Biochem: Ch 12, 4 Flashcards
open system
matter and energy can be exchanged with the environment
closed system
only energy can be exchanged with the envrionment
no work is performed in a ___ system because
closed
pressure and volume remain constant
entropy
measure of energy dispersion in a system
ΔU =
Q - W
ATP
mid level energy molecule
ATP contains ____ that are stabilized upon …
high energy phosphate bonds that are stabilized upon hydrolysis by resonance, ionization, and loss of charge repulsion
ATP provides energy through
hydrolysis and coupling to energetically unfavorable reactions
ATP can participate in ____ as a _____
phosphoryl group transfers
phosphate donor
ATP is formed from
substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation
ATP consists of
adenosine molecule attached to 3 phosphate groups
ATP is consumed through
hydrolysis or the transfer of a phosphate group to another molecule
what is the result of one phosphate group being removed from ATP?
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
what is the result of two phosphate groups being removed from ATP?
adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
ATP hydrolysis is most likely to be encountered in the context of
coupled reactions
ATP cleavage
transfer of high energy phosphate group from ATP to another molecule
this activates or inactivates the target molecule
how does coupling with ATP hydrolysis alter the energetics of a reaction?
ATP hydrolysis yields about 30 kJ/mol of energy, which can be harnessed to drive other rxns forward
this may either allow a nonspontaneous reaction to occur or increase the rate of a spontaneous reaction
explain why ATP is an inefficient molecule for long term storage
intermediate energy storage molecule and not energetically dense
the high energy bonds and presence of significant change make it an inefficient molecule
long term storage molecules are characterized by
energy density
stable, nonrepulsive bonds
(primarily seen in lipids)
many redox reactions involve
electron carrier to transport high energy electrons
electron carrier can be either
soluble or membrane bound
flavoproteins
type of electron carrier
derived from riboflavin (vitamin B2)
high energy electron carrier exs
NADH, NADPH, FADH2, ubiquinone, cytochromes
equilibrium is an undesirable state for most biochemical reactions bc
organisms need to harness free energy to survive
postprandial (absorptive) state
aka well fed
insulin secretion is high and anabolic metabolism prevails
observed in short term fasting (overnight)
prolonged fasting
aka starvation
increase glucagon and catecholamine (epinephrine) secretion
at max, 2/3 of brain’s energy can be derived from ketone bodies
anabolism
synthesis of biomolecules
catabolism
breakdown of biomolecules for energy
types of cells that are insensitive to insulin
nervous tissue and red blood cells
counterregulatory hormones
oppose the actions of insulin
act on skeletal muscles, adipose tissue, liver
counterregulatory hormones ex
glucagon, cortisol, epinephrine, norepinephrine, growth hormone
what tissue is least able to change its fuel source in periods of prolonged starvation?
cells that rely solely on anaerobic respiration are least adaptable to different energy sources
ex: red blood cells - stay reliant on glucose
during what stage is there the greatest decrease in the circulating concentration of insulin?
postabsorptive state
effects of insulin on metabolism
inc vs dec
- dec in blood glucose levels by increasing cellular uptake
- dec: triaglycerol breakdown in adipose tissue, formation of ketone bodies by liver
- inc rate of anabolic metabolism
- inc: glucose and triacylglycerol uptake by fat cells, lipoprotein lipase activity, triacycglycerol synthesis
insulin secretion by _____ is regulated by _____
pancreatic beta cells
blood glucose levesl
effects of glucagon on metabolism
inc blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in liver
glucagon secretion by _____ is stimulated by _____
pancreatic alpha cells
low glucose and high amino acid levels
effect of glucocorticoids on metabolism
inc blood glucose in response to stress by mobilizing fat stores and inhibiting glucose uptake
inc the impact of glucagon and catecholamines
effect of catecholamines on metabolism
inc glycogenolysis in liver and lipolysis in adipose tissue
inc basal metabolic rate through their sympathetic nervous system activity
effect of thyroid hormones on metabolism
module the impact of other metabolic hormones
inc basic metabolic rate
T3 and T4
T3 is more potent than T4, but has a shorter half life and is available in lower conc in the blood
T__ is converted to T__ in the ___
T4
T3
tissues
insulin is a ___ hormone
peptide
thyroid hormones are ___ hormones
amino acid derivative
cortisol is a ___ hormone
steroid
glucose is absorbed by ___ via ___
peripheral tissues
facilitated transport mechanisms that utilize glucose transporters located in cell membrane
effect of cortisol on metabolism
inc lipolysis and amino acid mobilization
dec glucose uptake in certain tissues
hepatocytes
