Lung bacterial/viral/mycotic infections Flashcards
Histoplasmosis
Where is it seen? Who gets it? Presentation? Pathology

- Midwest (Ohio/Tennessee valley) - Carried by dung of starlings and bats – often seen in cave explorers, spelunkers, chicken farmers.
- Presentation: non-productive cough; can simulate TB: coin lesions, consolidations, miliary spread, and cavitation >> marked dystrophic calcification of granulomas (most common cause of calcifications in the spleen)
- Pathology: granulomatous inflammation with caseous necrosis; yeast form in macrophages
- Treatment: usually self-limiting; amphotericin B or itraconazole

Cryptococcus neoformans
Describe it. Found where? Presentation? Treatment?

- Budding yeast w/ narrow-based buds surrounded by thick capsule
- Found in pigeon excreta
- Primary lung disease (40%): granulomatous inflammation with caseation
- Treatment: fluconazole
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Describe it. Seen where? in who? Presentation? Pathology?
Treatment

- Yeast have broad-based buds and nuclei
- Occurs in Great Lakes region, central, & southeastern US
- Most often associated with fishing, hunting, gardening, exposure to beaver dams; male dominant
- produces skin and lung disease: skin lesions simulate squamous cell carcinoma
- Granulomatous inflammation with caseous necrosis
- Treatment: liposomal amphotericin B

Cocciodioidomycosis
Describe it. Where do you see it? how do you get it? Presentation? Pathology? Treatment?

- spherules with endospores in tissues
- Contracted by inhaling arthrospores in dust (increased after earthquakes) in the southwest (valley fever)
- Flu-like symptoms and erythema nodosum (painful nodules on lower legs; inflammation of subcutaneous fat)
- Granulomatous inflamation with caseous necrosis
- Treatment: self limited; if severe, itracoazole or fluconazole

Asperigillus fumigatus
Describe it. Presentations/ Pathogenesis? Treatment?

- Fruiting body and narrow-angled (<45 degrees), branching septate hyphae
- Aspergilloma: fungus ball (CXR) develops in preexisting cavity (TB) in the lung >> massive hemoptysis
- Allergic bronchopulmonary asperigillus: type I and type III hypersensitivities; IgE increased, eosinophilia; intense inflammation of airways and mucus plugs in terminal bronchioles >> repeated attacks >> bronchiectasis and interstitial lung disease >> treat w/ corticosteroids
- Vessel invader with hemorrhagic infarctions and necrotizing bronchopneumonia
- Treatment: voriconazole

Pneumocystis jiroveci

- no ergosterol in plasma membrane
- cysts and trophozoites: cysts attach to type I pneumocytes
- primarily an OI with CD4 count< 200 (AIDS defining)- immune comprimized
- Predominantly produces pulmonary disease >> fever, dyspnea, sever hypoxemia, diffuse intra-alveolar foamy exudates with cup-shaped cysts in silver or Giesma stains; CXR shows diffuse alveolar and insterstitial infiltrates
- Treatment: TMP-SMX

Primary TB
Pathogenesis?
Features?

- from initial exposure (aerosolized MT) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- results in focal caseating necrosis in lower lung and hilar lymph nodes
- foci undergo fibrosis and calcification >> Ghon complex *subpleural
- asymptomatic +PPD
- Pathogenesis: 1st 3 weeks = bacteremia, no symptoms; > 3 weeks = cell mediated immunity (IFN-y from Th1 cells crucial for macrophage activation >> TNF release >> epithelioid histiocytes)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
a.k.a.?

It is persistent inflammation of lower airways that results in obstruction to air flow through lungs.
asthma (cats),
chronic bronchial disease

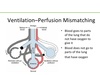
With COPD , ventilation and perfusion are _______ in lungs leading to chronic ______. Air flow is obstructed by thickening of bronchial walls due to edema or _____ _____. Excessive _______ mucus production. _____ of bronchial smooth muscle and interstitial fibrosis. It is most often reported in cats as ____ ____ and in mature ___-___ dogs.
mismatched
hypoxemia
cellular infiltratoin
endobronchial
Spasticity
feline asthma and small-breed
Cats affected with COPD experience panting, gagging, adn periodic episodes of wheezing and labored ______; cyanosis and syncope occur with _____ cases. Dogs exhibit dry, harsh coughing (it may be worse at ____ or after excitement), wheezing, decreased exercise tolerance, cyanosis and labored _____. Cough may end with _____.

expiration
severe
night
expiration
gagging

The most common lung pattern of COPD is a _____ pattern. Severe cases present with ______ and may progress to emphysema. Lungs are often _____ with focal or diffuse areas of decreased opacity due to air _____ or emphysema. Bronchial occlusion with excessive mucous or exudate leads to lung lobe _____ (lobar atelectasis). The _____ _____ lung lobe is the MOST affected, especially with _____ asthma.

Bronchial
bronchiectasis
hyperinflated
trapping
collapse
RIGHT MIDDLE
feline

With COPD unstructured ______ pattern is common due to chronic inflammation and fibrosis. Intercostal muscles may _____ outward (concave) due to increased ______ effort and respiratory fatigue. Sometimes sternebrae deviate _____ due to chronic, exaggerated, _____ effort (mimics pectus excavatum). Right heart enlargement may develop due to ____ ______.

interstitial
bulge
expiratory
ventrally
expiratory
cor pulmonale- abnormal enlargement of the right side of the heart as a result of disease of the lungs or the pulmonary blood vessels.

Atelectasis is the collapse of part or all of a lung due to loss of _____ ___. It may be caused by bronchial obstruction, loss of blood supply, or inability of a lung to ______. Airay obstruction leads to atelectasis within minutes or hours, depending on the ____ of obstruction.

alveolar air
expand
degree
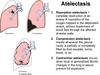
Loss of blood supply results in atelectasis within ___ hrs. Positional atelectasis occurs in the ______ (down) lung within a few minutes during anesthesia but it is reversible. Obstruction of the ____ ____ lung lobe is common in cats with asthma due to acumulation of bronchical ______. Clinical signs are related to underlying etiology and my include pain, cough, tachypenia, dyspnea, or hemoptysis.
DDFs for lung collapse?

24
dependent
right middle
exudate
Pneumonia
Pulmonary contusion/hemorrage

Pulmonary Emphysema is an abnormal increase in size of air spaces (alveoli) ____ to the terminal bronchioles. It may be focal or diffuse, congenital or aquired. Congenital lobar emphysema results in aplasia or hypoplasia of bronchiolar _____. Aquired emphysema is caused by chronic _____ lung dz that irreversibly expands alveoli or destroys alveolar ____.

distal
cartilage (reported in Pekingese, Shih Tzu, and Jack Rusell Terriers
obstructive
walls



