Gametes - PCOS Case Flashcards
HEADDSS
Home
Education
Activities
Drugs
Diet
Sex
Suicide
CAH =
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Female Athlete Triad
hypothalamic amenorrhea
high level of intensity of exercise reduces body fat to a level so low that menstruation could be affected
aldosterone, cortisol, tesotosterone and estradiol production

what happens if someone is lacking the enzyme 21-OH
cannot produce aldosterone, cannot produce cortisol
-ve feedback on anterior pituitary to stop it overproducing ACTH
No -ve feedback so lots of ACTH
ACTH present, DHEA can still be produced as well as testosterone
CAH
No 21-OH enzyme, don’t produce cortisol but will overproduce adrenal androgens
Not enough cortisol -> hypoglycaemia
weak and dizzy between meals (cortisol maintains blood glucose levels) ⇒ muscle wastage
Pathophysiology of PCOS
metabolic and reproductive endocrine disorder
most common cause of female infertility

causes of PCOS
obesity
excess of ovarian androgen production
hyperinsulinemia (T2D)
intrauterine environment
genetic factors
hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
how might PCOS present
Excess insulin - both androgens and oestrogen, stimulates keratinocytes to hyper divide - increased proliferation
Insulin and IGF-1 linked to this increase in keratinocyte proliferation

genetic studies of PCOS
increased prevalence of PCOS related traits in siblings with indications for an autosomal dominant model of inheritance
prevalence - 51-66% in 1st degree relatives
genes associated with increased risk of PCOS
CYP11a
HSD17B5
D19S884
CYP11a
cholesterol - pregnenalone
HSD17B5
androstenedione - testosterone
D19S884
PCOS susceptibility locus - associated with insulin resistance
INSR
insulin receptor has been validated as a risk locus for PCOS
intrauterine environment and PCOS
2nd trimester amniotic fluid testosterone levels are elevated in female foetuses of PCOS vs normal mothers
the apparent of IU milieu in poorly controlled diabetics who end with stillborn foetuses showed ovarian changes similar to those seen in PCOS
link between androgen excess in utero and the maternal environment remains unclear

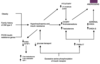
disorders of HPO axis
Increased GnRH vfrom hypothalamus
excessive LH secretion relative to FSH by pituitary gland
LH stimulates ovarian thecal cells to produce Xs androgen (Granulosa cells also produce inhibin - FSH goes up, inhibin works to stop anymore but we don’t have the same mechanism for LH so it continues to form)
ineffective suppression of LH pulse frequency by estradiol and progesterone
andorgen excess increases LH by blocking hypothalamic inhibitory feedback of progesterone
Kisspeptin
a hypothalamic peptide coded by the Kiss1 gene
novel neuromodulator that acts upstream of GnRH
sensitive to sex steroid feedback and metabolic cues
recognised as a crucial regulator of the onset of puberty, the regulation of sex hormone mediated secretion of gonadotrophins and the control of fertility

insulin resistance and PCOS
common feature
occurs in both obese and non-obese PCOS women
anomalies in insulin receptor mediated transduction
obesity has synergystic effect on glucose metabolism and IR
criteria for IR syndrome

relationship between insulin and androgens

ALTERED INSULIN
HYPERLIPIDAEMIA
ALTERED HPO
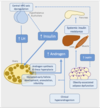
effect of increased insulin levels
increased insulin levels can stimulate androgen production
insulin can stimulate adrenal steroidogenesis by enhancing sensitivity to adrenocorticotrophic hormone and increasing pituitary LH release
insulin lowering therapies can restore menstrual cycles in some anovulatory women with PCOS
defects in insulin receptors have been found in up to 1/2 of women with PCOS
PCOS - lipid profiles and obesity
obesity has high prevalence in PCOS cases
70% of patients with PCOS have an abnormal lipid profile
- high TGs
- low HDL cholesterol
pathways leading to androgen excess in PCOS
morphology of polycystic ovary
12+ follicles measuring 2-9mm in diameter and/or increased ovarian volume (> 10 cm3)
follicles are usually PERIPHERAL in location