maintenance of blood glucose levels by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in response to pancreatic hormone stimulation
liver function
processing of lipids and cholesterol, bile, urea, and toxins
adipose tissue stores __ under the influence of ___ and releases them under the influence of ___
lipids
insulin
epinephrine
skeletal muscle metobolism
differes based on current activity level and fiber type
resting muscle metabolism
conserves carbs in glycogen stores
uses free fatty acids from bloodstream
active muscle metabolism
may use anaerobic metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation of glucose, direct phosphorylation from creatine phosphate, or fatty acid oxidation
depending on fiber type and exercise duration
cardiac muscle metabolism
uses fatty acid oxidation in both wwell fed and fastin gstates
brain and nervous tissue metabolism
consume glucose in all metabolic states except for prolonged fasts, where it comes from ketone bodies
chylomicrons
carry triacyglycerols absorbed from gut
creatine phosphate
transfers a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP
what is the preferred fuel for most cells in the well fed state? what is the exception and its preferred fuel?
preferred: glucose
exception: cardiac muscle - prefers fatty acid
metabolic rates can be measured using
calorimetry, respirometry, consumption tracking, or measurement of blood conc of substrates and hormones
respiratory quotient (RQ)
estimated composition of fuel that is actively consumed by the body
hormones that play a role in body mass
leptin, ghrelin, orexin
long term changes in body mass result from changes in
lipid storage
what must happen for weight change?
changes in consumption or activity must surpass a threshold
the threshold is ___ for weight gain than for weight loss
lower
calorimeters
measure basal metabolic rate (BMR)
orexin
increase appetite
involved in alterness and sleep wake cycle
ghrelin
increases appetite
stimulates secretion of orexin
leptin
decreases appetite by suppressing orexin production
how is the respiratory quotient expected to change when a person transitions from resting to brief exercise?
as a person begins to exercise, the proportion of energy erived from glucose increases
this transition to almost exclusively carb metabolism will cause the respiratory quotient to approach 1
True or False? Coupled reactions tend to occur simultaneously.
True. Coupled reactions tend to occur simultaneously.
ATP has three phosphate groups directly next to one another. What about this structure makes ATP a high-energy molecule?
Phosphate groups are very negatively charged, and negatively charged groups do not want to be next to each other. This is a high-energy situation.
Think about it like two similar charges being next to each other. The closer the charges, the higher the electric potential energy. As these charges separate, the high amount of electric potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
If ATP hydrolysis has a very negative ∆G value, why doesn’t ATP hydrolyze spontaneously all the time? How is our body able to control when ATP hydrolysis occurs?
Although ATP hydrolysis has a very negative ∆G value, the reaction has a very high activation energy (Ea). When an enzyme is used in conjunction with ATP, the Ea is lowered, allowing the reaction to occur. This way, reactions with ATP will primarily occur only in the presence of the needed enzyme.
Which of the following are also names for the Absorptive State?
I. Postprandial State
II. Well-Fed State
III. Counterregulatory State
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
The Absorptive State can also be called the Well-Fed State and the Postprandial State.
Adipose Tissue can receive which of the following for subsequent energy storage?
I. Triglycerides
II. Fatty Acids
III. Glucose
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Adipose Tissue can receive Triglycerides from VLDLs. It can also receive glucose, which it will then convert into Fatty Acids and subsequently Triglycerides.
Mike just ate a big Thanksgiving feast. Which state is Mike likely in?
(A) Absorptive
(B) Post-absorptive
(C) Excretion
(D) Filtration
(A) Absorptive
The absorptive state is also known as the “well-fed state” and is characterized by energy storage.
The Post-absorptive State is also known as the “fasting state” and is characterized by energy utilization.
How long after the last meal would it take to transition from the Postabsorbtive “Fasting state” to the Prolonged Fasting “Starvation” state?
(A) 1 day
(B) 1 hour
(C) 12 hours
(D) 3 days
(A) 1 day
After 1 day (24 hours) since the last meal, the Starvation State will start.
The Absorptive State is most closely associated with _____________. The Post-absorptive State is closely associated with ___________.
(A) catabolism, catabolism
(B) catabolism, anabolism
(C) anabolism, anabolism
(D) anabolism, catabolism
(D) anabolism, catabolism
The Absorptive State is most closely associated with anabolism (macronutrient storage). The Post-absorptive State is closely associated with catabolism (macronutrient breakdown).

