L46: Female Reproductive Anatomy Flashcards
What structures (as a whole) does the female reproductive system consists of? (5)
Vulva
Vagina
Uterus
Uterine tubes
Ovaries
What are ovaries?
Female gonads that are responsible for oogenesis and steroidogenesis
What does ovulation induce? (3)
- Stigma tear 2. Oocyte completes meoisis 1 3. Ovulation occurs
In the CL of the ovaries, granulosa cells are called?
Granulosa lutein cells
In the CL of ovaries, theca cells are called?
Theca lutein cells
If there is no implantation, the CL degenerates and undergoes___?
Luteolysis
If implantation occurs H from the trophoblast signals the endometrium not to relase____ so that the CL does not undergo ____
PGFa2; Luteolysis
In most mammals, CL maintains_____
entire pregnancy
PGFa2 induces _____ and CL dies due to _____
loss of blood vessles; ischemia
2 cells = 2 ______
Gonadotropins
What is unique about the wall of circular muscle of the myometrium of the uterus?
Thick
The mucosa of the peritoneum has what type of cells in the UTERUS?
Columnar epithelium
What cells make up ectocervix?
strat squa nonkert epit
What type of cells are present in the mucosa of the vagina?
Strat sqa epit
In a lactating animal, what is there less of and what is there more of?
Less stroma, more developed parenchyma
In a nonlactating animal, what is ther emore of what is there less of?
More storma, less developed parenchyma
Estrogen is associated with?
Ductal growth
Progesterone is asssociated with?
Acinar growth
Prolactin is associated with?
Milk production
What are the secretions of mammary gland?
- Colostrum 2. Milk
What is produced first after giving birth? Milk or colostrum?
Colostrum- produced shortly after birth
Features of colustrum vs milk
Colostrum: protein-rich, IgA antibodies Milk: lipid droplets, proteins, IgA
Structures/ cell of mammarly gland?
Simple column epit with smoot hmuscle cells
3 hormones associated with mammary gland?
Prolactin, progest, estrogen
What is ovulation?
The process of follicle rupture to expel the oocyte as a result of the LH prevulatory surge
What is oogenesis? What type of function?
Oocyte formation ; Exocrine function
What is steroidogenesis?
Production and release of sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone)
What is the cortex of ovaries made of (cells)? AKA what cells?
Germ cells and somatic cells (granulosa and theca cells)
What is the medulla of ovaries made of?
CT, vessels and nerves
What is this structure of? (microstructure)

Ovaries
What is this (structure) and what do the numbers indicate?

Ovarian structures
- Ovarian follicle
- CL (2a: function CL, 2b: Regressing CL)
- Corpus albicans
- Hilum
What is this structure? What do each of the colors indicate? (orange, green, red, black)

Follicle of ovaries
- Theca cells
- Granulosa cells
- Oocyte
- Estroma
What is this structure and what is it categorized under?

Primordial follicle
Recruitment, Preantral
What is this structure and what is it categorized under?

Primary follicle
Recruitment, preantral
What is this structure and what is it categorized under?

Secondary follicle
Selection, Preantral
What is this structure and what is it categorized under?

Tertiary (dominat) follicle
Selection, antral
What is this structure and what is it categorized under?

Atretic (subordinate) follicle
Antral
What is this series of pictures showing?

Ovulation
What is this picture showing?

Ovulation
What is this structure? What is it?

Corpus hemorrhagicum
Ruptured follicle fills with blood; clot forms
What is this structure? What is it?

Corpus luteum
Clot dissipate, walls collapse and theca and granulosa cells transform into luteal cells that secrete progesterone
What is this structure? What is it?

Corpus albicans
If pregnancy does occur, the cells degenerate by influence of PFGa2 are replaced by collagen-rich scar
What is A , what is B on the corpus luteum structure?

A: granulosa cells
B: Theca cells
What is this a structure of?

Uterine tubes
In this SEM of a uterine tube, what 2 cells are in the mucosa?

3a: ciliated cells
3b: peg cells (prod secretions)
In this TEM of a uterine tube, what 2 cells are in the mucosa?

3a: ciliated cells
3b: peg cells
Label the different parts and under which layer on this uterine wall cartoon of the mesometrium. (top to bottom)

Perimetrium
____
Myometrium:
Longitudinal muscle
CT
Circular muscle
____
Endometrium:
CT
Epithelium
On the uterine walls, what phase is indicated?
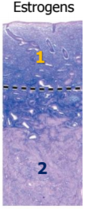
Follicular phase
On the uterine walls, what phase is indicated?

Luteal phase
What do the numbers on layers of uterine wall indicate?

Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
What is this and what do the numbers indicate?

Cervix of the uterus
- Endocervix
- Transition zone
- Ectocervix
- Cervial glands
What is this and what do the number indicate?

Cervix
- Uterine body
- Vagina
What structure is circled on this blue box?

Cervix
What is this structure and what do the numbers indicate?

Vagina
1- Mucosa
1a: strat sqau epit
1b: lamina propria
2- Mscularis (smooth muscle)
What is the structure and what do the numbers indicate?

Mammary glands
- Parenchyma and stroma
- Lactiferous ducts
- Lactiferous sinus
- Teat
What is this and what do the structures indicate?
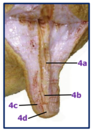
4a. Papillary duct
4b. Teat sinus
4c. Teat orifice
What is this and what do the structures indicate?

- Lobes
- Lobule
- Lactiferous ducts
- Lactiferous sinus
- CT
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue
What is the stage of what the mammary gland is in? Identify numbers

Lactating
- Lobes
- Lobule
- Lactferous ducts
- CT
What stage is mammary glands in? What do numbers indicate?

Nonlactating
- Lobes
- Lobule
- Lactiferous ducts
- CT
From left to right, what species do each mammary gland location/number represent?
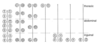
Sow, Bitch, Cat, Woman, Cow, Ewe, Mare
What is the structure of the endocervix of the uterus?
Strat colum epit


