MSK cadavers lower limb Flashcards
label the pelvis diagram


venous drainage of the lower limb


what does the greater and lesser saphenous vein drain into and where do they ascend next to
greater= femoral vein
where do lymphatics of the great and lesser saphenous vein drain
great saphenous vein: Superficial inguinal nodes
small saphenous vein: popliteal lymph nodes
What do the following ligaments prevent:
- ilio-femoral
- pubofemoral
Ilio-femoral: hyperextension
Pubofemoral: hyperabduction


name this ligament

ischiofemoral ligamen- is the weakest, hence why posterior hip locations are most common
label this diagram

(anatomy tv cadavers)

Insersion & innervation for iliopsoas
Lesser trochanter of the femur
innervation= femoral n
label this diagram


what is the arterial supply to the hip
medial and alteral circumflex femoral arteries, branches of the profunda femoris artery
(mainly medial circumflex artery)
label this image: hip lateral/external rotators

1) Piriformis
2) Obturator Internus
4) Superior and Inferior Gamelli
5) Quadratus Femoris

which muscles are involved in internal rotation of hip & what is their insertion?
Gluteus medius & minimus
Insersion = Greater troachanter
Tensor fascia Lata - iliotibial tract
To which part of the tibia does the pattelor tensdon insert?
tibial tubercle
Function, insersion & innervation of the quadriceps
Rectus femoris= Flexion of hip & extension of knee
Vastus lateralis, medialis & intermedius = extension of the knee
femoral nerve (L2-4)
insertion point= quadriceps tendon, proximal to patella. this then continues as the patellar tendon, distal to the pattela, which inserts into the anterior tibia- tibial tuberosity
name this structure & its contents
where do the contents of this structure enter after leaving the canal.

Adductor canal
Contents= Femoral artery, femoral vein, nerve to the vastus medialis and saphenous nerve (branch of femoral nerve)
ends at the adductor hiatus
Where do the contents of this structure enter after leaving the adductor canal
Enter the popliteal fossa, after which the femoral artery & vein become the popliteal artery & vein
The adductor canal serves as a passageway for structures moving between the anterior thigh and posterior leg.
label the diagram


how do you surface landmark the femoral artery
Midinguinal point, between Superior Iliac Spine and pubic symphysis
what are the contents of the femoral canal
Fat & loose connective tissue
lymphatic vessels & deep lymph nodes
where can a femoral hernia most commonly occur
femoral ring- weak area of anterior abdominal wall- superior rounded opening of femoral canal
more common in females
which two important veins drain into the femoral vein in the femoral triangle
profunda femoris and the greater sahenous vein
What are the medial rotators of the hip joint?
tensor fasciae latae, gluteus minimus and gluteus medius
What are the lateral rotators of the hip joint?
Obturator externus & internus
Piriformis
Gemelli
Quadratur femoris
Gluteus maximus
Does the femoral nerve enter the femoral triangle medial or lateral to femoral vessels?
Lateral

nerve roots of the femoral and obturator nerve and their functions
L2, 3 & 4
obturator nerve innervates medial compartemnt of thigh (adductor muscles, except posterior part of adductor magnus)
femoral nerve innervates flexor muscles/anterior thigh compartment

what are the contents of the femoral sheath
Femoral artery, femoral vein & femoral canal
What are the ventral roots of the lumbar plexus?
L1-L4

What muscle is the adductor hiatus present in
Adductor magnus
Nerve roots of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve and its function
L2 & 3
supplies the skin of the lateral thigh

label the diagram of the lumbar plexus


what is the sensory function of the obturator nerve
Supplies the skin of the middle part of the medial thigh.



motor and sensory functions of the femoral nerve
Motor functions: Innervates the anterior thigh muscles that flex the hip joint (pectineus, iliacus, sartorius) and extend the knee (quadriceps femoris: rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and vastus intermedius),
Sensory functions: Supplies cutaneous branches to the anteromedial thigh (anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve) and the medial side of the leg and foot (saphenous nerve).

Listed below are muscles located within the thigh – which one is innervated by the femoral nerve?