Insulin will be released in periods of ______________, and glucagon will be released in periods of ___________.
(A) hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia
(B) hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia
(C) hyperglycemia, hyperglycemia
(D) hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
(D) hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
Insulin will be released in periods of hyperglycemia, and glucagon will be released in periods of hypoglycemia.
Insulin causes glucose ___________, and glucagon causes glucose _____________.
(A) storage, storage
(B) storage, release
(C) release, release
(D) release, storage
(B) storage, release
Insulin causes glucose storage, and glucagon causes glucose release.
Insulin will stimulate:
Gluconeogenesis or Glycolysis?
Glycogenesis or Glycogenolysis?
Lipogenesis or Lipolysis?
Insulin will stimulate:
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenesis
- Lipogenesis
After Insulin has stimulated Lipogenesis in the liver, how are the Fatty Acids stored?
(A) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and stored in the liver.
(B) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as VLDL.
(C) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as LDL.
(D) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as HDL.
(B) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as VLDL.
Triacylglycerols are often called Triglycerides, and VLDL stands for Very Low Density Lipoprotein.
Glucagon will stimulate:
Gluconeogenesis or Glycolysis?
Glycogenesis or Glycogenolysis?
Lipogenesis or Lipolysis?
Glucagon will stimulate:
- Gluconeogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Lipolysis
Compare the cause of Type I versus Type II Diabetes.
Type I Diabetes results from an inability of the pancreas to produce insulin. This usually occurs early on in life.
Type II Diabetes results from desensitized insulin receptors and usually occurs later in life.
Although we know relatively little regarding the mechanism of glucagon release from α-cells, we do know that it is triggered by:
(A) Glucose
(B) Glycogen
(C) Lipids
(D) Amino Acids
(D) Amino Acids
Although we know relatively little regarding the mechanism of glucagon release from α-cells, we do know that it is triggered by amino acids.
Samantha is also really hungry. What hormone will tell her hypothalamus that her stomach is empty?
(A) Insulin
(B) Glucagon
(C) Leptin
(D) Ghrelin
(D) Ghrelin
Ghrelin is produced when your stomach is “growling.”
Which of the following are Catecholamines and Counterregulatory Hormones?
I. Epinephrine
II. Noradrenaline
III. Cortisol
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(B) I and II only
Epinephrine/Adrenaline and Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline are Catecholamines and Counterregulatory Hormones.
carbohydrates are organized by
number of carbon atoms and functional groups
trioses
3 carbon sugars
tetroses
4 carbon sugars
aldoses
sugars with aldehydes as most oxidized group
ketoses
sugars with ketones as their most oxidized group
nomenclature is based on
D and L forms of glyceraldehyde
D-sugars
sugars with highest numbered chiral carbon with the OH group on right (in Fischer projection)

