L44-45: Urinary System I & II Flashcards
What are the organs of the urinary system? (4)
- Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Urinary bladder 4. Urethra
What is the primary function of the kidney?
To conserve body fluid, and electrolytes and remove metabolic waste
Kidneys receive ___% of cardiac output?
25%
What does the erythropoietin do in the kindey?
Help increase RBC creation
What does renin do in the kidney?
Maintain blood pressure
What vitamin does the kidney activate?
Vit D
What kind of morphology does the cattle kidney have?
Multilobar with lobar surface
What kind of morphology does the pig kidney have?
Multipyramidal with smooth surface
What is the morphology of a dog kidney?
Unipyramidal with smooth surface
What three things make up the renal hilum?
- Renal artery (in) - Renal vein (out) - Renal pelvis (out)
What does the renal capsule do?
Protective outer covering that overlies the renal cortex
What two layers make up the renal capsule?
- Outer capsule layer and Inner capsule layer
In the two layers that make up the renal capsule, what is their function?
Outer capsule layer: dense CT, protection Inner capsule layer: myofibroblasts, resists pressure changes
What does the green line indicate? Red line?

Green: Renal cpasule
Red: Renal cortex
What structure does each color represent?

Red: Capsule
Green: Cortex
Orange: Outer zone
Purple: Inner zone
What are the colored parts of the kidney? What do they all do conclusively?

Blue: Minor clayx
Pink: Major calyx
Yellow: Renal pelvis
Green: Ureter
They all drain urine from the kidney
What two things make up the renal lobe?

Renal pyramid and adjacent renal cortex (and column tissue)
Each renal lobe drains into ______

1 minor calyx
What is a renal paillae?
Projection into the minor clayx
What structure is indicated by the red arrow? What is its function?

Area cribrose: surface w/ openings of papillary duts
What is this a structure of?

Renal papillae
What are structures (2) associated with blood flow?
- Glomerulus
- Fenestrated capillaries
As far as blood flow in the glomerulous, where is blood going to and going away from? (2 different arterioles)
Going to : Afferent arteriole
Away from: Efferent arteriole
What type of glomerular capillaries will be utilized?
Type II
What is this a structure of?

Glomerulus
Label all red arrows starting from right corner going counterclockwise (there are really 3 structures, but a repetition of each); what do all these structures indicate?
RIGHT SIDE: Efferent arteriole, afferent arteriole, afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, LEFT SIDE: Glomerulus
All indicate BRANCHES OF THE RENAL ARTERY
2 functions/ “parts” of the efferent arteriole- what are they called? (not as easy-sounding as you think)

TOP: Peritubular cortical capillary network
BOTTOM: Vasa recta
What is the function of the peritubular cortical capillary network ? (3)
- Nourish tissue
- Reabsorption of ultrafiltrate in cortex
- Endothelium secretes erythropoietin
What is the function of the vasa recta? (2)
- Descend to medulla
- Regulate urine cc (counter current xchange)
Where does urine begin as?
Ultrafilturate (glomerular filtrate) of blood plasma
What does the urine contain and what does it maintain?
Contains metabolic waste products
Maintains water and electrolyte balance
What is the uriniferous tubule?
Functional unit that transports and modifies fluid to form urine
What makes up the uriniferous tubule?
Made of a nephron and collecting duct
What two parts are part of the nephron?
- Renal corpuscle
- Renal tubule
What kind of ducts are associated with the nephron?
Collecting ducts
What makes up the uriniferous tubule? (2)
Nephron + collecting tubules and ducts
What makes up a nephron? (2)
Renal corpuscle + renal tubule
What makes up a renal corpuscle? (2)
Glomerulus + glomerular capsule
What makes up a renal tubule? (3)
Proximal tubule + thin loop of Henle + distal tubule
There are two types of nephrons- what are they?
- Juxtamedullary
- Cortical
Describe the juxtamedullary nephron and its function
Long-looped, performs most urine concentration
Describe the cortical nephron and its function
Short-looped, performs most filtration/ absorption (85%)
What are the two directional “poles” assocaited with the renal corpuscle? What do each do?
- Vascular Pole- afferent arteriole enters, efferent exits
- Urinary pole- leads to renal tubule
What are the four long steps of how blood passes through the glomerulus?

- Blood enters glomerulus via afferent arteriole at the vascular pole
- Some blood plasma will exit the glomerulus thru the glomerular filtration barrier and enter the urinary space as ultrafiltrate
- Ultrafiltraute will enter the renal tubule at the end of the urinary pole
- Remaining blood will leave the glomerulus via efferent arterioles at the vascular pole
Glomerulus invaginates into the ________
Glomerular capsule
What is this a structure of?

Glomerulus
What layer of the glomerulus does the blue indicate? Green? What do each do?

Blue: Partietal layer- simple squamous epithelium
Green: Visceral layer- layer of podocytes that covers the glomerulus
In the renal corpuscle there are specialized cells that are indicated in brown and light pink around the blue. What are these two cells?

