MSCT Week 4: Lower Limb Flashcards
Major Functions of the Lower Limb
2 listed
- Support the body weight
- Move the body weight
Gluteal Region
between the iliac crest and the gluteal fold that defines the lower limit of the buttocks
Each of the two pelvic bones of the gluteal region is formed by?
childhood fusion of 3 bones
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Pubis

Anterior Thigh boundaries
between the inguinal ligament and the knee joint

Posterior Thigh Boundaries
Between the Gluteal Fold and the Knee
Thigh bone is?
Femur
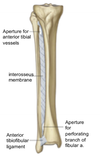
Leg Boundaries
between the knee and ankle joints
The bones of the leg?
- Tibia
- Fibula
Bones of the foot
3 listed
- Tarsals
- metatarsals
- phalanges
How is muscular energy reduced to maintain a standing position
The ligaments of the hip and knee joints and the shapes of the articular surfaces “locks” the joints in position to reduce the muscular energy required to maintain a standing position
Identify Anatomical Parts


Identify


Identify Movements


The Hip Joint Description & Function
2 parts
- a synovial joint between the head of the femur and cup-shaped acetabulum on the lateral surface of the pelvic bone
- it is a multi-axial ball and socket joint designed for stability and weight bearing
Acetabular Labrum Description & Function
2 listed
- the fibrocartilaginous collar on the rim of the acetabulum on the lateral surface of the pelvic bone
- it deepens the acetabulum and prevents the femoral head from moving inferiorly
Acetabular labral tears

Ligament of the head of the femur Description
connective tissue that attaches the head of the femur to the acetabular fossa
The femoral head is supplied by?
A branch of the obturator artery supplies femoral head through a branch inside the head of the femur ligament
The synovial membrane around the hip joint attaches to?
The articular surfaces of the femur and acetabulum
Identify


Identify


Fibrous capsule or membrane of the hip joint Description & Function
- surrounds the synovial membrane
- holds the femoral neck in the acetabulum
How many ligaments around the fibrous capsule of the hip? what are they called?
3
- Iliofemoral ligament
- Pubofemoral ligament
- Ischiofemoral ligament
Iliofemoral Ligament location
Anterior