L-sugars
sugars with highest numbered chiral carbon with the OH group on left (in Fischer projection)

D and L forms of the same sugar are
enantiomers
diasteriomers
non superimposable configurations of molecules with similar connectivity
differ by at least one, but not all, chiral carbons
include epimers and anomers
epimers
subtype of diasteromers
differ at exactly one chiral carbon
anomers
subtype of epimers
differ at anomeric carbon
glyceraldehyde
simplest aldose

numbering of carbons in monosaccaride
carbonyl carbon most oxidized - lowest number
aldehyde carbon of sugar can participate in
glycosidic linkages
glycosyl residues
sugars acting as substituents via glycosidic linkages
dihydroxyacetone
simplest ketone sygar
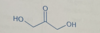
numbering of carbons in aldose
aldehyde carbon is number 1
numbering of carbons in ketose
carbonyl carbon is C2
D-fructose

D-glucose

D-galactose

D-mannose


D-fructose

D-glucose

D-galactose

D-mannose
optical isomers
aka stereoisomers
compounds that have the same chemical formula, differ in terms of spatial arrangement of comoobent atoms
absolute configuration
3D arrangement of the groups attached to the chiral carbon
D-isomers are equivalent with (__)
R
L-isomers are equivalent with (__)
S
as the number of chiral carbons increases, so does the number of
possible stereoisomers
number of steroisomers with common backbone =
2n
n = number of chiral carbons
D-glyceraldehyde determined to exhibit a ___ rotation
positive
D-glyceraldehyde determined to exhibit a ___ rotation
negative
how is direction of rotation determined
experimentally
fischer projection
horizontal lines
wedges - go out of page
fischer projection
vertical lines
dashes - into page
carbs
enantiomers
same sugars in different optical families
ex: D glucose and L glucose
carbs
diasteromers
sugars that are in same family (both are either ketoses or aldoses and have same number of carbons) that are not identical and are not mirror images of each other
carbs
epimers ex
D-ribose and D-arabinose - differ at C2

carbs
cyclization
ring formation of carbs
when rings form, ___ carbon can take on either a ___ or ___ conformation
anomeric
alpha or beta
cyclization
anomeric carbon
new chiral center formed in ring closure
was the carbon containing the carbonyl in straight chain form
alpha-anomers
have -OH on anomeric carbon trans to the free -CH2OH group (axial and down)

beta-anomers
have the -OH on the anomeric carbon cis to the free -CH2OH group (equatorial and up)

Haworth projections
provide a good way to represent the 3D structure of cyclic compounds
cyclic compounds can undergo
mutarotation
mutarotation
cyclic compounds shift from one anomeric form to another with the straight chain form as an intermediate

mutarotation results in
mixture that ontians both alpha and beta anomers at equilibrium conc
is alpha or beta anomeric conformation favored in solution?
alpha anomeric configuration is less favoried bc hydroxyl group of anomeric carbon is axial, adding to the steric strain of the molecule

monosaccarides
single carbohydrate units, with glucose as the most commonly observed monomer
monosaccharides can udnergo 3 main rxns:
redox, esterification, glycoside formation
aldoses can be oxidized to
aldonic acids
aldoses can be reduced to
alditols
sugars that can be oxidized are
reducing agents/sugars
reducing sugars can be detected by reacting with
Tollens’ or Benedict’s reagents
reducing sugars
sugars that can be oxidized
deoxy sugars
sugars with a -H replacing an -OH group
sugars can react with carboxylic acids and their derivatives, forming
esters
sugar esterification
when sugars react with carboxylic acids and their derivatives to form esters

phosphorylation
phosphate ester is formed by transferring a phosphate group from ATP onto a sugar
glycoside formation
basis for building complex carbs
requires the anomeric carbon to link another sugar

aldonic acids
oxidized aldoses
lactone
cyclic ester with carbonyl group on anomeric carbon

tollens’ reagent
used to detect the presence of reducing sugars
silver oxide dissolved in ammonia - [Ag(NH3)2]+
produces a silvery mirror when aldehydes are present
benedict’s reagent
used to detect the presence of reducing sugars
turns into red precipitate of Cu2O

tautomerization
rearrangement of bonds in a compound, usually by moving a hydrogen and forming a double bond
enol
compound with a double bond and an alcohol group
alditol
when the aldehyde group of an aldose is reduced to an alcohol
hemiacetals react with alcohols to form
acetals
glycosidic bonds
C-O bonds when acetals are made
furanosides
glycosides derived from furanose rings
pyranosides
glycosides derived from pyranose rings
breaking a glycosidic bond requires
hydrolysis
disaccharides form as a result of
glycosidic bonding between two monosaccharide subunites

polysaccharides form by
repeated monosaccharide or poly saccharide glycosidic bonding
sucrose

lactose

maltose

cellulose
polysaccharide
main structural component for plant cell walls
main source of fiber in human diet

starches
polysaccharide
main energy storage form for plants
ex: amylose and amylopectin

starches ex
amylose and amylopectin
glycogen
polysaccharide
main energy storage form for animals
homopolysaccharides
polysaccharide composed of the same monosaccharide
heteropolysaccharide
polymer made up of more than one type of monosaccharide

sucrose

lactose

maltose
Draw or visualize D-glucose versus D-fructose. These two compounds are considered:
(A) diasteriomers
(B) epimers
(C) constitutional isomers
(D) enantiomers
(C) constitutional isomers
These two compounds are considered constitutional isomers because they have the same molecular formula with different connectivity.
D-glucose is an aldose, while D-fructose is a ketose.

