MSCT Week 1: Back and Spinal Cord Flashcards
The vertebral column AKA
Spine
The Vertebral Column has how many vertebrae
33 Vertebrae
How many Cervical Vertebrae?
7
How many Thoracic Vertebrae?
12
How many Lumbar Vertebrae?
5
How many Sacral Vertebrae?
5
How many coccygeal Vertebrae?
3-5
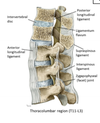
Surface Landmarks of the back
3 Listed
- vertebrae prominens
- scapula
- iliac crests
Useful landmarks for a lumbar puncture?
A horizontal line between the Iliac Crests passes through the spinous process of L4 and the L4-L5 disc
Identify


Natural Curvatures of the Vertebral column
- Kyphotic curvatures
- Lordotic curvatures
Kyphotic Curvatures
- Thoracic
- Sacral
The primary curvatures
- Kyphotic Curvatures: thoracic and sacral regions
The secondary curvatures
- Lordotic curvatures: Lumbar and Cervical regions
which curvatures are postnatal?
secondary curvatures
Lordotic curvatures: cervical and lumbar
Which spinal curvatures are present from birth?
- Primary curvatures
- Thoracic and sacral Kyphotic curvatures
Kyphosis is?
excessive forward curvature (flexion) of the thoracic spine. It may be congenital or posture related but it is usually due to a collapse of the vertebral bodies
Lordosis is?
excessive inward curvature (extension) of the lumbar spine that can develop temporarily during pregnancy, pathology, or excess weight
Scoliosis is?
an abnormal lateral curvature of the thoracic or lumbar spine. it may be congenital, idiopathic or caused by diseases such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy
Idiopathic definition
relating to or denoting any disease or condition that arises spontaneously or for which the cause is unknown.
Congenital definition
(especially of a disease or physical abnormality) present from birth.
Identify


Identify?

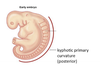
The secondary curvatures develop after _______ when …
- Birth
- infants learn to hold their head up and walk