Female repro organs Flashcards
What three structures constitute the birth canal?
Vagina
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Label


What are the 3 layers of the uterus

Endometrium: inner lining
Myometrium: muscle layer; smooth muscle cells
Serosa/perimetrium: thin, outer layer, epithelial cells

As pregnancy advances the uterus physiologically has an ‘upper’ segment and a ‘lower segment’
what area of the uterine body does the lower segment develop from
Isthmus of the uterus
When a caesarean delivery is done which part of the uterus is opened to deliver the baby?
Lower segment of the uterus

What is the normal position of the uterus?
Anterflexed and antiverted

What could happen if the position of the uterus is very retroverted and retroflexed, particularly in early pregnancy? Think of the position of the other organs…
When abdominal pressure increases the vagina is more likely to prolapse into the uterus as the vagina is directly inferior to the uterus
Label


What are the fornices of the vagina? How many are there?

Recesses of the vagina, around the cervix
- Anterior fornix
- Posterior fornix
- Lateral fornix

Through which vaginal fornix you can access the rectouterine pouch? What is the clinical significance of this?
Posterior fornix is closely related to the rectouterine pouch
This is a way of clearing an infection of the rectouterine pouch
Describe the broad ligament
Flat sheet of peritoneum associated with the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries
Extends from the lateral pelvic walls on both sides, and folds over the internal female genitalia, covering their surface anteriorly and posteriorly.
The ovarian, roud and suspensory ligament all lie within the broad ligament
Label


What ligaments are attached to the ovary & from where
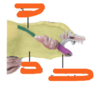
Ovarian ligament: Inferiorly, attaches ovary to the side of the uterus. It joins the uterus just below the origin of the fallopian tubes.
Suspensory ligament: Extends outwards from the ovary to the lateral abdominal wall

Name 3 ligaments associated with the uterus
Superior aspect: supported by broad ligament and round ligament
Middle aspect: supported by cardinal, pubocervical and uterosacral ligaments
What is the round ligament a remnant of?
Embryonic gubernaculum
Describe the round ligament of the uterus

The round ligament is a remnant of the embryonic gubernaculum.
It originates at the uterine horns (the points at which the fallopian tubes enter the uterus), and attaches to the labia majora, passing through the inguinal canal.

Which ligament (part of the pelvic fascia, which is one of the main supports of the uterus) is called the cardinal ligament of the uterus?
Transverse cervical ligament
The cardinal ligament (or Mackenrodt’s ligament, lateral cervical ligament, or transverse cervical ligament) is a major ligament of the uterus. It is located at the base of the broad ligament of the uterus. There are a pair of cardinal ligaments in the female human body.
Apart from pelvic fascia, what other structure in the pelvis is also an important support of the uterus?
Pelvic diaphragm (levator ani & coccygeus)
The uterine tubes are divided into 4 parts, what are these & label

- Fimbriae – finger-like, ciliated projections which capture the ovum from the surface of the ovary.
- Infundibulum – funnel-shaped opening near the ovary to which fimbriae are attached.
- Ampulla – widest section of the uterine tubes. Fertilization usually occurs here.
- Isthmus – narrow section of the uterine tubes connecting the ampulla to the uterine cavity.

Which part of the uterine tube does fertilization occur?
The ampulla
What is meant by an ectopic pregnancy?
what might a cornual ectopic pregnancy be?
- fertilised egg implants itself outside of the womb, usually in a fallopian tube
An ectopic pregnancy is an uncommon, but important clinical diagnosis to be aware of an requires urgent surgery due to the risk of blood loss
- Rare form of ectopic pregnancy where implantation occurs in the cavity of a rudimentary horn of the uterus (point where the uterus and fallopian tubes meet)
What ligaments attaches the ovary to the lateral pelvic wall and to the uterus

Ovarian ligament: uterus to ovary (1)
Suspensory ligament: ovary to lateral pelvic wall (2)
The blood supply to the gonads and genitalia is via which two major branches from the aorta
The ovarian (gonadal) and the internal iliac arteries
The ovarian artery corresponds to the male testicular artery, in that they are branches directly from the abdominal aorta