Below is an illustration of the cutaneous innervation of the lower limb. Which label corresponds to an area innervated by a branch of the femoral nerve?

C’ corresponds to the anterior cutaneous branches - derived from the anterior division of the femoral nerve. They supply the skin of the anteromedial thigh.
What muscles attach onto the pes anserinus on medial aspect of tibia?
Sartorius, gracillis and semitendinosus

Label this diagram

A= Pectineus
B= Femoral vein
C= Femoral artery
D= Femoral nerve
E= Iliacus
F= Sartorius
G= Rectus femoris
H= Iliotibial tract
I= Fascia latae
J= Adductor brevis
K= Adductor longus
L= Adductor magnus
M= Gracillis

What structure forms the lateral border of the adductor canal?
and the medial border?

Vastus medialis
medial border= sartorius

How to test motor function of femoral nerve
label this diagram of the pelvic girdle


Which sciatic foramen is the route for structures entering or leaving the pelvis?
Which sciatic foramen is the route for structures entering or leaving the perineum?
Lesser sciatic foramen
What two muscles attach onto the iliotibial tract, and what is its function
Gluteus maximus and tensor fasciae latae
- provides stabalisation to the lateral aspect of the knee
Function of Gluteus maximus muscle
Extension, lateral rotation, of the hip
Assists in abduction
Function of Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae
Abduction & internal rotation of hip

explain where it is safe to give intermuscular injections & why
Only in the upper lateral quadrant of the buttox
The sciatic nerve passes through the lower medial quadrant, this is so that we avoid damaging the sciatic nerve.

what are the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve & what is there functions
Tibial nerve
– Motor to the muscles of the posterior leg (calf muscles), and some of the intrinsic muscles of the foot.
- Seonsry to the skin of the posterolateral leg, lateral foot and the sole of the foot.
Common fibular nerve
– Motor to the muscles of the anterior leg, lateral leg, and the remaining intrinsic foot muscles.
- Sensory to the skin of the lateral leg and the dorsum of the foot.

Complete the sentence: The sciatic nerve leaves the pelvis and enters the gluteal region via the ______________ foramen
Greater sciatic foramen
A patient suffers iatrogenic sciatic nerve palsy following a total hip replacement. Which of the following movements will be unaffected?


Which of the following areas receives sensory innervation from the sciatic nerve or its branches?


Label this diagram of the sacral plexus


Label these muscles


What artery supplies blood to posterior muscle compartment of thigh?
profunda femoris- branch of femoral artery
what is a positive trendelenburg test
when a person with a lesion of the superior gluteal nerve is asked to stand on one leg, the pelvis descends to the unsupported side, indicating that the gluteus medius on the contralateral side is non-functioning.
What causes sciatica
Narrowing of the vertebral foramen which compressed nerve roots
Usually L5 vertebrae
Happens due to ageing decreasing flexibility of muscles, ligaments and joints
Why is the attachment of the MCL to the medial meniscus clinically important
Also, descrpibe the unhappy triad of knee injuries
It prevents the leg from extending to far inward, whilst keeping the knee stable and allowing it to rotate
A MCL rupture almost always will occur with a medial meniscus injury and an anterior crusciate ligament tear- unhappy triad
Why do ACL injuries cause major consequences to sportsmen
ACL injury or tear automatically means a long time out of playing sport.
The ACL is a vital component in providing stability to the knee joint, preventing the femur from sliding on the tibia.
After repair due to the poor blood supply to the ACL, it can take a long time to heal.
Although both cruciate ligaments can be damaged, a PCL tear/rupture is less common due to the force required by a direct blow on the tibia to cause injury, compared to the twisting decelerating motions required to disrupt the ACL
PCL ligament injury i.e. A man is an unrestrained passenger in the front seat of a car that strikes a utility pole. His tibia contacts the dashboard with great force.
ACL ligament injury i.e. twisting motion, sports with sudden stops/changes in direction. ACL is the weaker of the two crusciate ligaments
Function of the popliteus muscle
The popliteus muscle is a small but, nevertheless important muscle in helping release the fully extended or “locked” knee.
When flexing from a fully extended position, the muscle rotates the femur laterally on the tibia (or vice-versa), allowing for the unimpeded movement of the joint

label this diagram
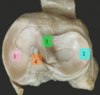
- Medial meniscus
- Lateral meniscus
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
what type of bone is the patella and what makes it move
sesamoid bone
flexion of the knee causes the patella to move inferiorly
label the bursae of the knee joint

