Gametes - Male Reproduction Flashcards
The testes are an ______ septa
Incomplete
How many lobules do the testes have
250
How many seminiferous tubules are there
1-4
Name the type of cells associated with the loose connective tissue of the testes
Interstitial cells of leydig
How are the testes gametogenic
Name the processes that take place in the testes
Produce mature spermatozoa
- Spermatogenesis
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermiation - seminiferous tubules
What is the endocrine function of the testes and what is it associated with
Testosterone - leydig cells
What cells start the process of spermatogenesis
Germ cells (at puberty)
What is produced by spermatogenesis
What are the 2 types
Increase in number by mitosis to form SPERMATOGONIA (type A and B)
What is unique about type B spermatogonia
Replicate DNA to have 46 double structured chromosomes to begin meiosis-1 and are called primary spermatocytes

Visual depiction of spermatogenesis

Define spermiogenesis
Spermatid to spermatozoa

What is present in the golgi phase of spermiogenesis
Explain the cap phase of spermiogenesis
- The golgi migrates towards the caudal part of the cell
- The distal centriole (DC) forms the axoneme (AX) or flagellum that projects away from the nucleus toward the lumen of the seminiferous tubule
- The acrosomic vesicle flattens and begins to form a distinct cap consisting of an outer acrosomal membrane (OAM), an inner acrosomal membrane (IAM) and the acrosomal contents (enzymes)

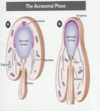
Explain the acrosomal phase of spermiogenesis
- The spermatid nucleus begins to elongate and the acrosome eventually covers the majority of the anterior nucleus
- The manchette forms in the region of the caudal half of the nucleus and extends down toward the developing flagellum
- The neck and the annulus are formed
- The annulus will become the juncture between the middle piece and the principal piece
- All components of the developing spermatid are completely surrounded by a plasma membrane
Explain the maturation phase of spermiogenesis
- Mitochondria form a spiral assembly around the flagellum that defines the middle piece
- the post nuclear cap is formed from the manchette microtubules
- The annulus forms the juncture between the middle piece and the principal piece

What is spermiation
Process by which mature spermatids are released from Sertoli cells into the seminiferous tubule lumen prior to their passage to the epididymis
How long does it take to get from spermatogonia to spermatozoa
64 days
Where are spermatozoa present
In some tubules and predominantly spermatids or primary spermatocytes in other
Temperature required for normal sperm production
2-3 degrees below core body temp
Structure of spermatozoa

Function of the nucleus of sperm
How is DNA stabilised
Active or inactive
- Haploid
- Condensed DNA stabilised by S-S bonds till fertilisation
- Inactive - no synthetic activity occurs
Function of the acrosome of the sperm
Enzymes facilitate sperm penetration
Function of plasma membrane of sperm
Very little cytoplasm in sperm - surrounds the entire tail
What does the mid peice of the sperm do
What is its structure
- Mitochondrial helix
- Gives energy for motility - ATP production










