Earthquake Intro & Injection Wells Flashcards
(23 cards)
What is an earthquake?
a sudden release of energy that has slowly accumulated in crustal rock
An earthquake is a sudden release of _____ that has slowly accumulated in crustal rock
energy
Where does the energy powering an earthquake accumulate?
in crustal rock
Where do most earthquakes occur?
at tectonic plate boundaries
The largest and most powerful earthquakes occur at ______ zones
subduction
What happens along plate boundaries?
along plate boundaries there are two plates that are slowly sliding past one another
The rocks in plate boundaries lock together and stick due to ______ between the rocks
friction
although the plates are locked together, as they continue to move what happens?
the rocks along the boundary start to deform like a plastic like of being deformation.
AS the plates continue to move the stored ______ overcomes the force of _______ and the plates slip past one another releasing energy in the form of an earthquake
energy, friction
What is the process of an earthquake?
- The rocks in plate boundaries lock and stick due to friction 2. the rocks start to deform because of there constant contact, friction, and tension/pressure/stress 3. the stored energy overcomes the force of friction and the plates slip past one another releasing energy
Major earthquakes occur when there has been a lot of ______ built up along a boundary that has been released
pressure
why do some plate boundaries produce frequent, small earthquakes?
they move incrementally throughout time and release small amounts of energy in frequent, small displacements
What can elastic rebound theory help us understand?
energy release in an earthquake
elastic rebound theory posits that continuing ____ along the fault results in a build up of ______ which is released in an earthquake
stress, energy

When rocks are ________ they can become somewhat elastic
pressurized
what does elastic mean in the context of rocks and earthquakes?
rocks can bend and snap back to their original state
What does elastic deformation do?
it stores energy in the form of potential energy
What happens when the energy build up in rocks caused from pressurization is released?
it causes vibrations in rock that travel through the Earth in seismic waves
What are injection wells?
the type of wells that are used to hydraulically fracture the Marcella shale can be used to inject waste under the ground can be used to inject carbon dioxide under the ground

What happens when hydraulic fracturing occurs?
It cracks the rocks under the Earth, and creates artificial permeability
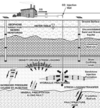
Most earthquakes resulting from injection wells are too ____ to be noticed
weak
how can injection cause an earthquake or ground shaking?
- weakens faults in already unstable areas 2. expansion or contraction of rocks, which will cause the ground to shake 3. cause saturation or very wet conditions in rocks that then leads to subsidence or shrinking of rock units 4. they can cause minerals to precipitate along faults which would cause the faults to expand a bit

anything that causes _______ or _______ underground is going to cause ground shaking
expansion, contraction


