Biochem: Ch 1 Flashcards
amino acids structure
amino group (-NH2)
carboxyl group. (-COOH)
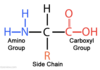
α-amino acids
amino and carboxyl group bonded to the same carbon (α-carbon)
aka proteinogenic amino acids
side chains of amino acids (R groups)
determine the properties of amino acids
all amino acids are ___ except for ___
chiral
glycine
thiol
-SH
general trend of nonpolar, nonaromatic amino acids
alkyl groups
(7)

general trend of aromatic amino acids
conjugated ring
(3)

general trend of polar amino acids
OH, amide, or thiol
(5)

general trend of negatively charged (acidic) amino acids
carboxylate/carboxylic acid
(2)

general trend of positively charged (basic) amino acids
pos charged N atom
(3)

general trend of hydrophobic amino acids
long alkyl side chains
hydrophobic amino acids are more likely to be found
in interior of proteins, away from water on surface of protein
general trend of hydrophilic amino acids
charged side chains and amides
hydrophilic amino acids are more likely to be found
surface of protein
what is the stereochemistry of chiral amino acids that appear in eukaryotic proteins?
L or D
exception?
L
no
what is the stereochemistry of chiral amino acids that appear in eukaryotic proteins?
(S) or (R)
exception?
(S)
cysteine
amino acids
ionizable groups tend to…
gain protons under acidic conditions
lose protons under basic conditions
at low pH, ionizable groups tend to be
protonated
at high pH, ionizable groups tend to be
deprotonated
pH < pKa
majority of species will be protonated
pH > pKa
majority of species deprotonated
pKa of carboxyl group
pKa1 = carboxyl group = 2
amino acids under acidic conditions
tend to be positively charged
carboxylic acid group –> fully protonated (-COOH) - neutral
amino group –> fully protonated (-NH3+) - pos charge
pKa of amino group
pKa2 = amino group = 9-10
amino acids at pH near pI of amino acid
amino acid is neutral zwitterion
carboxylic acid group –> deprotonated (-COO-) - neg charge
amino group –> fully protonated (-NH3+) - pos charge
zwitterion
molecule that has both a positive and negative charge
electrically neutral
pH at which an amino acid exists in a neutral form with zero charge amino acids under basic conditions
amino acid is negatively charged
carboxylic acid group –> deprotonated (-COO-) - neg charge
amino group –> deprotonated (-NH2) - neutral
titration curves of amino acids
two curves
three curves if side chain is charged

isoelectric point (pI)
pH at which an amino acid exists in a neutral form with zero charge.
how to calculate pI
average pKas of amino and carboxyl groups
when titration curve is really flat
at pKa values of the amino acid
solution is acting as a buffer
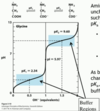
when titration curve is nearly vertical
pI of amino acid
molecule is especially sensitive to pH changes
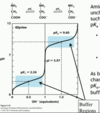
how to calculate pI of acidic amino acid
avg of pKa of COOH and R group
how to calculate pI of basic amino acid
avg of pKa of NH3+ and R group
amino acids with acidic side chains have isoelectric points ___ 6
below
amino acids with basic side chains have isoelectric points ___ 6
above
peptides are composed of
amino acid subunits
residues
amino acid subunits
dipeptides are composed of
two amino acid residues
tripeptides are composed of
three amino acid residues
oligopeptide
relatively small paptides
up to about 20 residues
polypeptides
residues over 20
residues in peptides are joined together throuh
peptide bonds
peptide bonds
specialized form of amide bond
form between -COO- group of one amino acid and NH3+ group of another –> forms functional group -C(O)NH-
peptide bond formation
rxn types
condensation/dehydration rxn –> removal of water molecule
acyl substitution rxn
peptide bond formation
peptide bond formation
- electrophilic carbonyl carbon on 1st amino acid attacked by nucleophilic amino group on 2nd amino acid
- hydroxyl group of carboxylic acid is kicked off

resonance in peptide bond
amide groups have delocalizable pi electrons in carbonyl and in lone pair on amino nitrogen
C-N bond in amide has partial double bond character –> rotation is restricted, making protein more rigid

