Gametes - Physiology of Foetal Growth Flashcards
IU growth - stage 1
Hyperplasia
4-20 weeks
rapid mitosis
increasing DNA content
IU growth -Stage 2
hyperplasia/hypertrophy
20-28 weeks
declining mitosis
increasing cell size
IU growth - stage 3
hypertrophy
28-40 weeks
rapid hypertrophy
rapid increasing cell size
rapid accumulation of fat, muscle, CT
when does symmetrical growth retardation occur
symmetrical => correct ratios
up to 20 weeks
(state of hyperplasia)
when does asymmetrical growth occur
stage 2 and 3
newborn may have larger head in proportion to the rest of the body
slow AC growth vs normal HC and FL
placental insufficiencies ⇒ glycogen utilisation by liver, liver shrinkage, decreased AC - preferential shunting to brain thus maintaining HC

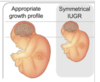
describe physical consequences of symmetrical IUGR
1/3 of all cases
foetus is proportionally small - head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur length (FL)
change in mean weight as duration progresses with singletons, twins, triplets and quadruplets

small for gestational age vs IUGR
small for others of same gestation - lowest 10th percentile
IUGR - brought about by a pathological reason
6 parameters by which IUGR can be prenatally diagnosed
- maternal history e.g. hypertension, smoking
- maternal examination - measurement of fundal height
- foetal ultrasound
- amniotic fluid vol
- blood flow measurements using a Doppler (blood flow to umbilical cord)
- biochemical data - estriol (low 24 hour urinary estriol excretion is associated with 21% of IUGR infants) and human Placental Lactogen, hPL/human Chorionic Sommatotrophin, hCS (produced by placenta and spares glucose for developing foetus)
risks associated with IUGR
increased perinatal morbidity and mortality x10
- increased foetal distress
- stillbirth
- neonatal hypoglycemia (twitchy movements)
- polycythemia (stimulated by hypoxia)
- meconium aspiration
- hypocalcemia (twitchy movements)
what is foetal growth affected by (3 factors)
genetics
potential genetic code
transcription - phenotype
physical environment
uterine capacity - restrictor
nutrient availability - metabolism
interaction between the 2
hormones
growth factors
transcription factors
what is nutritional regulation of growth regulated by
it is both a reaction to environmental conditions and acting on genetic potential
transfer of material across the placenta

how are AAs transported
against a conc gradient
what are AAs essential for
creation of transporters for moving molecules into conceptus
⇒ lack of functional transporters can lead to deficiency, despite availability
name the AA essential for foetal development
taurine
without a functioning transporter, a foetus can be taurine deficient
role of functional AAs (FAA)
primarily transport proteins
function of FAA Arginine
cell division
healing of wounds
removing NH3 from the body
immune function
release of hormone
function of FAA Cysteine
enzymes and oxidation
donates electron for breakdown of molecules
function of FAA Leucine
leucine is utilised in liver, adipose tissue, muscle
it is the only dietary AA that has the capacity to stimulate muscle protein synthesis
function of FAA glutamine
protein synthesis
regulation of acid-base balance
cellular energy - glucose uptake
nitrogen donation for anabolic rxns
carbon donation
non-toxic transporter of NH3 in the blood circulation
observations when GH is knocked out of mice
normal foetal growth
normal BW
after birth, growth is impaired
⇒ IGF-I and IGF-II are NOT regulated by GH during foetal development
observations when IGF-I is knocked out of mice
slow foetal development
low birth weights
mice also display marked lack of growth after birth as well
⇒ IGF-I is important for growth at all stages of development (before and after birth)
observations when IGF-II is knocked out of mice
slower foetal development with low birth weights
however after birth, mice grow at normal rates
⇒ IGF-II is an important foetal growth factor with unclear role in growth after birth

















