
During dorsiflexion of the ankle, the ankle joint is most unstable during plantarflexion