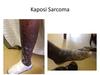
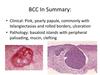
MSCT Week 6: Neoplasms of the Skin Flashcards
Question 1

This is a common benign proliferation of keratinocytes Seborrheic keratosis
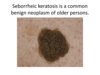
Seborrheic keratosis Clinical Description
5 listed
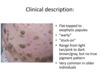
Sign of Leser-Trelat
Step 1

Identify

Seborrheic Keratosis
- well demarcated
- mushroom epidermis
- horn cysts(spaces in the tumor filled with keratin)
- benign
- regular looking cells
- wouldn’t see a lot of mitosis
A benign proliferation of keratinocytes
Seborrheic keratosis

What is this?

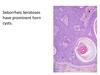
Mitoses and atypia in seborrheic keratosis

What is this depicting?
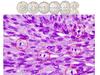
Mitoses and atypia
Question 2
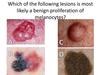
C is correct
A is Basal cell Carcinoma
B is a Melanoma
C is a benign Nemus
D Seborrheic Keratosis
Nevus definition
What does nevus mean?
What is a Nevi?

Nevus clinical characteristics

Benign Pigmented Lesions AKA
Nevus or Naevi
Identify


Identify
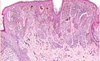
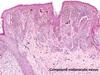
Identify
symmetrical
melanocytes get smaller with depth
would not expect to see atypia or mitoses
in a benign nevus

Benign Nevus Histology Characteristics
6 listed


Benign Naevia melanocytes get smaller as you go down

Question 3
Which of the following lesions is of most concer?

Correct Answer: A
A Melanoma
B Seborrheic Keratosis
C & D Benign Melanocytic Lesions
ABCDE of Melanoma
Subtypes of Melanoma
4 listed
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma
- Nodular Melanoma
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
- Lentig maligna Melanoma

Lentigo Maligna Melanoma

Acral Lentigous Melanoma

Nodular Melanoma
more deadly spreads vertically
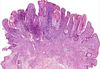
Superficial Spreading Melanoma


- Melanoma
- nests of melanocytes (should be in basal layer but are extending up through the epidermis)
- Atypical big melanocytes
- Mitoses
- Pagetoid spread of melanocytes (upward spread of melanocytes
- melanocytes dont get smaller deeper in the dermis

Melanoma
Mitoses in melanoma


Histologic Features of Melanoma vs Naevi

Question 4

- Depth of invasion
- Tumor thickness is the most important feature of melanoma
- 10 year survival decreases with melanoma depth