What vertebral level do the ovarian arteries originate?
L2 vertebrae
As it descends the artery passes within the suspensory ligament to supply the ovaries via the broad ligament.
Note that this vessel freely anastomoses with the uterine artery.
Into which vessels do the ovarian veins drain?
Left ovarian vein->left renal vein
Right ovarian vein -> Right inferior vena cava
what does the expression “water under the bridge” relate to?
The uterine artery crosses over the ureter at the level of ischial spine, junction of cervix and lateral part of fornix of vagina.
Label


When would the ureter and bladder be at risk of iotrogenic damage?
Hysterectomy or caeserian section
Which group of lymph nodes drain the ovary?
Para-aortic lymph nodes
Fill in the table- lymph drainge of female repro tract


What rib anatomical points does the breast extend from verically and horisontally
Vertically: 2nd to the 6th rib
Horizontally: lateral border of sternum to the mid-axillary line
What is the axillary process of the breast
Extension of the breast tissue into the axilla

What arteries supply the mammary glands

Branches of the subclavian and axillary arteries

Label- vasculature of the breast


Label: vasculature of the breast


FINISH LYMPH PART OF WB
List 4 functions of the placenta
- Gaseous Exchange
- Metabolism
- Endocrine secretion
- Passes immunity to fetus
How can you distuinguish between the fetal and the maternal side of the placent?

Fetal surface: smooth + contains the umbilical cord
Maternal surface: rough and spongy

At what stage of labour does the placenta physiologically seperate from the uterine wall?
3rd stage of labour
What is this showing?

Cut section of the umbilical cord: can see two umbilical arteries and a single umbilical vein
W= alantois

What is the function of umbilical arteries and veins in the foetal circulation?
Arteries: Carry deoxygenated fetal blood toward the placenta for replenishment
Veins: carry newly oxygenated and nutrient-rich blood back to the featus
What is the lymphatic drainage of the ovary?
Para-aortic nodes
What is the lymphatic drainage of the fundus and upper uterine body?
Pre-aortic nodes
What is the lymphatic drainage of most of the uterine body
External iliac lymph nodes
What is the lymphatic drainage of the uterine cervix and upper vagina
Internal iliac and sacral lymph nodes
What is the lymphatic drainage of the lower vagina
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
Which ligament of the female reproductive tract houses the uterine arteries and veins?
Cardinal ligament
The cardinal ligament lies at the inferior border of the broad ligament and contains the uterine artery and veins, and forms an attachment between the cervix and the lateral pelvic wall
The area the female urethra opens into is known as the?
Vaginal vestibule
The vestibule is the area between and surrounding the labia. The external vaginal orifice (vaginal opening) and urethra open onto the vestibule.
What vessels contract during the menstrual cycle?
Spiral arteries of the endometrium contract, leading to ischemia and sloughing of the functional layer
Label the parts of the uterus and the uterine tube


What is the breast composed of?
Highly modified exocrine glands
- Consists of 15-25 lobules with tubulo-acinar glands (parenchyma) and stroma (connective tissue)
In what fascia do we find the breasts?
lie in the superficial fascia of the pectoral region
What muscles is the deep surface of the breast related to?
Pectoralis major
Pectoralis minor
Serratus anterior
What does the umbilical vein persists as in an adult?
Ligamentum teres
What ligament connects the ovary to the side of the uterus
Ovarian ligament

What ligament connects the ovary to the lateral abdominal wall
suspensory ligament of the ovary

What ligament runs from the uterine horns to the labia majora and where does it pass
Round ligament, passing through the inguinal canal
WHat embryonically is the round ligament a remnant of
embryonic gubernaculum
What ligament attaches the cervix to the posterior surface of the pubic symphysis
Pubocervical ligament
What ligament extends from the lateral aspect of the uterus to the lateral pelvic wall
Broad ligament
complete the blanks