N-terminus
free amino end of peptide bond
C-terminus
free carboxyl end of peptide bond
breaking peptide bond rxn type
hydrolysis
using acid or base catalysis
peptide bond hydrolysis
hydrolytic enzymes break apart amide bond by adding hydrogen atom to amide nitrogen and OH group to carbonyl carbon
proteins
polypeptides
primary structure of protein
linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide
encodes all info needed for folding at all of the higher structural levels
primary structure is stabilized by
formation of covalent peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids
secondary structure of protein
local structure of neighboring amino acids
includes: alpha helices, beta pleated sheets
secondary structure is stbailzied by
hydrogen bonding between amino groups and nonadjacent carboxyl groups
alpha helices
clockwise coils around a central axis
alpha helices are stabilized by
intramolecular hydrogen bonds between carbonyl oxygen atom and amide hydrogen atom four residues down the chain
alpha helix structure
side chains of amino acids point away from helix core
alpha helix is important for
structure of keratin
keratin
fibrous structural protein found in human skin, hair, and fingernails
beta pleated sheets
rippled strands that can be parallel or antiparallel
rippled to accommodate as many hydrogen bonds as possible
beta pleated sheets are stabilized by
intramolecular hydrogen bonds between carbonyl oxygen atoms on one chain and amide hydrogen atoms on adjacent chain
beta pleated sheet structure
R groups of amino acids point above and below the plane of the sheet
secondary structure and proline
can interrupt secondary structure because of its rigid cyclic structure
- makes a kink in middle of alpha helix
- rarely found in:
- alpha helix
- EXCEPT in helices that cross cell membrane
- middle of beta pleated sheets
- alpha helix
- found in
- between chains of beta pleated sheets
- start of alpha helix
proteins can be divided into
+ ex
- fibrous proteins
- collagen
- globular proteins
- myoglobin
fibrous proteins
have structures that resemble sheets or long strands
globular proteins
structures that tend to be spherical
tertiary structure of protein
3D shape of single polypeptide chain
result of moving hydrophobic amino acid side chains into interior of protein
tertiary structure is stabilized by
hydrophobic interactions, acid base interactions (salt bridges), hydrogen bonding, disulfide bonds
tertiary structure
hydrophobic interactions
push hydrophobic R roups to interior of protein, which increases entropy of surrounding water molecules and creates negative Gibbs free energy
disulfide bonds occur when
2 cysteine molecules are oxidized and create a covalent bond to form cystine