Which of the following statement(s) is true of a diastereomers?
I. They have similar physical properties
II. They have different physical properties
III. They have similar chemical/biological properties
IV. They have different chemical/biological properties
(A) I and III Only
(B) II and IV Only
(C) I Only
(D) III Only
(B) II and IV Only
Diastereomers are molecules that are different from each other in terms of their physical and chemical/biological properties.
True or False? A sugar monomer in the D configuration will rotate plane-polarized light to the right.
False. Sugar monomers in the D configuration will sometimes rotate plane polarized light to the right and sometimes rotate it to the left. The D/L configuration has no correlation to the direction the compound will rotate plane polarized light.
Draw or visualize D-glucose versus D-mannose. These two compounds are considered:
(A) diasteriomers
(B) epimers
(C) constitutional isomers
(D) enantiomers
(B) epimers
These two compounds are considered epimers because they have the opposite stereochemistry designation (R/S) at a single stereocenter.

How many possible D-aldohexoses are there?
(A) 4
(B) 6
(C) 8
(D) 16
(C) 8
An aldohexose has 4 chiral centers. You can calculate the possible number of configurations using the formula 2^n where n is the number of stereocenters. 2^4 is 16, so there are 16 possible aldohexoses (8 D-aldohexoses and 8 L-aldohexoses).
Fill in the blank: Knowing that any specific Aldohexose has 4 chiral centers, it will have __________ enantiomer(s) and __________ diastereomer(s).
(A) 2 , 5
(B) 2 , 14
(C) 1 , 6
(D) 1 , 14
(D) 1 , 14
Knowing that Aldohexoses have 4 chiral centers, they can have 1 enantiomer and 14 diastereomer(s).
Note that any molecule can only have one Enantiomer, and that one of the 16 possible Aldohexoses is the original Aldohexose everything else is being compared to.
Draw or visualize D-glucose as a Fischer projection versus a Haworth diagram. Indicate which OH group attacks/attacked the carbonyl carbon in each.
The phrase “down right, up lefting” (which sounds like “downright uplifting”) can help you remember that the groups on the right in the Fischer projection should point down in the Haworth diagram, and the groups on the left should point up.

Draw or visualize a pyranose and a furanose.
The key difference is that a pyranose is a 6-membered ring with one O in the ring, whereas the furanose is a 5-membered ring with one O in the ring.

Draw or visualize D-glucose α and β anomers as Haworth projections. What differentiates the α from the β anomer?
In the α form, the OH group at the anomeric carbon points in the same (think “sαme”) direction (up/down) as the OH on C2, and the opposite direction of the CH2OH flag group.
In the β form, the OH group at the anomeric carbon points in the same direction as the CH2OH flag group, and the opposite direction of the C2 hydroxyl.

Describe the process of mutarotation.
Mutarotation is when the ring-form of the sugar opens up and then recloses again. This may cause the sugar to bounce back and forth between the α and β anomers.

What does the naming convention for dissacharides of α-Man1,3-Gal indicate?
α indicates that the anomeric carbon (C-1) of mannose involved in this bond is an α anomer. 1,3 indicates that the bond is between C-1 of mannose and C-3 of galactose.
Sucrose is considered a nonreducing sugar while lactose and mannose are considered reducing sugars. Why is this the case?
Lactose and mannose have an anomeric carbon that can undergo mutarotation to form an aldehyde group, which can be oxidized and act as a reducing agent.
Sucrose is considered a nonreducing sugar because it does not have an anomeric carbon available for mutarotation. Both sugar monomers are trapped in their cyclic forms.

CRB True or false? Any monosaccharide with an Acetal Ring is considered a Reducing Sugar.
False. Any monosaccharide with a Hemiacetal Ring is considered a Reducing Sugar.
Compare the structure of cellulose and amylose (starch).
Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of glucose with β-1,4 linkages.
Amylose is a polysaccharide composed of glucose with α-1,4 linkages.