- Mesangial cells
- Podocytes
What are the functions of mesangial cells?
- Modified smooth mm cells
- Secrete mesangium (ECM- support)
- Regulate glomerular distension (contraction)
- Keep GFB clean (phagocytosis)
What is the function of podocytes?
- Form visceral layer of glomerular capsule
- Part of the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB)
What are the pedicles of the podocyte? (black line)

Interdigitating process of the pdocytes; can be contracted by podocyte to reduce GFR
What are filtration slits?
Gaps between pedicels spanned by a diaphragm
What are the 3 features of glomerular filtration barrier?
- Endo cells of fenestrated capillaries (no diaphragms)
- Thick basal lamina with GAGs
- Podocyte filtration slits spanned by a slit diaphragm
The pass of the glomerular filtration barrier is restricted by what 2 things?*
- Size of openings
- Charge of GAGs
What three parts are needed to make a nephron? Colors

blue: Proximal tubule
Green : Thin loop of henle
Red : Distal tubule
What portions do the proximal tubule and distal tubule have in common?
- Convulted portion
- Straight portion
What is the loop of henle made up of? (3)
Proximal straight tubule + thin loop of Henle + distal straight tubule
What is the main function of the proximal tubule? (reabsorpt, secretion, has what portions)
- Reasborption into peritubular capillaries
- Calcitriol secretion
- Has convuluted and straight portions
In this TEM of the promixal tubule, what things are indiciated? (list as much)..What do these features facilitiate? (2)***

- Simple cuboidal epithe
- Microvilli LOTS!! (brush border)
- Lateral and basal folds
- Mitochon, vesicles, lysosomes
These features facilitate RAPID ION AND FLUID REABSORPTION!!!
What is this structure and what are characteristics of it? (3)*

Proximal Tubule
No clear cell borders due to folds
Irregular lumne due to brush border
Often star shaped*!
What is the main function of the thin loop of Henle?
Concentration of urine (countercurrent exchange with vasa recta)
What is indicated by this black arrow on the left? What do the cells of those look like (2 things)

Interstitium GAG-rich ECM, interstitial cells (these look like fibroblast and macrophage cells)
What is the main function of the distal tubule?
Selective secretion and reabsorption (“fine-tunes” ultrafiltrate)
What is the structure? What does this TEM indicate (list all)? (4)

Distal tubule
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
- No brush border (few short microvilli)
- Lateral and basal folds
- Abundant mitochondria
What do features of the distal tubule facilitate?*
Selective ion transport
What does this black arrow on this LM indicate?

Distal tubule
- No clear cell borders (folds)
- Smaller, more regular lumen than PT
What does the left question mark indicate? Right quesion mark?*

Left: Promixal tubule
Right: Distal tubule
What is the DISTAL TUBULE JUXTAGLOMELULAR APPARATUS?**
“Sensor” that helps maintain sodium homeostasis and regulates blood pressure
What two types of cells are indicated in this structure? (left black arrow, right black arrow)

Left black arrow: Juxtaglomerular cells
Right black arrow: Macula densa cells
What is the purpose of the juxtagomerular cells (granular cells) on the distal tubule?
Modified smooth muscle cells that store/ secrete renin
What is the purpose of the Macular densa cells (granular cells) on the distal tubule?
Sensitive to Na lvls in ultrafilturae; signal renin secretion
What do the left black arrow and right black arrow indicate?

Left: juxtaglomerular cells
Right: Macular densa cells
In the distal convoluted tubule, what happens to Sodium lvls?
Decreases
Macul densa cells –> _____ –> juxtaglomerular cells to secrete the renin!*
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
When the juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin, what two things happen?
- Increases blood pressure (vaso constrict)
- Increases blood volume (renal absorption)
What is this structure? Main functions?

Cortical and medullary collecting duct;
further “fine-tunes” ultrafiltrate (light and dark cells)
- Cuboidal epithlium, large regular lumen with distinct cell borders
What is this structure? Main function?

Papillary ducts (of Bellini)
Conduct urine into minor calyces
What is this a stucture of? (clinical)

Kidney cyst caused by tubular obstruction
What is the transitional epithelium also called?
Uroepithelium
What are the 3 features of uroepithelium?
- Highly distensible; unique to urinary system
- Stratified, impermeable to water and salts (urine)
- Varies in appearance based on functional state
What is each structure indicating and why?

Left: Undistended lumen- EMPTY
Right: distended lumen- FULL
What type of cells are on the 3 layers?

Stratified epithelium cells
Surface cells
Basal cells
What is significant about the top stratified layer of the uroepithelium?
- number of layers increases proximal-distal (~3 in calyces, ~6 in urinary bladder)
What is significant about the surface cell layer of the uroepithelium? (types of cells, and indication of undistended and distended cells)
Umbreall, dome, basket cells
- Undistended: round, bulge into lumen
- Distended: flattened
What is this structure?

Urinary bladder
What are some features of the urinary bladder? (4)
- Highly distensible; rugae (macroscopic folds)
- Thicker mucosa
- Muscularis (detrusor muscle): multidirecitonal
- Serosa adjacent to peritonal reflections
As far as the detrusor muscle (muscularis) of the urinary bladder, how would we know if it is in para or sympathetic?
Para: squeeze to let it expell
Symp: release sphincter, to exit body
In urinary bladder cancer, the lining of urinary tract are highly ______ and are in contact with chemicals excreted
Mitotic
Where is the most common site of urinary system tumorigenesis?
Transitional epithelium of the urinary bladder
What does this blue box on male urethra indicate and describe tissue type?

Prostatic urethra:
transitional epithelium
What does this purple box on male urethra indicate and describe tissue type?

Pelvic urethra:
stratified/pseudostrtified columnar epithelium
What does this pink box on male urethra indicate and describe cell type?
Penile urethra:
Strat squamous epith (nonkeratinized) - inside spongy body
What is the tissue type indicated in blue box on female urethra?

transitional epithelium
What is this tissue type in the pink box indicating on female urethra indicating?

Strat squamous epith (nonkeratinized) - inside spongy body
What is a clear difference between male and female urethra?
Female has shorter urethra than males
What is this circled? What does it do?
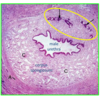
Paraurethral mucus gland
open to urethra of both males and females
What is the green box? What does it do?

Paraurethral mucus gland
open to urethra of both males and females


