Embryos - Female Reproductive System Flashcards
Sagittal view of pelvic region
Rectouterine pouch = pouch of douglas

Sagittal view of ovary
Structure of ovary

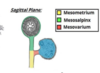
What does the mesovarium do
Supports and stabilises the ovary
What does each ovarian follicle contain
An egg cell
Overview of oogenesis
All oogonia have formed before birth

What is the difference between oogenesis and spermatogenesis
Daughter cells are different sizes in oogenesis
4 steps in ovarian cycle
- Formation of primary, secondary and tertiary follicles
- Ovulation
- Formation and degradation of the corpus luteum
- Degradation of corpus luteum
What is corpus algitans
Leftover scar tissue of the ovarian cycle
Ovarian cycle I

Ovarian cycle II

Describe the structure of the uterine tubes
INFUNDIBULUM - end closest to the ovary with numerous fimbriae
AMPULLA - middle portion: fertilisation occurs in ampulla of the uterine tube - 12 -24 hrs after ovulation
ISTHMUS - a short segment connected to the uterine wall

Functions of uterus
A muscular organ that provides mechanical protection, nutritional support and waste removal for the developing embryo and foetus
How is the uterus supported
By the broad ligament and 3 pairs of suspensory ligaments

Overview of uterus

Posterior view of uterus and associated structures

Myometrium
Outer muscular layer
Endometrium
A thin inner glandular mucosa
Perimetrium
Incomplete serosa
The 4 sublayers of the endometrium

Blood supply to uterus, ovaries and vagina

Menses of uterine/menstrual cycle
Degeneration of endometrium
Menses
Proliferative phase of uterine/menstrual cycle
Restoration of the endometrium
Secretory phase of uterine/menstrual cycle
Endometrial glands enlarge and accelerate their rates of secretion