- subcutaneous Prepatellar bursa
- Deep infrapatellar bursa
- Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa
- suprapatellar bursa

describe the clinical significance of the suprapatellar bursa communicating with the articular cavity of the knee joint
Prevents friction between moving structures. In most people it communicates with the knee joint and so can be a useful indicator of the presence of a knee effusion (increased amount of fluid within the synovial compartment of a joint)
Label this diagram



a= biceps femoris
b= sciatic nerve
c= semitendinosus
d= semimembranosus
e= gracilis
f= iliotibial tract
g= gluteus maximus

What type of injury causes a medial ligament tear
Blow to the lateral side of an extended knee/ excessive lateral twisting of a flexed knee which distrupts MCL and coconcominantly tears/detaches the medial meniscus from the joint capsule
ACL is taught during flecion may also tear subsequent to the rupture of MCL
What type of injury injures the PCL
What is the clinical test done for a PCL tear
PCL is strong
may rupture when a person lands on the tibial tuberosity when the knee is flexed. Usually occur in conjuction with tibial or fibular ligament tears
clinical test= posterior drawer sign (free tibia slides posteriorly under the fixed femur)
function & innervation of gracillis
- flexes the knee joint
- medially rotates the leg when the knee is flexed
- weak adductor of the thigh.
Innervated by obturator nerve
Label nerve a and b

a= femoral nerve
b= Scitatic n
Origin of sartorius
Rectus femoris
Sartorius- anterior superior iliac spin
Rectus femoris - anterior inferior iliac spine
Distil attachment for semimembranosus
Medial condyl of tibia

Proximal attachment for semi-membranosus and semi-tendinosus and biceps femoris long head
(hamstrings)
Ischial tuberosity
Hamstrings + adductor magnus isnert here

What are the main hip abductors & where is their insertion
Gluteus minimus, gluteus medius and piriformis
insertion at the greater trochanter of the femur
What actions are produced by the piriformis muscle
Lateral rotation & extension of the hip & abduction of hip when femur is flexed
What is the femoral sheath made of?
Connective tissue
Does the femoral nerve pass deep or superficial to the inguinal ligament?
The femoral nerve passes deep to the inguinal ligament
What arteries exposure and ligation in the adductor’s canal can be used for treating patients with aneurysm of popliteal artery
The femoral artery
From what muscle does the lumbar plexus emerge
Psoas major muscle
What are the nerve roots of the Ilioinguinal, Iliohypogastric & genitofemoral
L1-L2
What is the name of the deep fascia of the thigh
The fascia lata
This is thickened laterally, to form the iliotibial tract.
Which muscle does the sacral plexus lie on?
The piriformis
The sacral plexus is formed from…
The anterior rami of L4&5 and S1-4
What foramen does the sciatic nerve travel through
The greater sciatic foramen
Where does the sciatic nerve divide & what does it divide into
The apex of the popliteal fossa
Into the tibial and the common fibular nerve
where is the most common site of sciatica
L5 vertebrae
Compression of the nerve roots in this region can cause a syndrome called sciatica – where the proximal nerve compression can cause an ‘electric shock’ type pain passing from the back down to the toes (the dermatomal area supplied by the sciatic nerve).
Which is the most important muscle which helps to stabilize the knee joint?
Quadriceps
Label

Bones
- Patella 2. Fibula 3. Tibia 4. Femur
Articular Surfaces
a. Medial femoral condyle b. Lateral femoral condyle c. Lateral tibial condyle
d. Medial tibial condyle e. Tibial tuberosity
Complete


Which bursae communicates with the knee joint
The suprapatellar bursa allows for movement of the quadriceps tendon over the distal end of the femur.
In about 85% of individuals, this bursa communicates with the knee joint.
What else might be damaged with an anterior crusciate ligament injury
Medial meniscus & medial collateral ligament


