MSCT Week 5: Acne and Diseases of the Follicle Flashcards
Follicle Definition
the structure that produces the hair shaft
Basic types of hair shafts
- Vellus hairs
- Terminal hairs
Question 1

~100,000 hair follicles on the scalp
Question 2

~100 hairs
Facts about hair

Areas of skin without hairs
- Glaborous skin
- palms and volar surfaces of fingers
- soles of feet
- mucosal surfaces
Facts about hair loss

hair follicles are immunologically privledged sites

Hair follicle cycle of growth

Hair follicle cycle
Anagen & Catagen phases

Hair follicle cycle
Telogen & Exogen phases

Anagen phase
- the production phase of the follicle
- Estrogens prolong
- Androgens increase growth rate in more dependent follicles
- 85-90% of scalp follicles are in this phase at any one time
Catagen Phase
- Regression of follicle
- less than 1% of scalp follicles at any one time
- a hair follicle in this phase can spend 2-3 weeks regressing
Telogen Phase
Resting phase of follicle
10-15% of scalp follicles at any one time are in this phase
A follicle resting in this phase can retain a hair shaft for up to 3 months
Exogen Phase
- Shedding of the hair shaft
- actually occurs in early part of anagen phase as the follicle starts to regenerate and grow a new hair shaft
- Involves not only a mechanical displacement of old hair shaft by new hair shaft but a proteolytic process freeing the shaft from the follicle
- 100-150 hairs shed per day
Question 3

Around 20 cycles per lifetime
Question 4

80-85%
Acne epidemiology/associations/long-term effects

Acne Who is more likely to get acne?

Question 5

Blockage of the pilosebaceous unit with keratin debris
Acne Pathogenesis
4 steps

Acne Causative agent
Propionibacterium acnes
Question 6

All of the above
Acne Triggers
6 listed

Acne Severity
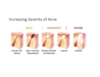
Acne types
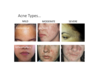
Acne Conglobata & Fulminans Descriptions
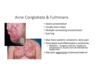
Acne Conglobata & Fulminans Treatment
Corticosteroids & Isotretinoin
Acne Fulminans description
Conglobata so severe that it elicits a systemic inflammatory response
Isotretinoin & Corticosteroids
Categorizing Acne for Treatment

Associated Inflammatory Symptoms of Acne
PAPA(SH): Pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma, gangrenosum, (cystic) Acne & Hidradenitis Suppuritiva
Comedonal Acne Treatment
- Topical Retinoid (BEST)
- Salicylic Acid
Mild Inflammatory or Mixed Acne Treatment
Combo topical therapy
- BP
- Antibiotic
- Retinoid
Moderate inflammatory or Mixed Treatment
Combo Topical Therapy
BP
Antibiotic
Retinoid
+
Oral antibiotic
Severe inflammatory or Mixed Treatment
4 listed
Combo Topical Therapy
Benzoyl Peroxide
Antibiotic
Retinoid
+
Consider hormonal or isotretinoin
Hormonal Acne Treatment
3 listed
OCP (oral Contraceptive Pills)
Spironolactone (BP med but blocks androgens)
+/-
Topicals
Nodulocystic Acne Treatment
1 listed
Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin is a
Oral retinoid
Question 7

Topical Retinoid Tretinoin
Question 8

Topical Antibiotics and or oral antibiotics
Treating Acne in Adolescence

Postinflammatory Dyspigmentation

Acne Scarring

Question 9

Neonatal cephalic pustulosis (malessezia) Acne mimic
Reassure
No treatment required

Infantile and Childhood Acne
Presents as?
Cause?
Scar?
Treat how?

Childhood Acne
Diagnosis?
Precocious puberty?
How to test?

Hidradenitis Suppuritiva
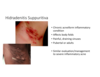
Question 10

- Folliculitis
- Hot Tub Folliculitis (Pseudomonas)
- Recent Hot Tub Exposure

Folliculitis

Other Folliculitis Examples

Question 11

80-90%
Subtypes of Alopecia
7 listed

Question 12

alopecia areata and Hypothyroidism is related
Lichen Planus Pilaris Pathology
Scar and destroy hair follicles
Alopecia Areata is related to…
Hypothyroidism
Alopecia Areata

Alopecia Areata Increases risk for
- autoimmune thyroid problems
- vitiligo
- Pernicious Anemia (immune system kills B12 absorbing cells) was fatal before injections
Alopecia Areata Scar formation
Non-scarring
Androgenic Alopecia in men and women

Trichotillomania

Question 13

Anagen
anagen vs telogen effluvium



