L45: Male Reproductive Anatomy Flashcards
The testes have two compartments, which have two functions- what are they?
- Seminiferous tubules
- Interstitial tissue
What are the top arrows indicating? Bottom?

Top: Seminiferous tubules
Bottom: Interstitial tissue
The seminiferous epithelium is made up of what two types of cells?
- Germ cells
- Sertoli cells
In the seminiferous tubules, what structures are the colored triangles indication?

Orange: Elongated spermatids
Yellow: Rounded spermatids
Green: Spermatocytes
Blue: Spermatogonia
What is indicated by the arrows?

Intercellular bridges
What cells are indicated by the blue arrows?

Sertoli cells
What is the main function* of the sertoli cells- what are other 3 functions?

Main: Provide physical and nutritional support to germ cells*
- Regulate mvmnt of cells and molecules into the epith
- Phagocytize degenerating germ cells
- Secrete molecules into the epithelium and to the interstitial tissue
What is the blood-testis barrier?
Cytoplasm of sertoli cells and tight junctions between adjacent sertoli cells
What are the two types of compartments indicated? What stage of sperm is present in each?

Adluminal compartment: Spermatocytes, spermatids
Basal compartment: spermatogonia, preleptotene spermatocytes
The adluminal comparment and the basal compartment of the seminiferous epithelium are part of what compartment?
Intratubular compartment
The sertoli cells secrete many different things; what is one key secretion that would aid in increasing sperm viability and energy?

Fructose
In the seminiferous tubule wall, what is indicated by the green arrows?

Peritubular myoid cells
What is inidicated by the red box in the tubular wall of seminiferous tubules? 2 functions?

Smooth muscle actin
- Contraction of tubules= flow
- Stim of stertoli cells
What is this a structure of?
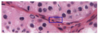
Tubular wall
What are the red arrows indicating on the tubular wall? Start from top left and clockwise

Sertoli cell
Basal lamina
Peritubular myoid cells
What is the black and blue arrows indicating in the intersitial tissue?

Black: Leydig cells
Blue: Blood vessles
The testes have 2 compartments, 2 cells, and 2 ______.
Gonadotropins
What type of testis development is this indicating?

Prenatal
What type of tesis development is this indicating?

Postnatal development
Sperm are carried by fluid through _______ducts to the epididymis
Excurrent ducts
What is 2? Function?

Tubuli recti
Simple, low columnar or cuboidal, epithelium devoid of germ cells
A structure of the excurrent duct- what is this? Describe.

Rete testis
Flattened channels; cuboidal ciliated cells
A structure of the excurrent duct- what is this? Describe.
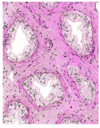
Efferent ducts
Columnar ciliated cels and columnar cells with microvilli!
What are the black arrows (top + bottom)? What structure is this a part of as a whole?

Top arrow: CT
Bottom: Epididymal duct
epididymis
Where is sperm stored?
Tail of epididymis
Where is sperm matured?
Head and body of epididymis
What is indicated by red circle and line of the epididymis and what portion of it?

Myenteric plexus in Tail
In the epididymis, describe this tissue.

Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
What is the red box indicating and what is the function of this structure?

Ductus deferens
Conveys the sperm to the pelvic urethra
What is the red box indicaitng?
Ductus deferens
What is the tissue type of this on the ductus deferens?

Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
What is this structure? (type specific)

Musculocavernous penis
What is this structure? (type specific)

Fibroelastic penis
What is this cross-section a part of? (type specific)

Musculocavernous penis
What is this cross-section a part of? (type specific)
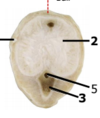
Fibroelastic penis
What is this cross-section a part of? (type specific)

Musculocavernous penis
What is this a structure of?

Penis
Out of the male glands: ampullary glands, vesciular glands, prostate, and bulbourethral gland, which species (horse, bull, boar, dog, cat) does NOT have a ampullary gland?
Boar
Out of the male glands: ampullary glands, vesciular glands, prostate, and bulbourethral gland, which species (horse, bull, boar, dog, cat) does NOT have a vesicular gland?
Dog and Cat
Out of the male glands: ampullary glands, vesciular glands, prostate, and bulbourethral gland, which species (horse, bull, boar, dog, cat) does NOT have a bulbourethral gland?
Dog
What is this a structure of? What does it secrete?

Ampullary glands;
Fluid rich in fructose and ergothionein (antioxidant aa)
What is this a structure of? What does this structure secrete?

Vesicular glands
Secretes alkaline viscid fluid rich in fructose and “coagulating” proteins
What is the stroma of the vesicular glands?
Fibroelastic capsule (smooth muscle + elastic fibers) that aextends as trabeculae
SEE number 1 in pic

What is this structure comparing in vesicular glands?

Non-castrated (Left) vs Castrated (right)
What is the blue arrow indicating on this horse penis structure?

Vesicular gland
What is the blue arrow indicating on this horse penis structure?

Ampullary gland
What is the blue arrow indicating on this horse penis structure?

Prostate
What is this structure and what is it secreting?

Prostate
Secreting a slightly acid fluid rich in acid phosphatse, citric acid, and proteins for semen liquefaction
What are the prostatic secretions and what is exclusive?
Condensed secretion, it may become calcified
What is this structure indicating and what is its secretion?

Bulbourethral gland
A clear viscid mucus-like fluid rich in sialoproteins and amino surgars for urethral cleaning and lubrication
What is the blue arrow indicating on this horse penis structure?

Bulbourethral gland
What is significant about this? What may it indicate clinically?*

ONLY Sertoli cells- NO germ cells
May indicate cryptorchidism!!!
What does this show?

Testicular tumors
What is this tumor type and what is being seen?*
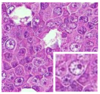
Seminoma;
HIGH presence of germ cells; round BIG nuclei; and HIGH nucleus to cytoplasm ration
What is this tumor type and what is being seen?*

Sertoli cell tumor;
HIGH presence of cells with rounded homogenous nuclei (cells with that phenotype that do not correspond to that of Leydig or germ cells)
What is this tumor type and what is being seen?*

Leydig cell tumor
High presenece of cells with typical leydig cell phenotype


