MSCT Week 6: Cutaneous Signs of Systemic Disease Flashcards
Skin findings and systemic disease
Question 1

Acanthosis Nigricans
Screen for Diabetes
Acanthosis Nigricans Clinical Features

Acanthosis Nigricans most commonly found where on the body?
- Posterior neck fold
- axillae most common
Acanthosis Nigricans is a sign of
Insulin Resistance
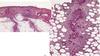
Identify features of histology

acanthosis
IDGF-1 causes thickening and overdevelopment of the epidermis
Acanthosis Nigricans should screen for diabetes mellitus by?
glucose tolerance test
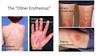
Malignant Acanthosis Nigricans Clinical Features

“Tripe Palms”
Think Malignant Acanthosis Nigricans
Strange manifestations of Malignant Acanthosis Nigricans
thickened velvety plaques

Diabetes and Skin

Diabetes and Skin: Diabetic Dermopathy Clinical Features
deposition of glycosylated proteins in the skin

Identify

Acanthosis Nigricans
Associations with Acanthosis Nigricans
no collagen vascular disease
some hereditary some syndromic
some insulin resistance

Why does this occur?

Diabetic Neuropathy
don’t realize that they are damaging their feet because they have lost sensation
What is this?

- Scleroderma from poorly controlled diabetes or from other disorders but diabetes is most common
- typically asymptomatic, infiltration of the skin (usually in the back) with mucin
- thickened hardened, can be pruritic
What is this?

Bullosis Diabeticorum
- non-infectious
- not-inflammed
- sterile blisters filled with water on the lower limbs and feet
What is this?

Necrobiosis Lipoidica
- typically occurs on the anterior shins
- the atrophic skin where vessels can be seen underneath
- yellowish hue
- if ulcerate are difficult to treat
What is this

Acquired Perforating Disorder
- common for diabetics on renal dialysis
- build up of abnormal collagen and elastin in the skin and the body tries to eliminate it
- epidermis tries to envelope abnormal collagen
- transepidermal elimination
- associated with renal failure
Acquired Perforating Disorder is associated with?
Renal failure
What is this?

Eruptive Xanthomas
- grouped yellow tender papules
- firm
- extensor surfaces and buttocks
- happen when cholesterol and triglycerides are very high
- This is an emergency
- as cholesterol is brought down they resolve
Question

Malignancy
This is called the sign of leser-Trelat
a large number of seborrheic keratoses suddenly appearing responding to same growth factor as does the malignancy

Sign of Leser-Trelat

Identify Histological Features

Pseudocysts
thickened epidermis
well defined basal layer
comedo blackhead like openings