CELL INJURY, ADAPTATIONS AND DEATH - 2 Flashcards
Covers ppts - Part 3 and 4 i.e. Cell Death , Intracellular accumulations and Cell death
List the Anti-apoptotic proteins
Location?
How do they prevent cell death?
Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Mcl-1
reside in the cytoplasm and in mitochondrial membranes
control mitochondrial permeability
prevent leakage of mitochondrial proteins that have the ability to trigger cell death
Mitochondrial protein whose release triggers activation of caspases
cytochrome c
The 2 kinases involved in necroptosis
receptor associated kinase 1 and 3 (RIP 1 & 3)
List 3 examples of physiologic apoptosis occuring due to Shrinkage of hormone-dependent tissue after withdrawal of the hormone
- endometrial cell breakdown during the menstrual cycle
- ovarian follicular atresia in menopause
- regression of the lactating breast after weaning
Name 3 organs likely to exhibit the same pattern of infarction as shown in the attached image
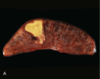
Spleen, heart and kidney
Pattern of necrosis wherein the architecture of dead tissues is preserved for a span of at least some days
Coagulative necrosis
Release of which biologically active cytokine is repsonsible for pyroptosis
Interleukin-1
Etiology of coagulative necrosis
Can occur due to ischemia caused by obstruction in a vessel
Identify the pattern of necrosis shown in the attached image

Fibrinoid necrosis
(Bright pink and amorphous)
Column B represents?

Apoptosis
a ladder pattern is seen due to the action of calcium and magnesium dependent endonucleases that cleave DNA at internucleosomal linker regions which occur at 180 base pair intervals in the genome.
See attached image.
Necrosis or apoptosis?

Necrosis
Give 1 word that best fits the description below:
“caspase-independent” programmed necrosis
necroptosis
1 example of Enzymatic fat necrosis
Acute pancreatitis

Identify the process resulting in the appearance shown in the attached image

Apoptosis
See the attached image. What is the underlying basis for its occurence?

Incomplete or defective apoptosis is responsible for syndactyly
Caspase that is activated in the extrinsic pathway
Caspase 8
See description below and identify whether it is Neccrosis or apoptosis
Reduced cell size
Fragmentation of nucleus into nucleosome sized fragments
Intact plasma membrane
Intact cellular contents
No surrounding inflammation
Apoptosis
List 2 conditions assoc with liquefactive necrosis
a. focal bacterial or, occasionally, fungal infections
b. Hypoxic death of cells within the CNS

Caspase that is activated in the intrinsic pathway
Caspase 9
4 conditions assoc with fibrinoid necrosis
- Immune mediated vasculitis –eg: Henoch Schonlein purpura, PAN
- Malignant hypertension
- Preeclampsia
- Hyperacute transplant rejection
How are apoptotic bodies made edible for phagocytes?
- secrete soluble factors that recruit phagocytes
- express thrombospondin
- coated with natural antibodies and proteins of the complement system
Process by which apoptotic cells are cleared
Phagocytosis
Pattern of necrosis characterized by digestion of the dead cells, resulting in transformation of the tissue into a liquid viscous mass
Liquefactive necrosis
Most likely etiology of caseous necrosis
Tuberculosis
Name 2 tissues commonly affected by Traumatic fat necrosis
female breast tissue, abdomen
Identify the pattern of necrosis described:
Development of superimposed bacterial infection in a limb that is ischemic
Wet gangrene
Give 1 word that best describes the following:
localized area of coagulative necrosis
Infarct
Column C represents?
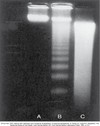
Necrosis
Diffuse smearing of DNA is noted
See the attached image. What would be the most likley gross appearance of the lung?

“caseous” (cheeselike) - friable white
- Gross appearance of the pancreas in fat necrosis due to acute pancreatitis
- What is the cause of the gross appearance?
- chalky yellow-white areas in the peripancreatic fat
- Fat saponification

Microscopic description of caseation on light microscopy
acellular and granular
usually located in the center of a granuloma