quaternary structure
interaction between peptides in proteins that contain multiple subunits
conjugate proteins
proteins with covalently attached molecules
attached molecule is a prosthetic group and may be a metal ion, vitamin, lipid, carbohydrate, or nucleic acid
denaturation
protein loses tertiary structure and loses its function
what happens when solute dissolves in solvent
nearby solvent molecules form solvation layer around that solute
makes nonspontaneous process
subunit
smaller globular peptides
functional form of protein
possible roles of formation of quaternary structures
- more stabile –> further reduces surface area of protein complex
- reduce amount of DNA needed to encode protein complex
- bring catalytic sides closer together –> allowing intermediates from one reaction to be directly shuttled to second reaction
- induce cooperativity/allosteric effects
what can lead to denaturation
heat and increasing solute concentration
what happens when heat denatures a protein?
temp inc –> avg kinetic energy inc –> energy becomes enough to overcome hydrophobic interactions that hold protein together
what happens when solutes denatures a protein?
+ex
- directly interfere with forces that hold the protein together
- urea
- can disrupt tertiary and quaternary structures by breaking disulfide bridges - reducing cystine back to two cysteine residues
- can overcome hydrogen bonds and other side chain interactions that hold alpha helices and beta pleated sheets intact
- SDS
- solubilize proteins - disrupting noncovalent bonds and promoting denaturation
- urea
body pH
~7.4
ionizable R groups pkas
Dont Express Hate Create Your Kindness Right
D3 E4 H6 C8 Y10 K11 R12
Name the six aliphatic amino acids.
GAVLIP (GAVe my LIPs - isn’t simplicity romantic?)
- Glycine (G)
- Alanine (A)
- Valine (V)
- Leucine (L)
- Isoleucine (I)
- Proline (P)
Name the three aromatic amino acids.
FWY
(FreeWaY - think electrons speeding around between carbons)
- Phenylalanine (F)
- Tryptophan (W)
- Tyrosine (Y)
Name the two sulfur-containing amino acids.
MC
(MC Donalds - think sulfurous french fries… eww…)
- Methionine (M)
- Cysteine (C)
Name the two (non-aromatic) hydroxy-containing amino acids.
ST (OHio STate - OH containing)
- Serine (S)
- Threonine (T)
Name the three basic amino acids.
RKH (RocK House - think of a guy rocking out on the “base” guitar)
- Arginine (R)
- Lysine (K)
- Histidine (H)
Name the two amide-containing amino acids that are derived from the acidic amino acids.
QN (QueeN - these are the only amino acid side chains with both Nitrogen and Oxygen; thus these amino acids are the rulers)
- Glutamine (Q)
- Asparagine (N)
Name the two acidic amino acids.
DE (DEad - this is what happens when you do ACID)
- Aspartate (D)
- Glutamate (E)
Which amino acids are polar?
The hydroxy-containing amino acids (STY), basic amino acids (RKH), acidic amino acids (DE), amide-containing amino acids (QN), and Cysteine (C). 11 in total.
Keep in mind that Proline (P) is sometimes considered polar and that Tyrosine (Y) is somewhat polar due to its possibility to hydrogen-bond, but could also be described as non-polar due to its aromatic ring.
Which amino acids are non-polar?
The aliphatic amino acids (GAVLIP), the non-Tyrosine aromatic amino acids (FW), and Methionine (M). 9 in total.
Keep in mind that Proline (P) is sometimes considered polar and Tyrosine (Y) is sometimes considered non-polar.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA makes RNA, which makes protein.
Draw out the resonance structures that make up a peptide bond.
The peptide bond resonance structures share electrons between the oxygen and nitrogen atoms.

Draw an amino acid with its four substituents. Circle the alpha carbon.

Proline has a unique amino group. In what way is it unique?
Proline’s amino group is a secondary instead of primary amino group. The R group of Proline is bound to the amino group, forming a ring.
Looking under a microscope, you see that there is a disruption in the pattern of a protein’s secondary structure. Which amino acid(s) is/are likely responsible for this pattern of disruption?
I. R
II. G
III. P
(A) I Only
(B) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) II and III Only
Proline and glycine are likely to cause a disruption in an alpha helix protein structure because proline has an inflexible secondary alpha amino group tied up with its side chain. This inflexible ring ends up adding a kink to the alpha helix.
Glycine has a hydrogen atom as its side chain, making it very small and flexible.
Remember this: glycine & proline = “alpha helix breakers.”
Which amino acid is able to form disulfide bridges within a polypeptide chain or between two different polypeptide chains?
(A) Phe
(B) Cys
(C) Gln
(D) Met
(B) Cys
Cysteine is able to form disulfide bridges within a polypeptide chain or between two different polypeptide chains.

An unknown, rare disease causes a breakdown of polypeptide chains by disrupting its tertiary and quarternary structure. Which amino acid is likely involved? Why?
(A) His
(B) Pro
(C) Gly
(D) Cys
(D) Cys
Disulfide bridges contribute to the tertiary and quarternary structure of a protein; thus, the pathology of the disease is most likely affecting the amino acid cysteine’s ability to form disulfide bridges in an oxidized environment (which typically favors the formation of disulfide bridges).
What is the difference between Cysteine and Cystine?
Cysteine refers to the reduced form.
Cystine refers to the oxidized form.
Think about the e being electrons, which are found in the reduced form (OIL RIG).

