MSCT Week 4: Musculoskeletal Embryology Flashcards
When does embryo folding occur?
occurs between 18-24 days after fertilization
What is embryo folding?
the Trilaminar embryo undergoes cranial - caudal and lateral folding to form the tube within a tube body plan
Identify process


As a result of embryonic folding the top of the yolk sac becomes?
what about the mesoderm surrounding this new structure?
the gut tube which is suspended within the tube of the body by mesoderm surrounding it which becomes the wall of the gut (connective tissue, smooth muscle, blood vessels)
As a result of embryonic folding, the endoderm becomes?
Epithelial lining of the gut
As a result of embryonic folding, the ectoderm becomes?
epithelium of the skin
As a result of embryonic folding, the mesoderm becomes?
becomes the components of the body wall and limbs (bone, connective tissue, smooth muscle, blood vessels)
Identify
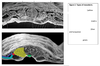
Lateral Plate Mesoderm is subdivided into?
- Somatic Mesoderm
- Splanchnic Mesoderm
Somatic mesoderm is in contact with?
The ectoderm
Splanchnic mesoderm is in contact with?
endoderm
After folding of the embryo, splanchnic mesoderm…
surrounds the gut tube and forms the wall of the gut
Splancha means?
Viscera or guts
Splancha Mesoderm AKA
Visceral Mesoderm
After embryoinic folding, the somatic mesoderm…
forms components of the body wall and limbs
Somatic mesoderm forms
3 listed
- connective tissue and smooth muscle in the body wall and limbs
- components of the body wall and limbs
- appendicular skeleton (bones of the limbs)
Paraxial mesoderm forms
2 listed
- the axial skeleton (vetebral column and ribs)
- skeletal muscle in the body wall and limbs
Limbs develop from
lateral plate mesoderm
When do Limbs develop?
4-8 weeks
How do limbs start developing?
Initiated by embryonic induction
Intermediate mesoderm produces FGF8
FGF8 induces the overlying ectoderm to form the apical ectodermal ridge
The AER is thickened ectoderm that maintains the proliferation of underlying somatic mesoderm cells (the progress zone) through production of FGF4 and FGF8; it promotes outgrowth of the limb bud along the proximal/distal axis (shoulder to fingers)
How limbs begin to develop
- Intermediate mesoderm produces FGF8
- FGF8 induces the overlying ectoderm to form the apical ectodermal ridge
- The AER is thickened ectoderm that maintains the proliferation of underlying somatic mesoderm cells (the progress zone) through production of FGF4 and FGF8; it promotes outgrowth of the limb bud along the proximal/distal axis (shoulder to fingers)
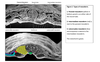
Limb development diagram

Progress zone

Process of embryonic induction of limbs
Lateral plate mesoderm is induced between weeks 4-8
intermediate mesoderm produces FGF8
FGF8 induces the lateral plate mesoderm to produce FGF10
FGF10 induces the overlying ectoderm to form the Apical Epidermal Ridge (AER)
The AER is thickened ectoderm that maintains the proliferation of underlying somatic mesoderm cells (the progress zone) through the production of FGF4 and FGF8; it promotes outgrowth of the limb bud along the proximal/distal axis (shoulder to fingers)

Experimental removal of the AER results in? & interpretation
Truncation of the limb (meromelia or amelia)
this confirmed a role for the AER in regulating the development of the proximal/distal axis of the limb
it demonstrated that the cells of the limb bud differentiate in a proximal to distal pattern

Selective loss of the AER facilitates the formation of?
the digits by reducing the amount of FGF in the region of the interdigital spaces, leading to cell death (apoptosis) and cessation of cell proliferation in these areas
Selective loss of AER causes?

