GI Flashcards
Branches & level of the celiac trunk
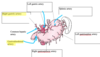
4 main veins draining the stomach
- Left Gastric vein which drains into the hepatic portal vein.
- Right Gastric vein which drains into the hepatic portal vein.
- Left gastro-omental vein which drains first to the splenic vein then to the hepatic portal vein.
- Right Gastro-omental vein which drains first to the superior mesenteric vein then to the hepatic portal vein
what veins join to form the hepatic portal vein
inferior & superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein

what two structures come together at the ampulla of vater

Common bile duct
Main pancreatic duct

What is the sphincter that controls the Ampulla of Vater?
The sphincter of oddi


Blood supply of jejunum and ilium
Where do the veins surrounding the jejunum and ileum drain to?
Lymph drainage
Superior mesenteric artery
Superior mesenteric vein. This unites with the splenic vein at the neck of the pancreas to form the hepatic portal vein.
Superior mesenteric lymph modes-Pre-aortic nodes at L1
large intestine


How is the large intestine peritonised?
Caecum: intraperitoneal
Ascending Colon: Retroperitoneal
Transverse Colon: Intraperitoneal
Descending Colon: Retroperitoneal
Sigmoid Colon: intraperitoneal
large intestine labelled


What two structures open into the caecum
terminal ilium and the ascending colon
What is McBurney’s point and why is it clinically useful?
Mcburneys point is a point that lies 1/3 of the distance laterally on a line drawn from the umbilicus to the right anterior superior iliac spine
Tenderness of McBurney’s point can be caused by acute appendicitis.

Colon arterial & venous supply


rectum arterial & venous supply


lobes of the liver


Round ligament of liver (also called as ligamentum teres) is the remnant of which embryological structure
what seperates the right and left lobes of the liver
Umbilical vein
What is the porta hepatis
The hilum of the liver, through which all the neurovascular structures (except hepatic veins) and hepatic ducts enter or leave the liver
structures entering/leaving:
Hepatic artery
Portal vein
Lymphatic vessels
Extrahepatic bile duct
Right and left hepatic ducts

structures in the portal triad
Portal vein
Hepatic artery
bile duct

label the biliary system


what is the function of bile
- Carry waste away
- Break down fats during digestion