Draw the fischer projection of both an L- and D-amino acid. Which bonds are pointing towards you? Which bonds are pointing away from you?
L-amino acid has an amino group shown on the Left side in a Fischer projection while the D-amino acid has an amino group shown on the right side of a Fischer projection.
Horizontal bonds are pointing towards you and vertical bonds are pointing away from you.
Which of the following is NOT one of the nonpolar amino acids?
(A) Glycine
(B) Proline
(C) Threonine
(D) Valine
(C) Threonine
Threonine has a hydroxyl group in its R-group, making it a polar amino acid.
Which amino acid would you expect to find facing the inside of the lipid bilayer in an integral membrane protein?
(A) D
(B) Y
(C) R
(D) L
(D) L (Leucine)
You would expect to find hydrophobic (nonpolar) amino acids, such as amino acids with alkyl groups and aromatic rings as their side chains facing the lipid bilayer.
Which of the Aromatic Amino Acids is most polar, and least likely to be seen facing the lipid bilayer?
(A) S
(B) W
(C) F
(D) Y
(D) Y
S (Serine) and Tyrosine (Y) each have a hydroxy (-OH) group in its R group. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons, which are free to hydrogen bond and contribute to the polarity of the molecule.
However, Serine is not aromatic, whereas Tyrosine is. This make Tyrosine the best answer.
Which amino acid would you expect to find on the surface of a soluble protein?
(A) E
(B) I
(C) P
(D) F
(A) E (Glutamate)
You would expect to find polar, hydrophilic amino acids with side chains containing O, S or N atoms.

Acidic, polar amino acids have R groups containing which functional group?
(A) Hydroxyl
(B) Carboxyl
(C) Amino
(D) Thiol
(B) Carboxyl
Acidic amino acid R-groups contain carboxylic acids as seen in Aspartic and Glutamic acid.
What functional groups do the R-groups of neutral, polar amino acids have that the R-groups of neutral, non-polar amino acids do not?
I. Thiol
II. Hydroxy
III. Amide
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Neutral polar amino acids often contain OH (Hydroxy Groups), S atoms (Thiol Groups), or Amide groups (Carboxylic Acid derivative with an Amino group). Neutral, non polar amino acids contain uncharged, alkyl or aromatic side chains.
Draw out parallel and antiparallel beta-pleated sheets, focusing on their differences.

True or False? Secondary structure is determined by interactions between the polypeptide’s backbone, while tertiary structure is determined by interactions between polypeptide R-groups.
True. Secondary structure is determined by interactions between the polypeptide’s backbone, while tertiary structure is determined by interactions between polypeptide R-groups.
The tertiary structure of a protein and quaternary structure of a protein are similar in that they are stabilized by the same interactions, which include which of the following?
I. Hydrogen Bonding
II. Disulfide Bonds
III. Peptide Bonds
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) I and II Only
The tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein are both stabilized by the same type of interactions, which are:
- Hydrogen bonding
- Van der Waals forces
- Disulfide bonding
- Hydrophobic interactions
What is the “solvation shell”? What is its role?
The solvation shell is the layer of solvent that surrounds a protein. An example of a solvation shell is when the partially-negative oxygen atoms of water molecules surround the positively charged amino acid residues on the exterior surface of a protein, thus stabilizing the conformation of this protein.
What method is best if you want to break only the ionic bonds in protein? Which level(s) of protein structure will be affected?
I. Secondary Structure
II. Tertiary Structure
III. Quarternary Structure
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) II and III Only
Changing the pH surrounding the protein will disrupt all ionic bonds in a protein, which mainly denature tertiary and quaternary structures of a protein.
Keep in mind that the Hydrogen Bonds are formed between the Carboxy Group and the Amino Group, forming the secondary structure of a polypeptide. When these are part of a peptide chain, it would take a very large change in pH to deprotonate or protonate them.
How would a chemical denaturant affect proteins? Which levels of protein structure would be affected?
I. Secondary Structure
II. Tertiary Structure
III. Quarternary Structure
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Chemical denaturants often disrupt the hydrogen bonding within a protein, thus affecting all levels of protein structure except for the primary structure.
Which of the following general statements about Amino Acids are true?
I. Bacteria can use D-amino acids in proteins, but humans typically do not.
II. Not all amino acids in the human body are in the genetic code and/or are incorporated into proteins.
III. All of the amino acids that are in the genetic code have their carboxyl and amine groups bound to the same carbon.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following statements are true:
I. Bacteria can use D-amino acids in proteins, but humans typically do not.
II. Not all amino acids in the human body are in the genetic code and/or are incorporated into proteins.
III. All of the amino acids that are in the genetic code have their carboxyl and amine groups bound to the same carbon (the alpha carbon).


