Gastro - Abdominal Pain Flashcards
What does SOCRATES stand for?
S = site O = net C = character R = radiation A = associations T = time course, duration E = exacerbating / relieving factors S = severity
What is region 1 of the 9 quadrants?

right hypochondriac region
What is region 2 of the 9 quadrants?

epigastric region
What is region 3 of the 9 quadrants?

left hypochondriac region
What is region 4 of the 9 quadrants?

right lumbar (flank) region
What is region 5 of the 9 quadrants?

umbilical region
What is region 6 of the 9 quadrants?

left lumbar (flank) region
What is region 7 of the 9 quadrants?

righth iliac region
What is region 9 of the 9 quadrants?

left iliac region
What is region 8 of the 9 quadrants?

suprapubic / hypogastric region
What is the blood supply for the foregut?
celiac trunk
What planes are used to divide the abdomen into 9 regions?

- subcostal plane (horizontal)
(corresponds to a line drawn joining the lower most bony point of the rib cage, usually 10th costal cartilage) - transtubercular plane (horiz)
(corresponds to a line uniting the two tubercles of the iliac crests) - mid-clavicular lines (vertical)
What vertebra does the transpyloric plane pass through?
L1
What organs of the abdomen are present at the transpyloric plane?
- Pylorus of Stomach
- Neck of Pancreas
- Fundus of Gallbladder
- Renal Hilum
- Duodenojejunal Flexure
- End of Spinal Cord (adult)
What vertebra does the subcostal plane pass through?
L3
What parts of the abdomen are present at the subcostal plane?
origin of inferior mesenteric artery
What vertebra does the supracristal plane pass through?
L4
What parts of the abdomen are present at the supracristal plane?
bifurcation of aorta
What organs are present in the right hypochondriac region?
gall bladder
What organs are present in the epigastric region?
stomach, duodenum + pancreas
What organs are present in the left hypochondriac region?
pancreas
spleen
What organs are present in the right lumbar / flank region?
kidney
What organs are present in the umbilical region?
small bowel
caecum
retroperitoneal structures
What organs are present in the left lumbar / flank region?
kidney
What organs are present in the right iliac region?
appendix
caecum
What organs are present in the suprapubic (hypogastric) region?
transverse colon
bladder
uterus
adnexae
What organs are present in the left iliac region?
sigmoid colon
What is a part of the foregut?
distal oesaphagus
stomach
liver
gall bladder spleen
proximal half of the 2nd part of duodenum
What is the blood supply for the hindgut?
inferior mesenteric trunk
What is a part of the midgut?
distal half of 2nd part of duodenum –> proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
What is the blood supply for the midgut?
superior mesenteric artery
What is included in the hindgut?
distal 1/3 of transverse colon –> rectum
What is the parietal peritoneum?
membranous sheet that lines abdominal cavity, attached to to the visceral peritoneum to form peritoneal cavity

What is visceral peritoneum?
membranous sheet that lines the organs within the peritoneal cavity
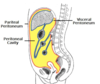
Which organs are intraperitoneal?
stomach
spleen
liver
first and fourth parts of the duodenum
jejunum
ileum
transverse colon
sigmoid colon
Which organs are retroperitoneal?
rest of the duodenum
ascending colon
descending colon
middle third of rectum
pancreas
What is the innervation of the parietal?
somatic
phrenic nerves
T6-L3
What is the innervation of the visceral?
autonomic
Sympathetic – T1 to T12, L1, L2
Parasympathetic – CN III, VII, IX, X, S2 to S4
What is the site of pain like for parietal?
well-localised
What is the site of pain like for visceral?
embryological origin
What is the character of pain like for parietal?
sharp, ache
What is the character of pain like for visceral?
dull, crampy, burning
What is the innervation for the foregut?
T5-T9
What is the innervation of the midgut?
T10-T11
What is the innervation of the hindgut?
L1-L2
Where is the site of pain for the foregut?
epigastrium
Where is the site of pain for the midgut?
umbilical
Where is the site of pain for the hindgut?
hypogastric
What are the 2 categories of pain usually?
inflammation - based
obstruction of a muscular tube
What kind of pain does inflammation present with?
Constant pain (‘aching’)
Made worse by movement
Persists until inflammation subsides
What kind of pain does obstruction present with?
Colicky pain (‘gripping’) Fluctuates in severity Move to try and get comfortable
What does prolonged obstruction cause?
causes distension:
Constant stretching pain
Different from ache of inflammation & not colicky
ischaemia
What organs + problems present with constant pain?
liver + gall bladder
kidney issues
spleen
What organs + problems present with colicky pain?
kidney stones, etc.
cholelithiasis
hepatolithiasis
choledocholithiasi
biliary colic
small bowel + large bowel issues
What is the character of pain like for ureteric, biliary + intestinal colic?

How does pain radiate when in the right hypochondriac region? Target Organ?
through the back + to the right
(gall bladder)
How does pain radiate when in the epigastric region? Target Organ?
straight through the back
(stomach, duodenum, pancreas)
How does pain radiate when in the left hypochondriac region? Target Organ?
through to the back + to the left
(pancreas)
How does pain radiate when in the right and left lumbar regions? Target Organs?
in the loin and radiates to the groin
(kidneys)
How does pain radiate in the umbilical region? target organs?
doesn’t normally radiate unless small bowel is consistently inflamed
(small bowel, caecum, retroperitoneal structures)
How does pain radiate in the iliac and hypogastric regions?
Lower abdominal pain rarely radiates
Pain from structures deep in the pelvis referred to lower back/perineum
What region of the abdomen does colicky abdominal pain refer to?
visceral sensation
Where do you usually feel pain from an inflamed area? Why?
felt over the inflamed area, due to somatic sensation
What does radiation of pain to other regions usually signify?
other structure are getting involved
Why might small bowel pain move?
pain doesn’t radiate but may move when somatic as well as visceral nerves become irritated
What disorders could pain in the RUQ represent?
Gallstones
Cholangitis
Hepatitis
Liver abscess
What disorders could pain in the epigastric region represent?
Oesophagitis
Peptic ulcer
Perforated ulcer
Pancreatitis
Biliary tract disease
What disorders could pain in the LUQ represent?
Splenic abscess
Acute splenomegaly
Splenic rupture
What disorders could pain in the right + left flanks represent?
Renal colic
Pyelonephritis
Ovarian cyst Ovarian mass
Ovarian torsion
What disorders could pain in the umbilical region represent?
Appendicitis (early)
Mesenteric adenitis
Meckel’s diverticulitis
What disorders could pain in the RLQ represent?
Appendicitis (late)
Crohn’s Disease
Ovarian cyst/torsion
Ectopic pregnancy
Hernias
Renal colic
What disorders could pain in the LLQ represent?
Diverticulitis
Ulcerative colitis
Constipation
Ovarian cyst/torsion
PID
Ectopic pregnancy
Hernias
Renal colic
What disorders could pain in the hypogastric region represent?
Urinary retention
Cystitis
Uterine fibroid
Endometriosis