Zone of Polaraizing Activity description
is a specialized mass of cells in the base of the limb bud that regulates development along the cranial (anterior)/caudal (posterior) axis
The ZPA is induced by? and does what?
- FGF8 from the AER and helps to maintain the structure and function of the AER
- through the production of retinoic acid (vitamin A)
- which initiates the expression of Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) (a secreted factor that regulates the anteroposterior axis

Shh AKA
Sonic Hedgehog
ZPA AKA
Zone of Polarizing Activity
Shh establishes
a gradient of homeobox genes (Hox) gene expression across the developing limb
Homeobox genes description
Hox genes are transcription factors that define the pattern of differentiation from thumb to little finger
Transplantation of the ZPA or implantation of a Shh bead to the anterior limb bud results in?
the formation of extra digits: polydactyly

Bone develops by one of two mechanisms these mechanisms are?
- Intramembranous Ossification
- Endochondral Ossification
Intramembranous Ossification
Formation of the flat bones of the skull and bones of the face
Mesenchyme is loosely organized and mainly mesodermal embryonic tissue that develops into connective and skeletal tissues, including blood and lymph
Mesenchyme cells differentiate into osteoblasts and produce primary or woven bone (irregularly arranged collagen fibers)
Woven bone is remodeled to lamellar bone (parallel alignment of collagen into sheets)
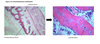
Endochondral ossification
- Formation of long bones, vertebral column, pelvis, sternum, and skull base
- Mesenchyme differentiates into chondroblasts, which produce a cartilage model
- The cartilage becomes vascularized and is replaced by bone matrix
- Cartilage remains the surface of the epiphysis as the articular cartilage and in between the epiphysis and diaphysis as the epiphyseal (growth) plate, which regulates growth in length

Epiphyseal plate and long bone growth
- a cartilaginous structure responsible for the growth in length of long bones
- proliferation occurs at the epiphyseal side of the plate and replacement by bone occurs at the diaphyseal side
- The bone continues to grow as long as the rate of cell devision equals the rate of cell death and ossification
- Active until about the 20th year of life

Paraxial mesoderm becomes organized into?
Segments called somitomeres
Somitomeres form in a?
craniocaudal sequence
Somitomeres of the head and neck
somitomeres 1-7 contribute mesoderm to the head and neck
Somitomeres not of the head and neck
condense into somites
Somites differentiate into?
- Sclerotome
- myotome
- dermatome
Somitogenesis

Each myotome splints into a?
Dorsal epimere and a ventral hypomere
Epimere develops into
intrinsic back muscles
Hypomere develops into?
limb and body wall structures
Dorsal and ventral condensation
are hypomere cells that migrate into the limb bud to become skeletal muscles of the limbs
Dorsal Condensation gives rise to?
Extensor Muscles
Ventral Condensation gives rise to?
Flexor Muscles
Dorsal and ventral condensation figure

Differentiation of somitic cells into skeletal muscle begins when?
the transcription factors myf -5 and Pax-3 begin a cascade of muscle-specific transcription factor and muscle-specific gene expression The cells that first express Myf-5 and Pax-3 are myogenic progenitor cells
The cells that first express Myf-5 and Pax-3 are?
myogenic progenitor cells
Myogenic Progenitor Cells
The cells that first express Myf-5 and Pax-3 are the myogenic progenitor cells
Name the process and transcription factors involved in skeletal muscle differentiation

Axons of motor neurons enter the limb bud during
the 5th week of development and grow into the dorsal and ventral muscle masses
Axons of sensory neurons enter the limb bud after…
the motor axons and supply segmental regions of the skin referred to as dermatomes
Dermatome description
is an area of skin innervated by a single spinal nerve and its dorsal root ganglion
dermatome formation figure

Limb defets and prevalence
6/10,000 live births and mainly hereditary
Weeks of development most susceptible to teratogen induce limb malformation
4-5th weeks
Categories of limb defects
3 listed
- Reduction defects
- Duplication defects
- Dysplasia
Reduction defects Description
part of (meromelia) or the entire limb (amelia) is missing
Phocomelia description
a type of reduction defect when hands or feet project directly from the shoulder or hip
Thalidomide
- is a teratogen prescribed to pregnant women for nausea between 1957 and 1962
- Thalidomide causes meromelia (5-wk) and amelia (4 wk) it defined the critical period of limb development (24-36 days)
- Mechanism is disruption of AER

Defect type

Duplication Defects
- Extra limb elements are present
- Mechanism is duplication of the ZPA
*
Polydactyly
Shh is ectopically expressed in anterior limb bud (as well as the usual posterior expression) can be inherited or teratogen induced

Dysplasia Description and Mechanism
- Malformation of part of the limb
- Mechanism is that the AER doesn’t break down between digits, so apoptosis doesn’t occur normally when forming digits
Syndactyly
Abnormal fusion of digits resulting from reduced apoptosis



