Histology Flashcards
What kind of epithelium lines the urinary bladder and ureter?
Urothelium or transitional epithelium
The advantage of this is that it is able to stretch significantly to accommodate large volumes of urine. The transitional epithelium also provides protection to the underlying tissues from acidic or alkaline urine.

What organ is this showing

The kidney
Destuinguish the cortex vs the medulla of the kidney

Cortex is full of globules whereas, the medulla is more tubule

Label this diagram

Renal corpuscle
Glomeruli have a side next to blood vessels- vascular side
And then one going into nephron- urinary side

Label this diagram


Label this diagram of the renal corpuscle


Complete this diagram
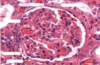

Epithelium of the proximal convoluted tubule
Simple tall cuboidal epithelium, with a brush border (microvilli).
Epithelium of the loop of henle
simple squamous epithelium
Epithelium of the distil convuluted tubule
Cuboidal, with few microvilli
Label this diagram


Which part of the kidney is this?

Kidney: Cortex
Renal corpuscles (Bowman’s capsule: simple squamous epithelium)
Proximal convoluted tubules (cuboidal+ microvilli)
Distal convoluted tubules (cuboidal)
Collecting tubule (cuboidal)
What does this show & describe its epithelium

The ureter
Transitional epithelium
Star shaped lumen
Inner longitudinal smooth muscle (SM)
Outer circular SM
What organ does this show & describe its epithelium

Bladder
Transitional epithelium
Inner longitudinal (IL) smooth muscle (SM)
Middle circular(MC) SM
Outer longitudinal (OL) SM
Lable


Label


Label


Lable


How are hormones stored in a thyroid gland?
Hormones are stored in cavities, surrounded by secretory cells. These make up a follicle. Within the cavity of the follicle, the hormone is bound to a glycoprotein and is called as colloid. During secretion the hormone is re-absorbed from the cavity, and then released into the surrounding interstitial spaces.
Fill in the blanks
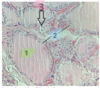
1 = Thyroid follicle: follicular cells + colloid
Thyroid cell- produce thyroid hormones & their surface contains TSH receptors
2 = Follicular epithelial cells
3 = Parafollicular (C cells)- secrete calcitonin - takes calcium & puts it back into the blood
NB. parafollicular cells arise, separately from the thyroid and migrate into it during development of the embryo
PARAFOLICULAR CELLS are secreted from the THYROID GLAND (not the parathyroid gland, this secretes parathyroid hormones which increase calcium levels)

What type of epithelium do you see lining the follicle?
Simple, non-stratified, cuboidal epithelial cell (found in all endocrine glands)
What hormone do the C cells and the thyroid gland secrete?
C cells= calcitonin
Thyroid gland = T3&T4
Arterial supply & venous drainage of the parathyroid glands
Arterial supply to both superior and inferior parathyroids is predominantly from the inferior thyroid arteries.
Venous drainage is via the veins draining the thyroid to the internal jugular veins.
What gland is shown here

Parathyroid gland
Label this diagram of a parathyroid gland

- chief cells- purple, chief (more of them)
- Oxyphill cells- red/pink
What is secreted by the parathyroid gland, from which cell & what is its function
Chief cells- secrete parathyroid hormone
- -* plays a key role in the regulation of calcium levels in the blood; removes calcium from bones, to enter the blood
- What cells does this hormone act upon and what is their subsequent action? Cells of the bone & the kidney-* removes calcium from bones, to enter the blood
Parathyroid hormone takes calcium from bones, putting it into the blood
Calcitonin takes calcium from the blood and puts it into the bones
Complete the labels

Parathyroid hormone
A= Fibrous capsule
B= Adipose tissue
C= chief cells (purple)
D= Oxyphill cells

Name this gland and name the arrows

Adrenal gland

What are the 3 main hormone types secreted from each of the 3 zones
- Zona glomerulosa -> mineral corticoids- like globules*
- Zona fasciculata ->glucocorticoids – like canes of sugar*
- Zona reticularis -> androgens (sex hormones)- big collection; messy, circles*
Complete the diagram


What organ is this?

Pancreas

Label this diagram


complete the diagram


what organ is this

the liver
complete the diagram & what organ is this
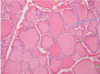
Thyroid gland

What cells form the boundary of a follicle
Simple cuboidal epithelium

What gland is this & fill in the blanks

Parathyroid gland

What gland is this from

anterior pituitary: 3 types of cells; basophils, acidophils & chromophobes
What gland is this from

Chief cells, oxyphils & fat globules
Pituitary gland
complete the diagram

- Anterior pituitary
- Posterior pituitary
- Pituitary stalk
What is this gland and fill in the blanks

anterior pituitary
clumps of cells (like parathyroid)
pink/red= acidophil cells
purple/blue= basophil cells (basic e.g. alkali)
Also have pale-staining cells- chromophobe, resting, not actually secreting hormones

Name this gland and fill in the blanks

Suprarenal gland

Name this gland & fill in the blanks


Complete the labels & name the gland

Suprarenal gland

Label & what gland is this

Adrenal gland

Label this and name the organ

Pancreas

label

Cortex
glomerulosa
fasiculata
reticularis
medulla
- note the medulla contains medullary veins


