Kaplan Organic Chem: Chapter 1 Flashcards
carbonyl group
carbon double bonded to an oxygen

aldehyde structure
carbonyl, R group, and H

ketone structure
carbonyl group and 2 R groups

alkanes
CnH2n+2
hydrocarbons that lack pi bonds
usually end with “ane”
methane, propane, butane
steps to nomenclature
- select parent chain –> longest chain
- for chains with equal lengths, choose the one with more substituents
- number the parent chain
- give first substituent the lower possible number
- if tie, choose chain where 2nd sub has the lower number
- name the subsituents based on where and how many
- arrange the subs alphabetically
- place the locants in front of each substituent
primary carbon
1°
depends on number of carbons directly attached

secondary carbon
2°

tertiary carbon
3°

quarternary carbon
4°
depends on number of carbons directly attached

Assessing Stability
- correct electronegativity
- size: bigger = more stable
- more resonance = more stable –> pi bond being spread
- induction: pull away from neg charged region more acidic –> sigma bonds
- orbitals: triple bond more acidic
- lone pair - 25% sp3 less stable
nomenclature
n-
“normal”
n-propyl –> straight chain alkane
nomenclature
multiple substituents of the same type
di-, tri-, tetra- etc
highlight the parent chain

longest chain must include hydroxyl group

highlight the parent chain


name substituents then name molecule

4-ethyl-2,3-dimethylheptane

hydrocarbons
compounds that only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
alcohols
contain at least one OH group
alkyl halides
alkanes with halogen subsituents
fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-
alkene
alkanes with double bonds
alkyne
alkanes with triple bonds
alkane name
1 carbon
methane
alkane name
2 carbons
ethane
alkane name
3 carbons
propane
alkane name
4 carbons
butane
alkane name
5 carbons
pentane
alkane name
6 carbons
hexane
alkane name
7 carbons
heptane
alkane name
8 carbons
octane
alchol nomenclature
-ol
chain is numbered so C attached to OH gets lowest possible number (even when multiple bonds present)
if alc is not highest priority function group –> hydroxy-
common name of ethanol
ethyl alcohol
common name of 2-propanol
isopropyl alcohol

alcohols with 2 hydroxyl groups are called
diols or glycols
-diol
must number each OH group for diols
geminal diols
aka hydrates
diols with OH groups on same carbon
vicinal diols
diols with OH groups on adjacent carbons
IUPAC name
C9H20
nonane
IUPAC name
C10H22
decane
in a molecule with 2 double bonds adjacent to each other and an alcohol, which functional group would take precedence in naming?
alcohol
aldehyde nomenclature
-al
when higher priority group takes precedence over carbonyl –> oxo-
common name of methanal
formaldehyde
common name of ethanal
acetaldehyde
common name of propanal
propionaldehyde
ketone nomeclature
-one
when higher priority group takes precedence over carbonyl –> oxo-, keto-
common name of propanone
acetone
For a molecule with a double bond, an aldehyde, and an alcohol, which functional group would determine the suffix when naming?
Ketones and aldehydes both take precedence over both alcohols and hydrocarbon chains, and the functional group that is the highest priority determines the suffix. Because the aldehyde is chain-terminating and therefore on carbon number 1, the aldehyde would determine the suffix when naming this compound.
carboxylic acid structure
carbonyl and hydroxyl group on terminal carbon
most oxidized functional group –> highest priority functional group

carboxylic acid nomeclature
-oic acid
common name for methanoic acid
formic acid
common name for ethanoic acid
acetic acid
common name for propanoic acid
propionic acid
ester structure
carboxylic acid derivative
OH replaced with OR
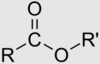
ester nomeclature
-oate
amide structure
carboxylic acid derivative
OH replaced by amino group

amide nomenclature
-amide
subs attached to nitrogen atom labeled with a N- –> indicates that group is bonded to parent molecule via nitrogen atom
anhydride structure
derivative of carboxylic acid

anhydride nomenclature
replace acid with anhydride




